|
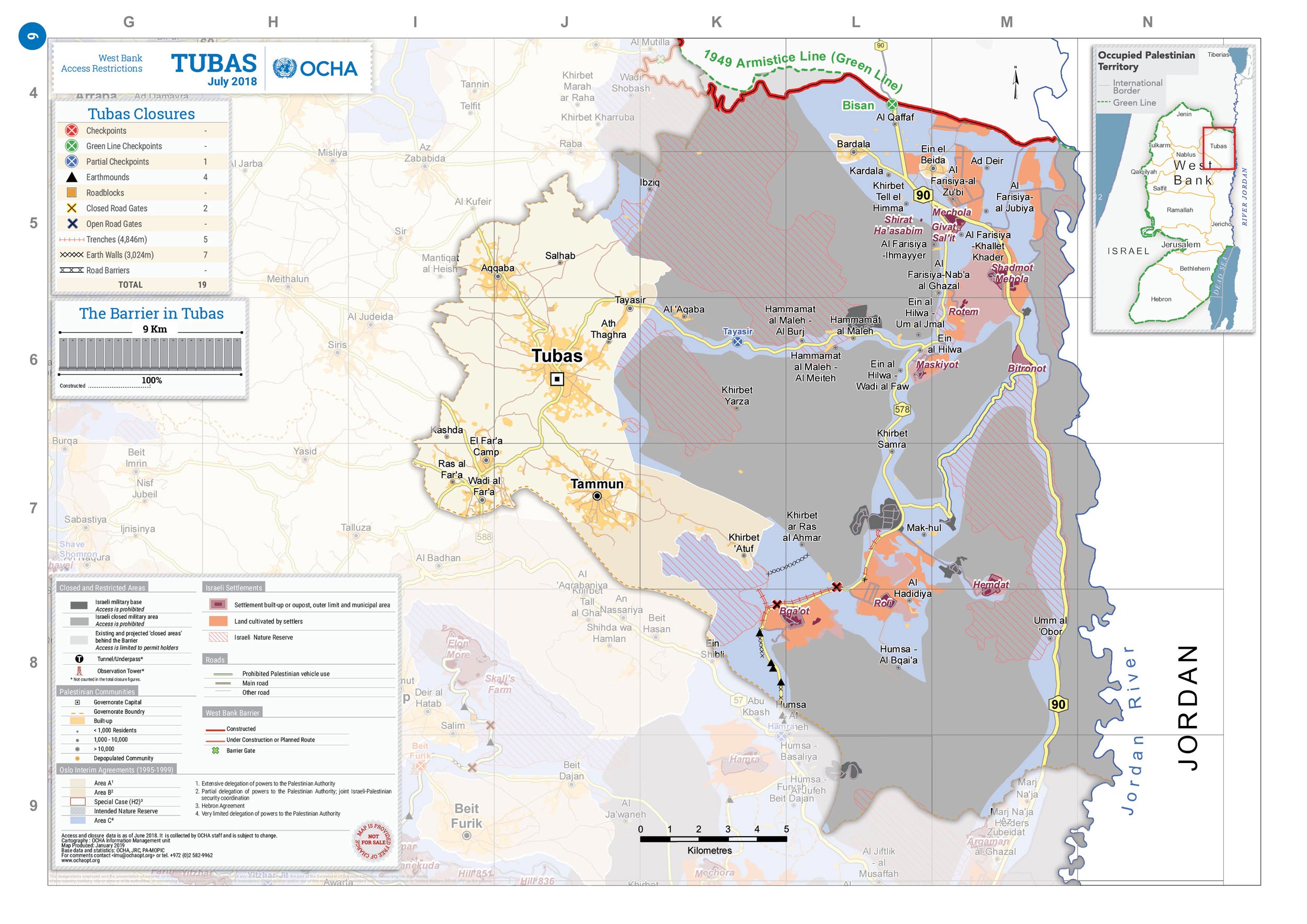
Tayasir
Tayasir ( ar, تياسير, also spelled Tiaseer) is a Palestinian village in the Tubas Governorate in the northern West Bank. It is located 3 kilometers northeast of Tubas and 22 kilometers northeast of Nablus. Nearby localities include al-Aqabah to the east, al-Bikai'a to the northeast, Salhab to the north, 'Aqqaba to the west and ath-Thaghra to the southwest. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), Tayasir had a population of 2,489 in 2007. increasing in the 1931 census to 192 inhabitants, all Muslim, except for 5 Christians, with 36 occupied houses.Mills, 1932, p65 In the 1945 statistics the population was 260 Muslims,Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics, 1945, p19/ref> with 23,258 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p61/ref> Of this, 763 dunams were used for plantations and irrigable land, 5,3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubas (city)
Tubas (; ar, طوباس, ''Tûbâs'') is a Palestinian city in the northeastern West Bank, located northeast of Nablus, west of the Jordan Valley. A city of over 63,000 inhabitants, it serves as the economic and administrative center of the Tubas Governorate of the State of Palestine. Its urban area consists of 2,271 dunams (227 hectares). It is governed by a municipal council of 15 members and most of its working inhabitants are employed in agriculture or public services. Tubas has been identified as the ancient town of Thebez (), a Canaanite town famous for revolting against King Abimelech. During the late 19th century, during Ottoman rule in Palestine, Arab clans living in the Jordan Valley came to live in Tubas, and it became a major town in the District of Nablus, particularly known for its timber and cheese-making. It came under the British Mandate of Palestine in 1922, was annexed by Jordan after their capture of the town in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and then occupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salhab
Salhab ( ar, سلحب, also known as Khirbet Salhab) is a small Palestinian village in the Tubas Governorate in the northeastern West Bank, located four kilometers north of Tubas. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS) census, it had a population of 45 living in five households in 2007. Ceramic objects from the Byzantine era have been found here. Ottoman era In 1596, it appeared in Ottoman tax registers as "Salhab", a village in the ''nahiya'' of Jabal Sami in the '' liwa'' of Nablus. It had a population of eight households and two bachelors, all Muslim. The villagers paid taxes on wheat, barley, summer crops, olive trees, goats and beehives; a total of 4,000 Akçe. In his 1870 visit, French explorer Victor Guérin described Salhab as "A little town, now destroyed, on a hill whose rocky sides are pierced by numerous cisterns. The place which it occupied is now covered with confused materials, the remains of demolished dwellings, and disposed for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubas Governorate
The Tubas Governorate ( ar, محافظة طوباس, Muḥāfaẓat Ṭūbās) is an administrative district of the Palestine in the northeastern West Bank. Its district capital or ''muhfaza'' is the city of Tubas. In 2007, the population was 50,267, . raising to 60,927 in 2017. Localities There are 23 localities located within the governorate's jurisdiction.Cities * |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are: Persian (Farsi/Dari), Malay ( Jawi), Uyghur, Kurdish, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi, Balti, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu, Kashmiri, Rohingya, Somali and Mandinka, Mooré among others. Until the 16th century, it was also used for some Spanish texts, and—prior to the language reform in 1928—it was the writing system of Turkish. The script is written from right to left in a cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Press
Olive oil extraction is the process of extracting the oil present in olive drupes, known as olive oil. Olive oil is produced in the mesocarp cells, and stored in a particular type of vacuole called a lipo vacuole, i.e., every cell contains a tiny olive oil droplet. Olive oil extraction is the process of separating the oil from the other fruit contents (vegetative extract liquid and solid material). It is possible to attain this separation by physical means alone, i.e., oil and water do not mix, so they are relatively easy to separate. This contrasts with other oils that are extracted with chemical solvents, generally hexane. The first operation when extracting olive oil is washing the olives, to reduce the presence of contaminants, especially soil which can create a particular flavor effect called "soil taste". Olive presses People have used olive presses since Greeks first began pressing olives over 5,000 years ago. Roman olive presses survive to the prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotto
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave used by humans in both modern times and antiquity, and historically or prehistorically. Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high tide. Sometimes, artificial grottoes are used as garden features. The '' Grotta Azzurra'' at Capri and the grotto at Tiberius' Villa Jovis in the Bay of Naples are examples of popular natural seashore grottoes. Whether in tidal water or high up in hills, grottoes are generally made up of limestone geology, where the acidity of standing water has dissolved the carbonates in the rock matrix as it passes through what were originally small fissures. Etymology The word ''grotto'' comes from Italian ''grotta'', Vulgar Latin ''grupta'', and Latin ''crypta'' ("a crypt"). It is also related by a historical accident to the word ''grotesque''. In the late 15th century, Romans accidentally unearthed Nero's ''Domus Aurea'' on the Palatine Hill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
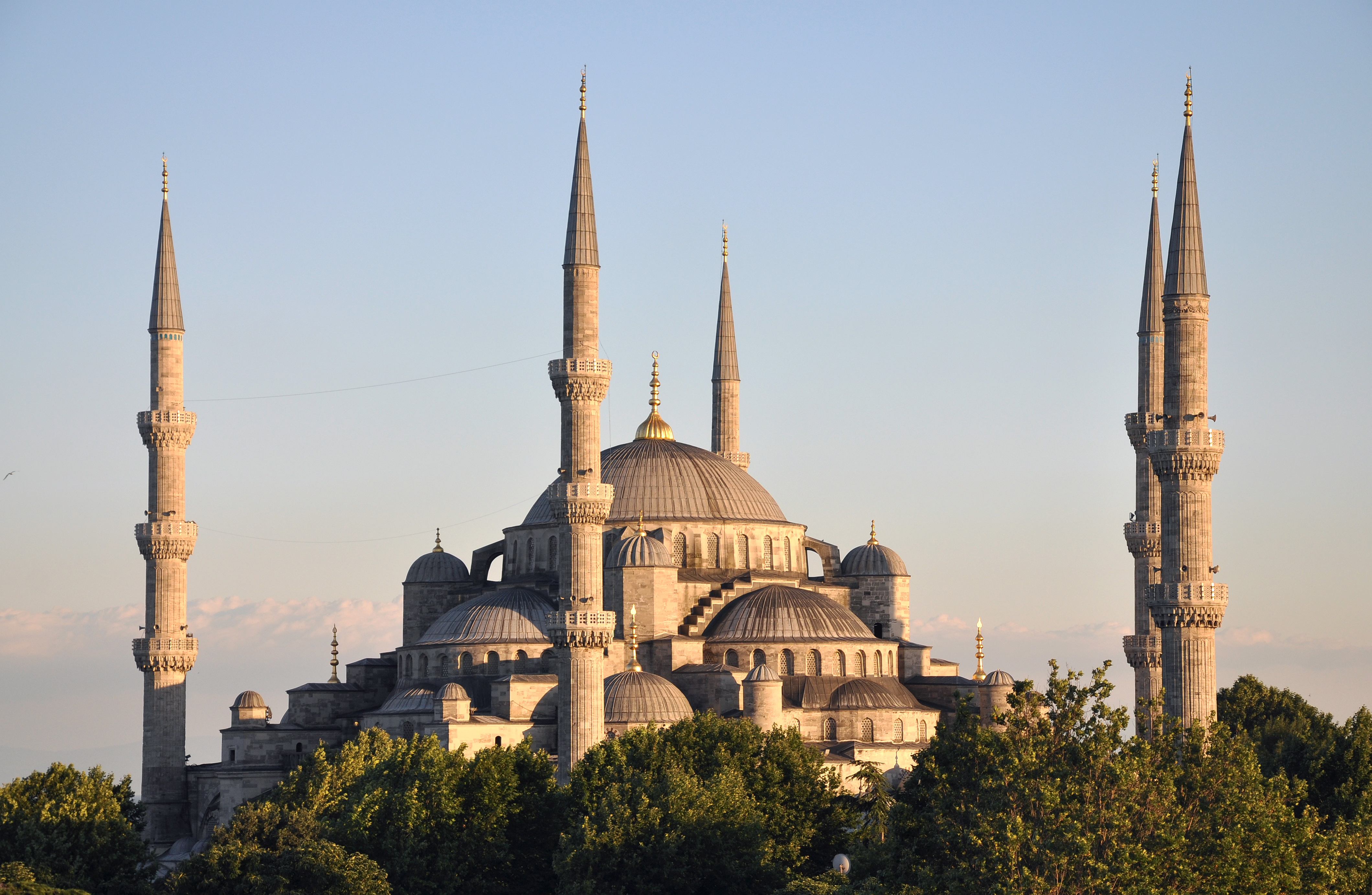
Mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, including outdoor courtyards. The first mosques were simple places of prayer for Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture, 650-750 CE, early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets from which calls to prayer were issued. Mosque buildings typically contain an ornamental niche ('' mihrab'') set into the wall that indicates the direction of Mecca (''qiblah''), Wudu, ablution facilities. The pulpit (''minbar''), from which the Friday (jumu'ah) sermon (''khutba'') is delivered, was in earlier times characteristic of the central city mosque, but has since become common in smaller mosques. Mosques typically have Islam and gender se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, Media, Parthia and Persis), Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands (Turkey's Eastern Anatolia Region, Armenia, northwestern Iran, southern Georgia, and western Azerbaijan), the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date it ends varies. The term covers the Bronze Age and the Iron Age in the region, until either the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, that by the Macedonian Empire in the 4th century BC, or the Muslim conquest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine (region)
Palestine ( el, Παλαιστίνη, ; la, Palaestina; ar, فلسطين, , , ; he, פלשתינה, ) is a geographic region in Western Asia. It is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine (i.e. West Bank and Gaza Strip), though some definitions also include part of northwestern Jordan. The first written records to attest the name of the region were those of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, which used the term "Peleset" in reference to the neighboring people or land. In the 8th century, Assyrian inscriptions refer to the region of "Palashtu" or "Pilistu". In the Hellenistic period, these names were carried over into Greek, appearing in the Histories of Herodotus in the more recognizable form of "Palaistine". The Roman Empire initially used other terms for the region, such as Judaea, but renamed the region Syria Palaestina after the Bar Kokhba revolt. During the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux Pilgrim
The ''Itinerarium Burdigalense'' ("Bordeaux Itinerary"), also known as the ''Itinerarium Hierosolymitanum'' ("Jerusalem Itinerary"), is the oldest known Christian ''itinerarium''. It was written by the "Pilgrim of Bordeaux", an anonymous pilgrim from the city of Burdigala (now Bordeaux, France) in the Roman province of Gallia Aquitania. It recounts the writer's journey throughout the Roman Empire to the Holy Land in 333 and 334 as he travelled by land through northern Italy and the Danube valley to Constantinople; then through the provinces of Asia and Syria to Jerusalem in the province of Syria-Palaestina; and then back by way of Macedonia, Otranto, Rome, and Milan. Interpretation and analysis According to the ''Catholic Encyclopedia'': Another reader, Jaś Elsner, notes that, a brief twenty-one years after Constantine legalized Christianity, "the Holy Land to which the pilgrim went had to be entirely reinvented in those years, since its main siteancient Jerusalemhad been sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |