|
Tanjung Malim
Tanjung Malim, or Tanjong Malim, is a town in Muallim District, Perak, Malaysia. It is approximately north of Kuala Lumpur and 120 km south of Ipoh via the North–South Expressway. It lies on the Perak-Selangor state border, with Sungai Bernam serving as the natural divider. Today, "Tanjung Malim" usually refers to the territory under administration of Tanjung Malim District Council or ''Majlis Daerah Tanjung Malim (MDTM)'', which includes the smaller towns adjacent to the town such as Proton City, Behrang, Behrang 2020, Sungkai and Slim River. "Tanjung Malim" is lately also referred to the ''Old Town'' and ''New Town'' divided by the KTM Komuter rail at its heart, from which the town grew. Commuter train services from Tanjung Malim started on 1 June 2009. History and background Name An early settlement nearby Sungai Bernam is named Kampung Kubu (Fort Village). The Bugis community planted jambu fruit trees along the river bank. As population grew over time, the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
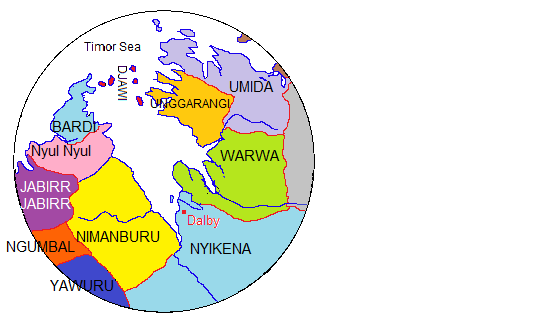
Jawi Language
Jawi or Djawi or Djaui, is a moribund language, nearly extinct dialect of the Bardi language of Western Australia, the traditional language of the Jawi people. There are no longer any known fluency, fluent speakers, but there may be some partial speakers. The name has also been spelt Chowie, Djaoi, Djau, Dyao, and Dyawi. Classification Jawi is a Non-Pama–Nyungan languages, Non-Pama–Nyungan language of the Nyulnyulan languages, Nyulnyulan family, most closely related to Bardi language, Bardi. Bowern discusses how Jawi and Bardi may have converged within the last hundred years. Jawi people were hit hard by influenzaSunday Island Mission Records in the early years of the 20th century. Their traditional lands are Sunday Island (King Sound), Sunday Island and the islands of the Buccaneer Archipelago to the northeast. References Cited references General references * * * Bird, W.; Hadley, S. (not dated). "Native vocabulary: Sunday Island", unpublished manuscript. Further r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton City
Proton City (Malay: ''Bandar Proton'') is a township with industrial, commercial and residential activities spread over 4,000 acres (16 km²) in Muallim District, Perak, Malaysia. It houses the RM1.8 billion Proton car assembly plant. Proton City aims to be fully developed by 2020. Undertaken by Proton City Development Corp, a joint venture between DRB-HICOM and Proton itself. A core member of Proton Holdings, it started in 1996 with an initial investment of RM2.5 billion, beginning with the construction of the Proton plant. The Proton plant has a workforce of more than 2,000 and most of them are expected to live in the area. When Proton City is fully developed, it would have a population of about 240,000. The first settlement in the area - 252 units of apartments - have been handed over to the buyers. These apartments have common facilities that include car and motorcycle parking bays, children's playground, BBQ area, car wash areas, mosque and a nursery/kindergarten on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan Communist Party
The Malayan Communist Party (MCP), officially the Communist Party of Malaya (CPM), was a Marxist–Leninist and anti-imperialist communist party which was active in British Malaya and later, the modern states of Malaysia and Singapore from 1930 to 1989. It was responsible for the creation of both the Malayan Peoples' Anti-Japanese Army and the Malayan National Liberation Army. The party led resistance efforts against the Japanese occupation of Malaya and Singapore during World War II, and later fought a war of national liberation against the British Empire during the Malayan Emergency. After the departure of British colonial forces from the Federation of Malaya, the party fought in a third guerrilla campaign against both the Malaysian and Singaporean governments in an attempt to create a communist state in the region, before surrendering and dissolving in 1989. Today, due to historical connotations surrounding the MCP, communism as an ideology remains a taboo political top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan National Liberation Army
The Malayan National Liberation Army (MNLA), often mistranslated as the Malayan Races Liberation Army, was a communist guerrilla army that fought for Malayan independence from the British Empire during the Malayan Emergency (1948–1960) and later fought against the Malaysian government in the Communist insurgency in Malaysia (1968–1989). Their leader was a trade union activist known as Chin Peng who had previously been awarded an OBE by the British for waging a guerrilla war against the Japanese occupation of Malaya. Many MNLA fighters were former members of the Malayan Peoples' Anti-Japanese Army (MPAJA) which had been previously trained and funded by the British to fight against Japan during the Second World War. In 1989 the Malayan Communist Party signed a peace treaty with the Malaysian state and the MNLA and the Party settled in villages in southern Thailand. History The MNLA was a guerrilla force created by the Malayan Communist Party (MCP). Many MNLA fighters were p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. Unlike the term "British India", which excludes the Indian princely states, British Malaya is often used to refer to the Federated and Unfederated Malay States, which were British protectorates with their own local rulers, as well as the Straits Settlements, which were under the sovereignty and direct rule of the British Crown, after a period of control by the East India Company. Before the formation of the Malayan Union in 1946, the territories were not placed under a single unified administration, with the exception of the immediate post-war period when a British military officer became the temporary administrator of Malaya. Instead, British Malaya comprised the Straits Settlements, the Federated Malay States, and the Unfederated Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan Emergency
The Malayan Emergency, also known as the Anti–British National Liberation War was a guerrilla war fought in British Malaya between communist pro-independence fighters of the Malayan National Liberation Army (MNLA) and the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth. The communists fought to win independence for Malaya from the British Empire and to establish a socialist economy, while the Commonwealth forces fought to combat communism and protect British economic and colonial interests.Siver, Christi L. "The other forgotten war: understanding atrocities during the Malayan Emergency." In APSA 2009 Toronto Meeting Paper. 2009., p.36 The conflict was called the "Anti–British National Liberation War" by the MNLA, but an "Emergency" by the British, as London-based insurers would not have paid out in instances of civil wars. On 17 June 1948, Britain declared a state of emergency in Malaya following attacks on plantations, which in turn were revenge attacks for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klang War
The Klang War or Selangor Civil War was a series of conflicts that lasted from 1867 to 1874 in the Malay state of Selangor in the Malay Peninsula (modern-day Malaysia). It was initially fought between Raja Abdullah bin Raja Jaafar, the administrator of the Klang Valley, and Raja Mahadi bin Raja Sulaiman. It was joined by Tengku Kudin (Tengku Dhiauddin, also spelt Ziauddin), a Kedahan prince, as well as other Malay and Chinese rival factions. The war was eventually won by Tengku Kudin and Abdullah's son, Raja Ismail. Background In 1854, the sultan of Selangor Sultan Muhammad Shah appointed Raja Abdullah bin Raja Ja'afar as governor of the Klang Valley. Raja Abdullah and his brother Raja Juma'at had previously helped Raja Sulaiman settle a debt incurred during a failed mining venture, and was therefore rewarded with the governorship of the Klang Valley. Raja Mahdi (alternately ''Raja Mahadi''), the grandson of Sultan Muhammad Shah, was the son of Raja Sulaiman who previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Kecil
Raja Kecil (d. 1746), or Raja Kecik, also known as Sultan Abdul Jalil Rahmat Shah (r. 1722–1746), was the first sultan of the Sultanate of Siak Sri Indrapura. A controversial figure, due to his origin tales and the rebellion he led, Raja Kecil united a multi-ethnic force in eastern Sumatra to defeat the Johor sultanate in 1718. He then ruled Johor for four years, before retreating to eastern Sumatra, where he established a new state along the Siak River in 1722. Raja Kecil continued to oversee periodic attacks on Johor for another decade, while he consolidated control over trade routes between the Melaka Straits and the resource-rich interior of Sumatra. After 1735, he allowed two of his sons, Raja Mahmud (Sultan Muhammad Abdul Jalil Jalaluddin Shah) and Raja Alam (Sultan Abdul Jalil Alamuddin Shah), to oversee the kingdom, which he ruled in name only. Raja Kecil died in Buantan, the capital of Siak Sri Indrapura, and his grave remains an important site for residents of the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugis
The Bugis people (pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar and Toraja), in the south-western province of Sulawesi, third-largest island of Indonesia. The Bugis in 1605 converted to Islam from Animism. The main religion embraced by the Bugis is Islam, with a small minority adhering to Christianity or a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called ''Tolotang''. Despite the population numbering only around six million, the Bugis are influential in the politics in modern Indonesia, and historically influential on the Malay peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Lesser Sunda Islands and other parts of the archipelago where they have migrated, starting in the late seventeenth century. The third president of Indonesia, B. J. Habibie, and a former vice president of Indonesia, Jusuf Kalla, are Bugis. In Malaysia, the former prime minister Muhyiddin Yassin has Bugis ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Idris Education University Sultan Abdul Jalil Campus Entrance (220712)
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), despite both referring to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei and Oman are the only independent countries which retain the tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KTM Komuter
KTM Komuter is a commuter rail system in Malaysia operated by Keretapi Tanah Melayu (KTM). It was introduced in 1995 to provide local rail services in Kuala Lumpur and the surrounding Klang Valley suburban areas. Services were later expanded to other parts of Malaysia with the introduction of the Northern and Southern sectors. The service uses air-conditioned electric multiple units in 3 and 6 car formations. KTM Komuter contributed RM146.2 million to group revenue in 2017, carrying a total of 37.235 million passengers. The total number of passengers travelling with KTM Komuter in 2017 shows a decrease of 10.2%. This can be attributed to reduced service frequency due to the ongoing Klang Valley Double Tracking (KVDT) rehabilitation project. Network Current Network Central Sector KTM Komuter's 287 km (109 mi) network in the Central Sector mainly covers the Klang Valley. It has 53 stations. It consists of two cross-city routes, namely the Port Klang Line (Tanjung Malim to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slim River
Slim River ( Jawi: سليم ريۏر; zh, 仕林河; Tamil Tamil may refer to: * Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia **Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils **Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia * Tamil language, nativ ...: சிலிம் ரீவர்) is a small town in Muallim District, Perak, Malaysia. It is about 100 km (driving time 45 minutes) from Kuala Lumpur. It is situated in the southern part of Perak and is 20 km north of Tanjung Malim. It is about 100 km (driving time 1 hour) from Ipoh. The town is surrounded by many small villages. History The town is named after a nearby river, Sungai Slim. The word Sungai means river in Malay language, Malay. The river was actually named after an English captain with last name Slim in the 19th century. He accidentally went up the river instead of the Perak River which was the main waterway back then. Slim River was a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


