|
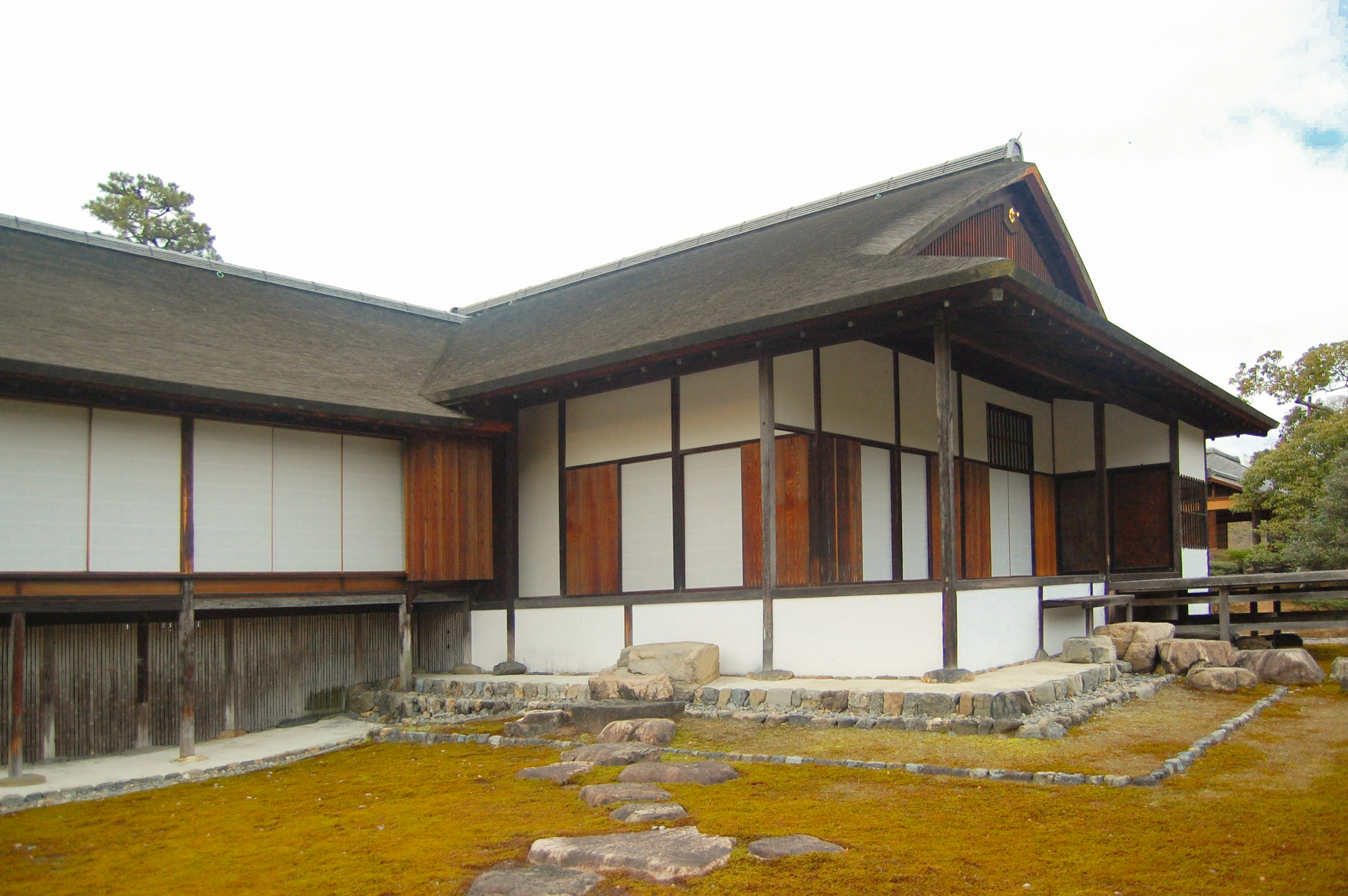
Tekigai-sō
250px, Tekigai-sō The was the residence of pre-war Japanese Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe, located in the Ogikubo neighborhood of Suginami, Tokyo, Japan. The building and surrounding gardens were designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 2016. Overview The Tekigai-sō is a one-story wooden structure designed by the noted architect Itō Chūta for Tatsukichi Irisawa, a doctor with the Imperial Household Agency in 1927. Located on a hill with a slope to the south, the villa had a view over the Zenpukuji River to Mount Fuji in the distance. Although in the very traditional ''sukiya-zukuri'' style, the design incorporated high ceilings, as Irisawa preferred western-style interior with chairs, and had several exotic design details reflecting Ito's travels in China, India and the Middle East. The building was purchased by Konoe in 1937, who remodeled the interior into a more traditional Japanese style. Konoe also added to the structure and constructed a separate ''kura'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumimaro Konoe
Prince was a Japanese politician and prime minister. During his tenure, he presided over the Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the breakdown in relations with the United States, which ultimately culminated in Japan's entry into World War II. He also played a central role in transforming his country into a totalitarian state by passing the National Mobilization Law and founding the Imperial Rule Assistance Association. Despite Konoe's attempts to resolve tensions with the United States, the rigid timetable imposed on negotiations by the military and his own government's inflexibility regarding a diplomatic resolution set Japan on the path to war. Upon failing to reach a peace agreement, Konoe resigned as Prime Minister on 18 October 1941, prior to the outbreak of hostilities. However, he remained a close advisor to the Emperor until the end of World War II. Following the end of the war, he committed suicide on 16 December 1945. Early life Fumimaro Konoe was born in To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukiya-zukuri
is one type of Japanese residential architectural style. ''Suki'' means refined, well cultivated taste and delight in elegant pursuits and refers to enjoyment of the exquisitely performed tea ceremony. The word originally denoted a building in which tea ceremony was done (known as a ''chashitsu'') and was associated with ''ikebana'' flower arranging, and other Japanese traditional arts. It has come to indicate a style of designing public facilities and private homes based on tea house aesthetics. Historically and by tradition, ''sukiya-zukuri'' is characterised by a use of natural materials, especially wood. In contemporary architecture, its formal and spatial concepts are kept alive in modern materials such as steel, glass and concrete. Origins In 1587, Toyotomi Hideyoshi (1536–98) employed the tea master Sen no Rikyū as his advisor on aesthetic matters. In the compound of Hideyoshi's imposing Jurakudai castle in Kyoto Rikyū designed an eighteen mat building known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hideki Tōjō
Hideki Tojo (, ', December 30, 1884 – December 23, 1948) was a Japanese politician, general of the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA), and convicted war criminal who served as prime minister of Japan and president of the Imperial Rule Assistance Association for most of World War II. He assumed several more positions including chief of staff of the Imperial Army before ultimately being removed from power in July 1944. During his years in power, his leadership was marked by extreme state-perpetrated violence in the name of Japanese ultranationalism, much of which he was personally involved in. Hideki Tojo was born on December 30, 1884, to a relatively low-ranking samurai family in the Kōjimachi district of Tokyo. He began his career in the Army in 1902 and steadily rose through the ranks to become a general by 1934. In March 1937, he was promoted to chief of staff of the Kwantung Army whereby he led military operations against the Chinese in Inner Mongolia and the Chahar-Suiyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Commander Of The Allied Powers
was the title held by General Douglas MacArthur during the United States-led Allied occupation of Japan following World War II. It issued SCAP Directives (alias SCAPIN, SCAP Index Number) to the Japanese government, aiming to suppress its "militaristic nationalism". The position was created at the start of the occupation of Japan on August 14, 1945. In Japan, the position was generally referred to as GHQ (General Headquarters), as SCAP also referred to the offices of the occupation (which was officially referred by SCAP itself as ), including a staff of several hundred US civil servants as well as military personnel. Some of these personnel effectively wrote a first draft of the Japanese Constitution, which the National Diet then ratified after a few amendments. Australian, British Empire, and New Zealand forces under SCAP were organized into a sub-command known as British Commonwealth Occupation Force. These actions led MacArthur to be viewed as the new Imperial force in Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. Some Chinese historians believe that the Japanese invasion of Manchuria on 18 September 1931 marks the start of the war. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia. China fought Japan with aid from Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States. After the Japanese attacks on Malaya and Pearl Harbor in 1941, the war merged with other conflicts which are generally categorized under those conflicts of World War II a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teijirō Toyoda
was a career naval officer who served as Minister for Foreign Affairs in 1941 and as admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Biography Early life Toyoda was born in Wakayama Prefecture as the son of a former samurai retainer of the Wakayama Domain. He studied at Tennoji junior high school before entering the Tokyo Foreign Languages School where he studied English. He graduated as the top student out of 171 cadets in the 33rd term of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy in 1905. The Russo-Japanese War ended in November 1905 during the time of Toyoda’s graduation and he was assigned as a midshipman to serve in Southeast Asia on the cruisers , Katori, destroyer ''Yayoi'', and cruiser . After completing naval artillery and torpedo warfare course, he was promoted to ensign and assigned to the battleship , followed by . In 1910, Lieutenant Toyoda studied an advanced artillery course at the Navy Staff College a second grade student for a year, and then was as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koshirō Oikawa
was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy and Naval Minister during World War II. Biography Oikawa was born into a wealthy family in rural Koshi County, Niigata Prefecture, but was raised in Morioka city, Iwate prefecture in northern Japan. He was a graduate of the 31st class of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy, ranking 76th out of 188 cadets. As a midshipman, he served on the cruisers and . During the Russo-Japanese War, still as a midshipman, he served on the during the Battle of Tsushima. As a lieutenant, Oikawa served on the cruiser , and the battleship . He was given his first command, the destroyer on 28 April 1911. He subsequently served on the , before attending the Naval Staff College in 1914. On graduation, Oikawa was promoted to lieutenant commander, and was appointed aide-de-camp to Crown Prince Hirohito in 1915–1922. After his promotion to captain on 1 December 1923, Oikawa was assigned the cruiser , followed by the the following year. He t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoriyasu Arima
was a Japanese politician before and during World War II. His wife was the daughter of Prince Takeda Tsunehisa. Biography Arima was born in Tokyo as a son of the former ''daimyō'' of Kurume Domain (now part of Fukuoka Prefecture). He studied agricultural science at the Tokyo Imperial University, and later became a professor there. He read Karl Marx and Max Stirner, and other radical philosophers, and became attracted to the agrarian movement and radical political ideas. Arima founded the ''Nihon Nomin Kumiai'' (Japan Farmer's Union) together with Kagawa Toyohiko. He was active in various social programmes, including the establishment and support of night school, women's education, farmer's rights, and the rights of the ''burakumin'', and was chairman of a cultural association aimed at improving education and cultural awareness in rural areas. Arima was elected to the House of Representatives in the Diet of Japan in 1924 under the Rikken Seiyūkai party. In 1929, after he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Rule Assistance Association
The , or Imperial Aid Association, was the Empire of Japan's ruling organization during much of World War II. It was created by Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoe on 12 October 1940, to promote the goals of his ("New Order") movement. It evolved into a "statist" ruling political party which aimed at removing the sectionalism in the politics and economics in the Empire of Japan to create a totalitarian one-party state, in order to maximize the efficiency of Japan's total war effort in China. When the organization was launched officially, Konoe was hailed as a "political savior" of a nation in chaos; however, internal divisions soon appeared. Origins Based on recommendations by the , Konoe originally conceived of the Imperial Rule Assistance Association as a reformist political party to overcome the deep-rooted differences and political cliques between bureaucrats, politicians and the military. During the summer of 1937, Konoe appointed 37 members chosen from a broad political spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |