|
Technosaurus
''Technosaurus'' (meaning "Tech lizard", for Texas Tech University) is an extinct genus of Late Triassic silesaurid dinosauriform, from the Late Triassic Cooper Canyon Formation (Dockum Group) of Texas, United States. For about 20 years after its description, it was thought to be a basal ornithischian dinosaur, but better remains of other Triassic archosaurs have cast doubt on this interpretation. As named, it was a chimera of different animals. Description and history ''Technosaurus'' is based on TTUP P9021, which initially consisted of a premaxilla (tip of the upper jaw), two lower jaw pieces, a back vertebra, and an astragalus. ''Technosaurus'' and its type species, ''T. smalli'', were named by Sankar Chatterjee in 1984. He described it as a fabrosaurid, a clade of small early ornithischians now considered to have been an artificial grouping. Material from the quarry where P9021 was found is disassociated and comes from a variety of Late Triassic animals, which would p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankar Chatterjee
Sankar Chatterjee (born May 28, 1943) is a paleontologist, and is the Paul W. Horn Professor of Geosciences at Texas Tech University and Curator of Paleontology at the Museum of Texas Tech University. He earned his Ph. D. from the University of Calcutta in 1970 and was a Post-doctoral Fellow at the Smithsonian Institution from 1977-1978. Chatterjee has focused on the origin, evolution, functional anatomy, and systematics of Mesozoic vertebrates, including basal archosaurs, dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and birds. He has researched Late Triassic reptiles in India, such as phytosaurs, rhynchosaurs, and prolacertiformes. He is best known for his work on vertebrates recovered in the 1980s from the Post Quarry in the Late Triassic Cooper Canyon Formation (Dockum Group) of West Texas. The material includes the large rauisuchian ''Postosuchus'', which was named for the nearby town of Post. It also included controversial specimens Chatterjee identified as being avian (''Protoavis''). The ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosauriformes
Dinosauromorpha is a clade of avemetatarsalian archosaurs (reptiles closer to birds than to crocodilians) that includes the Dinosauria (dinosaurs) and some of their close relatives. It was originally defined to include dinosauriforms and lagerpetids, with later formulations specifically excluding pterosaurs from the group. Birds are the only dinosauromorphs which survive to the present day. Classification The name "Dinosauromorpha" was briefly coined by Michael J. Benton in 1985. It was considered an alternative name for the group "Ornithosuchia", which was named by Jacques Gauthier to correspond to archosaurs closer to dinosaurs than to crocodilians. Although "Ornithosuchia" was later recognized as a misnomer (since ornithosuchids are now considered closer to crocodilians than to dinosaurs), it was still a more popular term than Dinosauromorpha in the 1980s. The group encompassed by Gauthier's "Ornithosuchia" and Benton's "Dinosauromorpha" is now given the name Avemetatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooper Canyon Formation
The Cooper Canyon Formation is a geological formation of Norian age in Texas and New Mexico.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004).Dinosaur distribution (Late Triassic, North America)" In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 518–521. . Type area of the formation is situated in Garza County, Texas. An equivalent formation in eastern New Mexico is named Bull Canyon Formation. Some researchers argue that the latter name should be abandoned. The formation consist of reddish siltstone and mudstone with lenses of sandstone and conglomerate. Thickness of the formation in the type area is 161.5 meters. It increases to the south, and in some places exceeds 200 m. The formation contains diverse fossils, including vertebrate remains. Vertebrate fauna Temnospondyls Allokotosaurs Archosaurs and related Procolophonomorphs Misc. See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropodomorpha
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had long necks and tails, were quadrupedal, and became the largest animals to ever walk the Earth. The '' prosauropods,'' which preceded the sauropods, were smaller and were often able to walk on two legs. The sauropodomorphs were the dominant terrestrial herbivores throughout much of the Mesozoic Era, from their origins in the Late Triassic (approximately 230 Ma) until their decline and extinction at the end of the Cretaceous. Description Sauropodomorphs were adapted to browsing higher than any other contemporary herbivore, giving them access to high tree foliage. This feeding strategy is supported by many of their defining characteristics, such as: a light, tiny skull on the end of a long neck (with ten or more elongated cervical vertebrae) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incertae Sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty at specific taxonomic levels is indicated by ' (of uncertain family), ' (of uncertain suborder), ' (of uncertain order) and similar terms. Examples *The fossil plant '' Paradinandra suecica'' could not be assigned to any family, but was placed ''incertae sedis'' within the order Ericales when described in 2001. * The fossil ''Gluteus minimus'', described in 1975, could not be assigned to any known animal phylum. The genus is therefore ''incertae sedis'' within the kingdom Animalia. * While it was unclear to which order the New World vultures (family Cathartidae) should be assigned, they were placed in Aves ''incertae sedis''. It was later agreed to place them in a separate order, Cathartiformes. * Bocage's longbill, ''Motacilla bocagii' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuvosaurus
''Shuvosaurus'' (meaning "Shuvo's lizard") is a genus of beaked reptile from the Late Triassic of western Texas. Despite looking superficially similar to a theropod dinosaur, it is actually more closely related to crocodilians. Discovery and classification ''Shuvosaurus'' was described by Sankar Chatterjee in 1993 after it was discovered by his son Shuvo in the early 1990s.Chatterjee, S. (1991) An unusual toothless archosaur from the Triassic of Texas: the world's oldest ostrich dinosaur? Abstract, Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 8(3): 11A. It was initially interpreted as a Triassic member of the Cretaceous dinosaur family Ornithomimidae because it had toothless jaws. Like the avian placement of ''Protoavis'', the ornithomimosaur placement of ''Shuvosaurus'' was greeted with scepticism by others, and in their 1995 monograph on Late Triassic tetrapods from the American Southwest, Robert Long and Philip Murry considered ''Shuvosaurus'' to be possibly the same species as their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
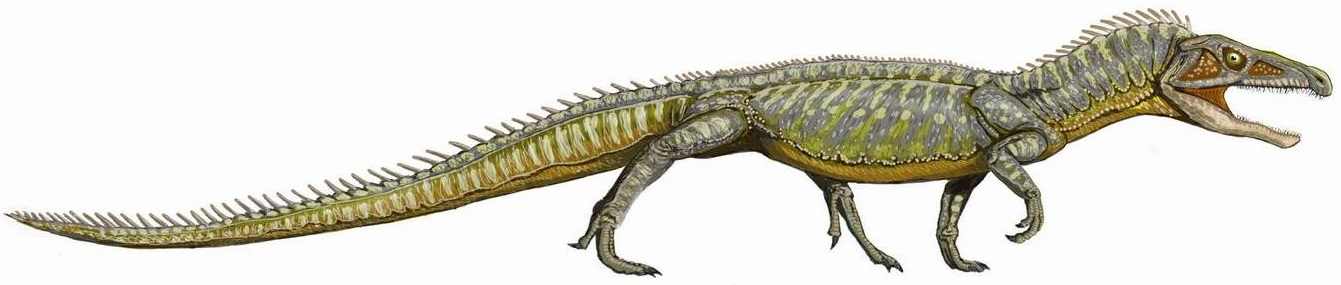
Silesaurids
Silesauridae is an extinct family of Triassic dinosauriforms. It is most commonly considered to be a clade of non-dinosaur dinosauriforms, and the sister group of dinosaurs. Some studies have instead suggested that most or all silesaurids comprised an early diverging clade or a paraphyletic grade within ornithischian dinosaurs. Silesaurids have a consistent general body plan, with a fairly long neck and legs and possibly quadrupedal habits, but most silesaurids are heavily fragmentary nonetheless. Furthermore, they occupied a variety of ecological niches, with early silesaurids (such as ''Lewisuchus'') being carnivorous and later taxa (such as ''Kwanasaurus'') having adaptations for specialized herbivory. As indicated by the contents of referred coprolites, ''Silesaurus'' may have been insectivorous, feeding selectively on small beetles and other arthropods. Classification Silesauridae is typically considered the sister group to Dinosauria. The group was named in 2010 by Max C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the lateral and medial malleoli) that articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of its surface area covered by articular cartilage. It is also unusual in that it has a retrograde blood supply, i.e. arterial blood enters the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rauisuchia
"Rauisuchia" is a paraphyletic group of mostly large and carnivorous Triassic archosaurs. Rauisuchians are a category of archosaurs within a larger group called Pseudosuchia, which encompasses all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilia Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...ns than to birds and other dinosaurs. First named in the 1940s, Rauisuchia was a name exclusive to Triassic archosaurs which were generally large (often ), carnivorous, and quadrupedal with a pillar-erect hip posture, though exceptions exist for all of these traits. Rauisuchians, as a traditional Taxonomy, taxonomic group, were considered distinct from other Triassic archosaur groups such as early dinosaurs, Phytosaur, phytosaurs (crocodile-like carnivores), Aetosaur, aetosaurs (armored herbivor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosauropod
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had long necks and tails, were quadrupedal, and became the largest animals to ever walk the Earth. The ''prosauropods,'' which preceded the sauropods, were smaller and were often able to walk on two legs. The sauropodomorphs were the dominant terrestrial herbivores throughout much of the Mesozoic Era, from their origins in the Late Triassic (approximately 230 Ma) until their decline and extinction at the end of the Cretaceous. Description Sauropodomorphs were adapted to browsing higher than any other contemporary herbivore, giving them access to high tree foliage. This feeding strategy is supported by many of their defining characteristics, such as: a light, tiny skull on the end of a long neck (with ten or more elongated cervical vertebrae) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |