|
Telencephalic
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum prenatal development, develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric Lateralization of brain function, left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallium (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, pallium refers to the layers of grey and white matter that cover the upper surface of the cerebrum in vertebrates. The non-pallial part of the telencephalon builds the subpallium. In basal vertebrates the pallium is a relatively simple three-layered structure, encompassing 3–4 histogenetically distinct domains, plus the olfactory bulb. It used to be thought that pallium equals cortex and subpallium equals telencephalic nuclei, but it has turned out, according to comparative evidence provided by molecular markers, that the pallium develops both cortical structures (allocortex and isocortex) and pallial nuclei ( claustroamygdaloid complex), whereas the subpallium develops striatal, pallidal, diagonal-innominate and preoptic nuclei, plus the corticoid structure of the olfactory tuberculum. In mammals, the cortical part of the pallium registers a definite evolutionary step-up in complexity, forming the cerebral cortex, most of which consists of a progressively e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum Animation Small
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of the five major divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex, and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. There are four principal gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the central sulcus, running parallel to it and contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three Brain vesicle, primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
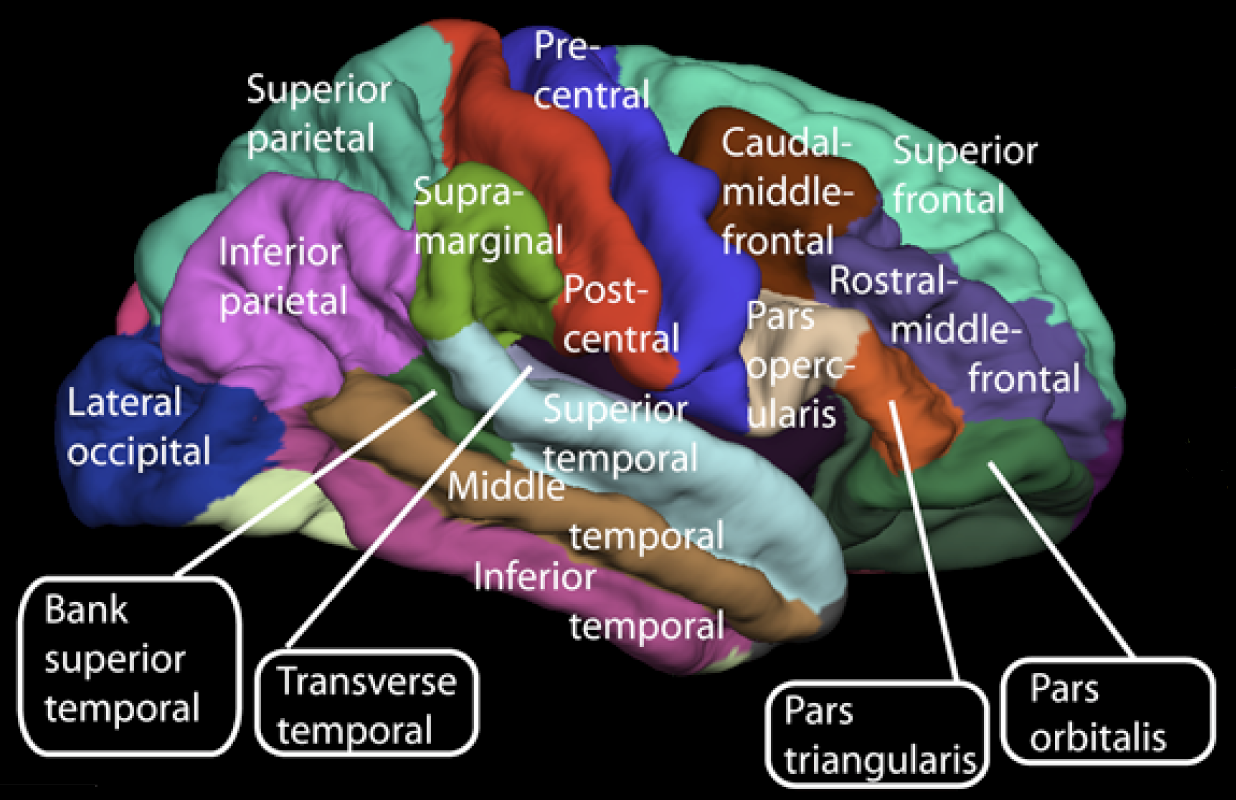
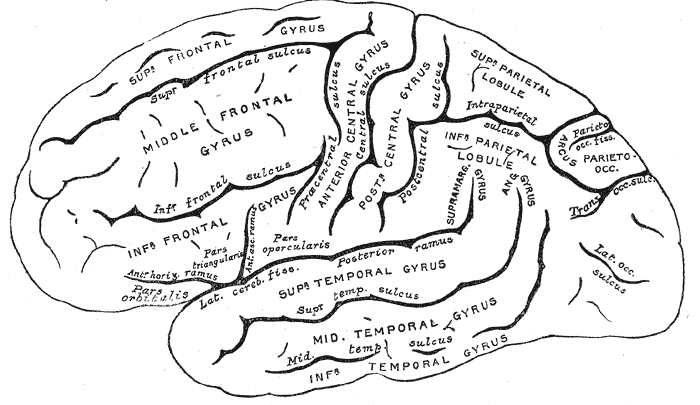
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Surface Of Cerebral Cortex - Gyri
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to: Healthcare *Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction *Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle *Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap Phonetics *Lateral consonant, an l-like consonant in which air flows along the sides of the tongue **Lateral release (phonetics), the release of a plosive consonant into a lateral consonant Other uses *''Lateral'', journal of the Cultural Studies Association *Lateral canal, a canal built beside another stream *Lateral hiring, recruiting that targets employees of another organization *Lateral mark, a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the edge of a channel * Lateral stability of aircraft during flight *Lateral pass, a type of pass in American and Canadian football *Lateral support (other), various meanings *Lateral thinking, the solution of problems through an indirect and creative approach *Lateral number, a proposed alternate term for imagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Fissure
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater (one of the meninges) called the falx cerebri. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain. Structure Falx cerebri All three meninges of the cortex (dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater) fold and descend deep down into the longitudinal fissure, physically separating the two hemispheres. Falx cerebri is the name given to the dura mater in-between the two hemispheres, whose significance arises from the fact that it is the outermost layer of the meninges. These layers prevent any direct connectivity between the bilateral lobes of the cortex, thus requiring any tracts to pass through the corpus callosum. The vasculature of falx cerebri sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish-white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather than c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distinguished from white matter in that it contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons, while white matter contains relatively few cell bodies and is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axons. The colour difference arises mainly from the whiteness of myelin. In living tissue, grey matter actually has a very light grey colour with yellowish or pinkish hues, which come from capillary blood vessels and neuronal cell bodies. Structure Grey matter refers to unmyelinated neurons and other cells of the central nervous system. It is present in the brain, brainstem and cerebellum, and present throughout the spinal cord. Grey matter is distributed at the surface of the cerebral hemispheres (cerebral cortex) and of the cerebellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortices
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the neurocranium, cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, gyrification, cortical folding i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |