|
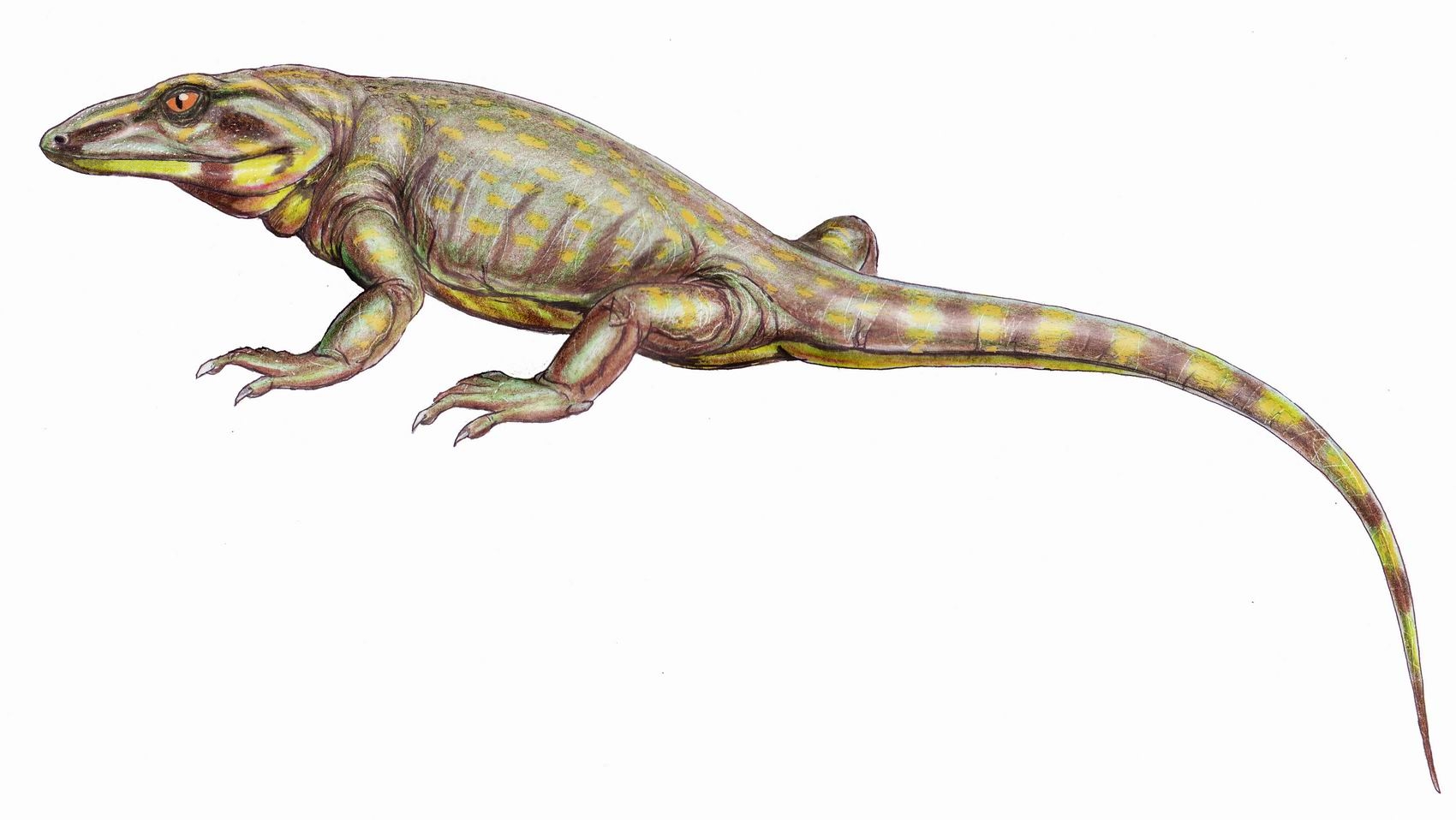
Tambacarnifex
''Tambacarnifex'' (meaning " Tambach butcher") is an extinct genus of varanodontine synapsids known from the Early Permian Tambach Formation of Free State of Thuringia, central Germany. It was first named by David S. Berman, Amy C. Henrici, Stuart S. Sumida, Thomas Martens and Valerie Pelletier in 2013 and the type species In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ... is ''Tambacarnifex unguifalcatus''. Below is a simplified version of the cladogram found by Berman ''et al.'', 2013. References Varanopids Prehistoric synapsid genera Artinskian Cisuralian synapsids of Europe Permian Germany Fossils of Germany Fossil taxa described in 2013 {{paleo-synapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 In Paleontology
Plants Cnidarians Arthropods Bryozoans Brachiopods Molluscs Echinoderms Conodonts Fishes Amphibians Research * Laloy ''et al.'' (2013) reinterpret the Eocene frog species ''Rana cadurcorum'' from the Quercy Phosphorites (France) as a junior synonym of '' Thaumastosaurus gezei''. Newly named temnospondyls Newly named lepospondyls Newly named lissamphibians Turtles Research * A study on the anatomy of the brain and inner ear of the Jurassic turtle ''Plesiochelys etalloni'' is published by Paulina Carabajal ''et al.'' (2013). Newly named turtles Thalattosaurs Ichthyopterygians Lepidosauromorphs Newly named sauropterygians Newly named rhynchocephalians Newly named lizards Newly named snakes Archosauromorphs Newly named basal archosauromorphs Archosaurs Other reptiles Synapsids Non-mammalian synapsids Research * The postcranial skeleton of therocephalian '' Ictidosuchoides'' is described by Heidi Fourie (2013). New taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopids
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanodontine
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an '' Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambach Formation
The Tambach Formation is an Early Permian-age geologic formation in central Germany. It consists of red to brown-colored sedimentary rocks (red beds) such as conglomerate, sandstone, and mudstone, and is the oldest portion of the Upper Rotliegend within the Thuringian Forest Basin. The overall geology records a history with three distinct stages of sedimentation within a mountainous environment. First, tectonic activity forms a basin (the Tambach Basin) dominated by high-energy debris flows, sheetfloods, and braided rivers. These incise underlying rhyolitic rock, depositing a coarse conglomerate known as the Bielstein Conglomerate. Second, calmer conditions allow the basin to widen, and the conglomerate is marginalized by finer sediments which were previously only common at the center of the basin, such as the characteristic Tambach Sandstone. These finer sediments were deposited through repeated sequences of flooding, followed by calm water, followed by exposure to air. The ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanodontinae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanopidae
Varanopidae is an extinct family of amniotes that resembled monitor lizards and may have filled a similar niche, hence the name. Typically, they are considered synapsids that evolved from an ''Archaeothyris''-like synapsid in the Late Carboniferous. However, some recent studies have recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid reptiles. A varanopid from the latest Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Description No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammalian standards. They had long tails, lizard-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artinskian
In the geologic timescale, the Artinskian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is a subdivision of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Artinskian likely lasted between and million years ago (Ma) according to the most recent revision of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) in 2022. It was preceded by the Sakmarian and followed by the Kungurian. Stratigraphy The Artinskian is named after the small Russian city of Arti (formerly ''Artinsk''), situated in the southern Ural mountains, about 200 km southwest of Yekaterinburg. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Alexander Karpinsky in 1874. Base of the Artinskian The base of the Artinskian Stage is defined as the first appearance datum (FAD) of the conodont species '' Sweetognathus whitei'' and ''Mesogondolella bisselli''. In order to constrain this age, the ICS subcommission on Permian stratigraphy informally proposed a candidate GSSP in 2002, later followed by a formal proposal in 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycterosaurus
''Mycterosaurus'' (Greek as mykter/mykteros meaning nose/snout, sauros meaning “lizard”) is an extinct genus of synapsids belonging to the family Varanopidae. It is classified in the varanopid subfamily Mycterosaurinae. ''Mycterosaurus'' is the most primitive member of its family, existing from 290.1 to 272.5 MYA, known to Texas and Oklahoma. It lacks some features that its advanced relatives have. ''Mycterosaurus'' is a relatively small carnivore, estimated to be around 60 cm (23 inches) long with synonyms of ''Eumatthevia bolli'', and possibly ''Basicranodon fortsillensis''. Restored, ''Mycterosaurus'' appears spindly and grotesque in contrast to the majority of "pelycosaurs" in its proportions and especially unlike edaphosaurs, which are commonly stocky in build. The number of valid ''Mycterosaurus'' species have varied over the years, with a total of two classifications of ''Mycterosaurus longiceps'' and ''Mycterosaurus smithae.'' However, recent analysis has l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Germany
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisuralian Synapsids Of Europe
The Cisuralian is the first series/epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the Pennsylvanian and followed by the Guadalupian. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mountains in Russia and Kazakhstan and dates between 298.9 ± 0.15 – 272.3 ± 0.5 Mya. The Cisuralian is often synonymous with the informal terms early Permian or lower Permian. It corresponds approximately with the Wolfcampian in southwestern North America. The series saw the appearance of beetles and flies and was a relatively stable warming period of about 21 million years. Name and background The Cisuralian is the first series or epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the last Pennsylvanian epoch (Gzhelian) and is followed by the Permian Guadalupian Epoch. The name "Cisuralian" was proposed in 1982, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Synapsid Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanops
''Varanops'' is an extinct genus of Early Permian varanopid synapsids known from Texas and Oklahoma of the United States. It was first named by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1911 as a second species of ''Varanosaurus'', ''Varanosaurus brevirostris''. In 1914, Samuel W. Williston reassigned it to its own genus and the type species is ''Varanops brevirostris''. Discovery ''V. brevirostris'' is known from the holotype FMNH UC 644, a three-dimensionally preserved nearly complete and articulated skeleton including a nearly complete skull and mandibles. It was collected in the Indian Creek, 35 site (=''Cacops'' Bonebed), from the Arroyo Formation of the Clear Fork Group, Baylor County of Texas, dating to the early Kungurian stage of the Cisuralian Epoch, about 279.5-272.5 million years ago. Many well preserved specimens from the same locality and horizon of the type specimen, including FMNH UR 2423, nearly complete skull and mandibles, MCZ 1926, complete sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |