|
Tailless Aircraft
In aeronautics, a tailless aircraft is an aircraft with no other horizontal aerodynamic surface besides its main wing. It may still have a fuselage, vertical tail fin (vertical stabilizer), and/or vertical rudder. Theoretical advantages of the tailless configuration include low parasitic drag as on the Horten H.IV soaring glider and good stealth characteristics as on the Northrop B-2 Spirit bomber. Disadvantages include a potential sensitivity to trim. Tailless aircraft have been flown since the pioneer days; the first stable aeroplane to fly was the tailless Dunne D.5, in 1910. The most successful tailless configuration has been the tailless delta, especially for combat aircraft, though the most familiar tailless delta is the Concorde airliner. NASA has used the 'tailless' description for the novel X-36 research aircraft which has a canard foreplane but no vertical fin. Aircraft configuration A tailless aircraft has no other horizontal surface besides its main wing. The aer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
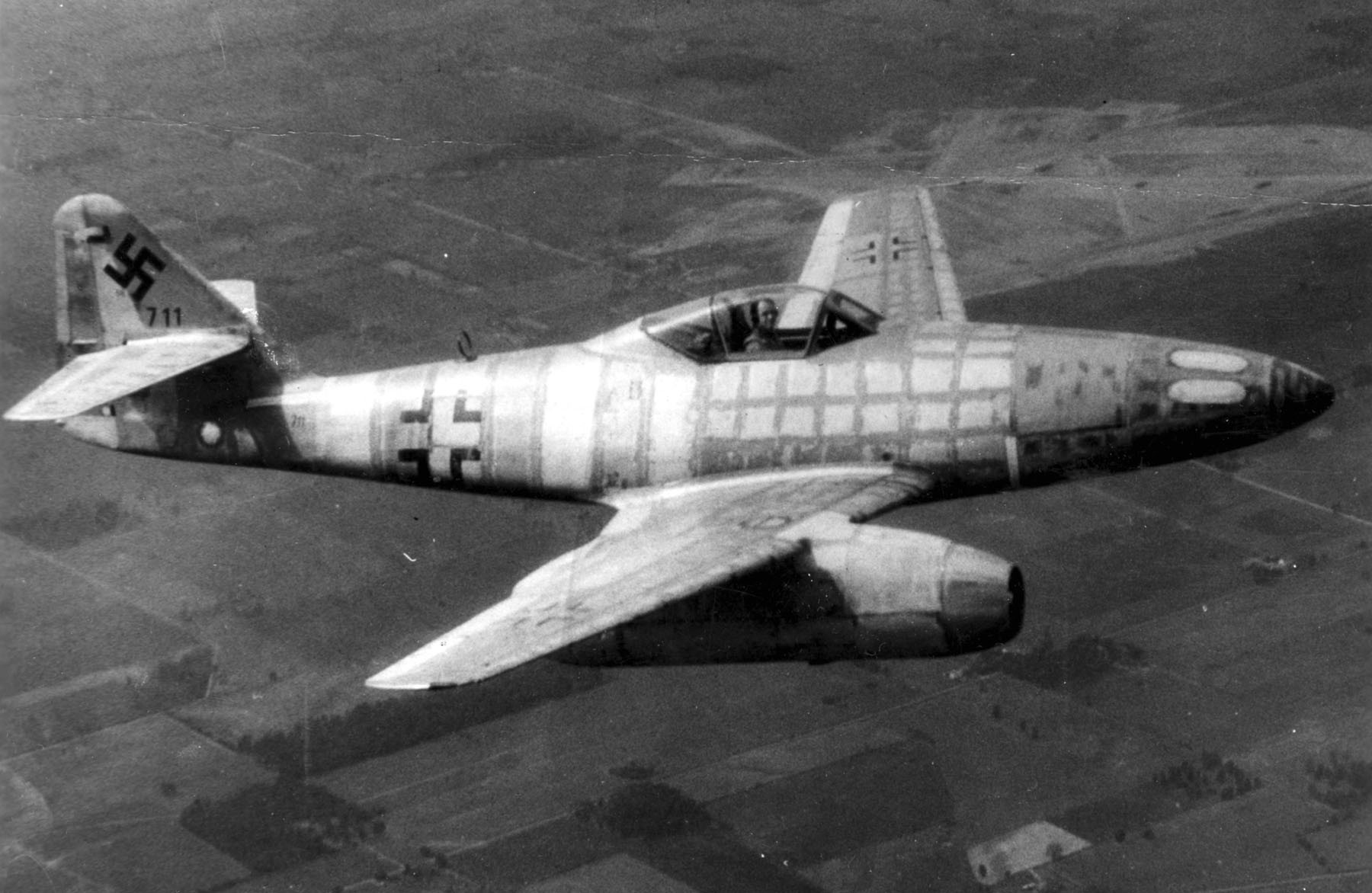
DH 108 Swallow Tg283
DH, Dh, dh, or dH may refer to: Places * DH postcode area, in the United Kingdom for the area of Durham and surrounding towns * Diamond Head, Hawaii, a volcanic tuff cone on Oʻahu Organisations * D+H, a Canadian financial services company * Department of Health (United Kingdom), a department of the UK government * DH Press, the Dark Horse Comics imprint that publishes novels * Deccan Herald, an Indian newspaper Science and technology * Denavit–Hartenberg parameters, a type of robotics convention * Dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin disease * DH register, the high byte of a DX register in x86-compatible microprocessors * Diffie-Hellman key exchange (D-H), a specific method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a public channel * District heating, a method of heating multiple buildings from a central location * Doubled haploidy, a genetic status * Deuterium:protium (D:H), a ratio in deuterium-depleted water *°dH, deutsche Härte, a unit of Hard water, water hardness * Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas X-36
The McDonnell Douglas (later Boeing) X-36 ''Tailless Fighter Agility Research Aircraft'' was an American stealthy subscale prototype jet designed to fly without the traditional empennage found on most aircraft. This configuration was designed to reduce weight, drag and radar cross section, and increase range, maneuverability and survivability. Design and development The X-36 was built to 28% scale of a possible fighter aircraft, and was controlled by a pilot in a ground-based virtual cockpit with a view provided by a video camera mounted in the canopy of the aircraft. For control, a canard forward of the wing was used as well as split ailerons and an advanced thrust vectoring nozzle for directional control. The X-36 was unstable in both pitch and yaw axes, so an advanced digital fly-by-wire control system was used to provide stability. First flown on 17 May 1997, it made 31 successful research flights. It handled very well, and the program is reported to have met or exceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horten Brothers
Walter Horten (born 13 November 1913 in Bonn; died 9 December 1998 in Baden-Baden, Germany) and Reimar Horten (born 12 March 1915 in Bonn; died 14 March 1994 in Villa General Belgrano, Argentina), sometimes credited as the Horten Brothers, were German aircraft pilots. Walter was a fighter pilot on the Western Front, flying a Bf 109 for Jagdgeschwader 26 in the first six months of World War II; he eventually became the unit's technical officer. Reimar was also trained as a Me 109 pilot; however, later in August 1940, he was transferred to the glider pilot school in Braunschweig. He earned his PhD in mathematics from the University of Göttingen, having resumed his studies in 1946 with help from Ludwig Prandtl. The Hortens designed the world's first jet-powered flying wing, the Horten Ho 229. Biography Early lives Between the World Wars, the Treaty of Versailles limited the construction of German military airplanes. In response, German military flying became semi-clandestine, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine. A solid body moving through a fluid produces an aerodynamic force. The component of this force perpendicular to the relative freestream velocity is called lift. The component parallel to the relative freestream velocity is called drag. An airfoil is a streamlined shape that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their geometry: those for subsonic flight generally have a rounded leading edge, while those designed for supersonic flight tend to be slimmer with a sharp leading edge. All have a sharp trailing edge. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitching Moment
In aerodynamics, the pitching moment on an airfoil is the moment (or torque) produced by the aerodynamic force on the airfoil if that aerodynamic force is considered to be applied, not at the center of pressure, but at the aerodynamic center of the airfoil. The pitching moment on the wing of an airplane is part of the total moment that must be balanced using the lift on the horizontal stabilizer. More generally, a pitching moment is any moment acting on the pitch axis of a moving body. The lift on an airfoil is a distributed force that can be said to act at a point called the center of pressure. However, as angle of attack changes on a cambered airfoil, there is movement of the center of pressure forward and aft. This makes analysis difficult when attempting to use the concept of the center of pressure. One of the remarkable properties of a cambered airfoil is that, even though the center of pressure moves forward and aft, if the lift is imagined to act at a point calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is a two-dimensional object in three-dimensional space. In the case of a solid object, the boundary formed by these lines or partial lines is called the ''lateral surface''; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is a conical surface. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
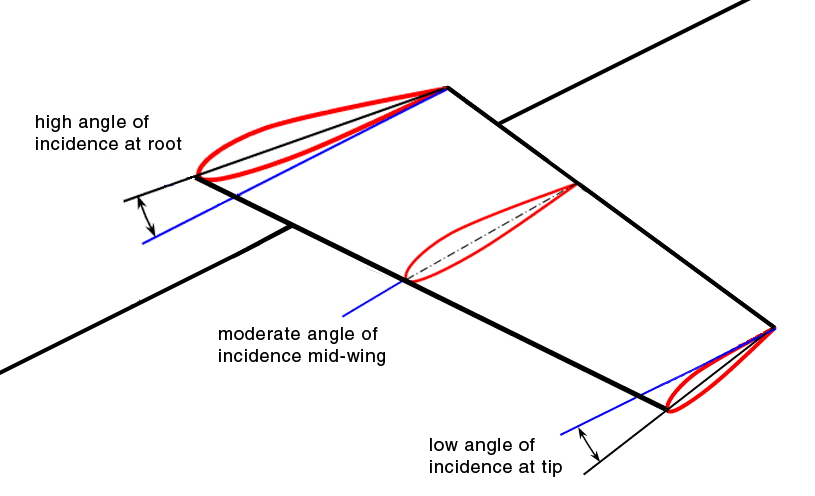
Washout (aviation)
Washout is a characteristic of aircraft wing design which deliberately reduces the lift distribution across the span of an aircraft’s wing. The wing is designed so that the angle of incidence is greater at the wing roots and decreases across the span, becoming lowest at the wing tip. This is usually to ensure that at stall speed the wing root stalls before the wing tips, providing the aircraft with continued aileron control and some resistance to spinning. Washout may also be used to modify the spanwise lift distribution to reduce lift-induced drag. Design considerations Washout is commonly achieved by designing the wing with a slight twist, reducing the angle of incidence from root to tip, and therefore causing a lower angle of attack at the tips than at the roots. This feature is sometimes referred to as structural washout, to distinguish it from aerodynamic washout. Wingtip stall is unlikely to occur symmetrically, especially if the aircraft is maneuvering. As an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Incidence (aerodynamics)
On fixed-wing aircraft, the angle of incidence (sometimes referred to as the ''mounting angle'' or ''setting angle'') is the angle between the chord line of the wing where the wing is mounted to the fuselage, and a reference axis along the fuselage (often the direction of minimum drag, or where applicable, the longitudinal axis). The angle of incidence is fixed in the design of the aircraft, and with rare exceptions, cannot be varied in flight. The term can also be applied to horizontal surfaces in general (such as canards or horizontal stabilizers) for the angle they make relative the longitudinal axis of the fuselage. The figure to the right shows a side view of an airplane. The extended chord line of the wing root (red line) makes an angle with the longitudinal axis (roll axis) of the aircraft (blue line). Wings are typically mounted at a small positive angle of incidence, to allow the fuselage to have a low angle with the airflow in cruising flight. Angles of incidence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swept Wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction. Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigated in Germany as early as 1935 by Albert Betz and Adolph Busemann, finding application just before the end of the Second World War. It has the effect of delaying the shock waves and accompanying aerodynamic drag rise caused by fluid compressibility near the speed of sound, improving performance. Swept wings are therefore almost always used on jet aircraft designed to fly at these speeds. The term "swept wing" is normally used to mean "swept back", but variants include forward sweep, variable sweep wings and oblique wings in which one side sweeps forward and the other back. The delta wing is also aerodynamically a form of swept wing. Reasons for sweep There are three main reasons for sweeping a wing: 1. to arrange the center of gravity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Static Stability
In flight dynamics, longitudinal stability is the stability of an aircraft in the longitudinal, or pitching, plane. This characteristic is important in determining whether an aircraft pilot will be able to control the aircraft in the pitching plane without requiring excessive attention or excessive strength. The longitudinal stability of an aircraft, also called pitch stability, refers to the aircraft's stability in its plane of symmetry about the lateral axis (the axis along the wingspan). It is an important aspect of the handling qualities of the aircraft, and one of the main factors determining the ease with which the pilot is able to maintain level flight. Longitudinal static stability refers to the aircraft's initial tendency on pitching. Dynamic stability refers to whether oscillations tend to increase, decrease or stay constant. Static stability If an aircraft is longitudinally statically stable, a small increase in angle of attack will create a nose-down pitching mom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
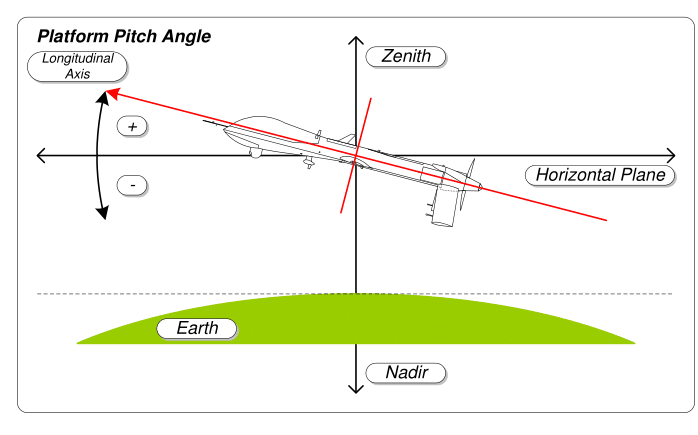
Pitch (flight)
An aircraft in flight is free to rotate in three dimensions: '' yaw'', nose left or right about an axis running up and down; ''pitch'', nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and ''roll'', rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. The axes are alternatively designated as ''vertical'', ''lateral'' (or ''transverse''), and ''longitudinal'' respectively. These axes move with the vehicle and rotate relative to the Earth along with the craft. These definitions were analogously applied to spacecraft when the first manned spacecraft were designed in the late 1950s. These rotations are produced by torques (or moments) about the principal axes. On an aircraft, these are intentionally produced by means of moving control surfaces, which vary the distribution of the net aerodynamic force about the vehicle's center of gravity. Elevators (moving flaps on the horizontal tail) produce pitch, a rudder on the vertical tail produces yaw, and ailerons (flaps on the wing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic Center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magnitude varies with the choice of where the lift is chosen to be applied. The aerodynamic center is the point at which the pitching moment coefficient for the airfoil does not vary with lift coefficient (i.e. angle of attack), making analysis simpler. : =0 where C_L is the aircraft lift coefficient. The lift and drag forces can be applied at a single point, the center of pressure, about which they exert zero torque. However, the location of the center of pressure moves significantly with a change in angle of attack and is thus impractical for aerodynamic analysis. Instead the aerodynamic center is used and as a result the incremental lift and drag due to change in angle of attack acting at this point is sufficient to describe the aerodynamic fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |