|
Tai Kang
Tai Kang () was the third king of the Xia Dynasty. He was the son of the king Qi of Xia and paternal grandson of Yu the Great and queen Nu Jiao. Biography Tai Kang loved to hunt and did not rule well. According to the '' Bamboo Annals'', Tai Kang took the throne in the year of ''Guiwei''. His capital was in Zhenxun (斟鄩). In his first year, while he went hunting beyond the Luo river, Houyi came and occupied Zhenxin. Tai Kang died 4 years later, or according to the book Lushi, 10 years later. According to ''Records of the Grand Historian'', he ruled about 19 years and lost his regime. "Taiping Yulan" claims he was a tyrant who ruled for 29 years, then lost his regime and vanished. He was succeeded by his brother Zhong Kang and nephew Xiang of Xia. In some sources, Tai Kang was drowned in a lake. In literature The '' Book of Documents'' features ''Songs of the Five Sons'' (五子之歌) among the documents of Xia (Chapter 8). According to the introductory note, the doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
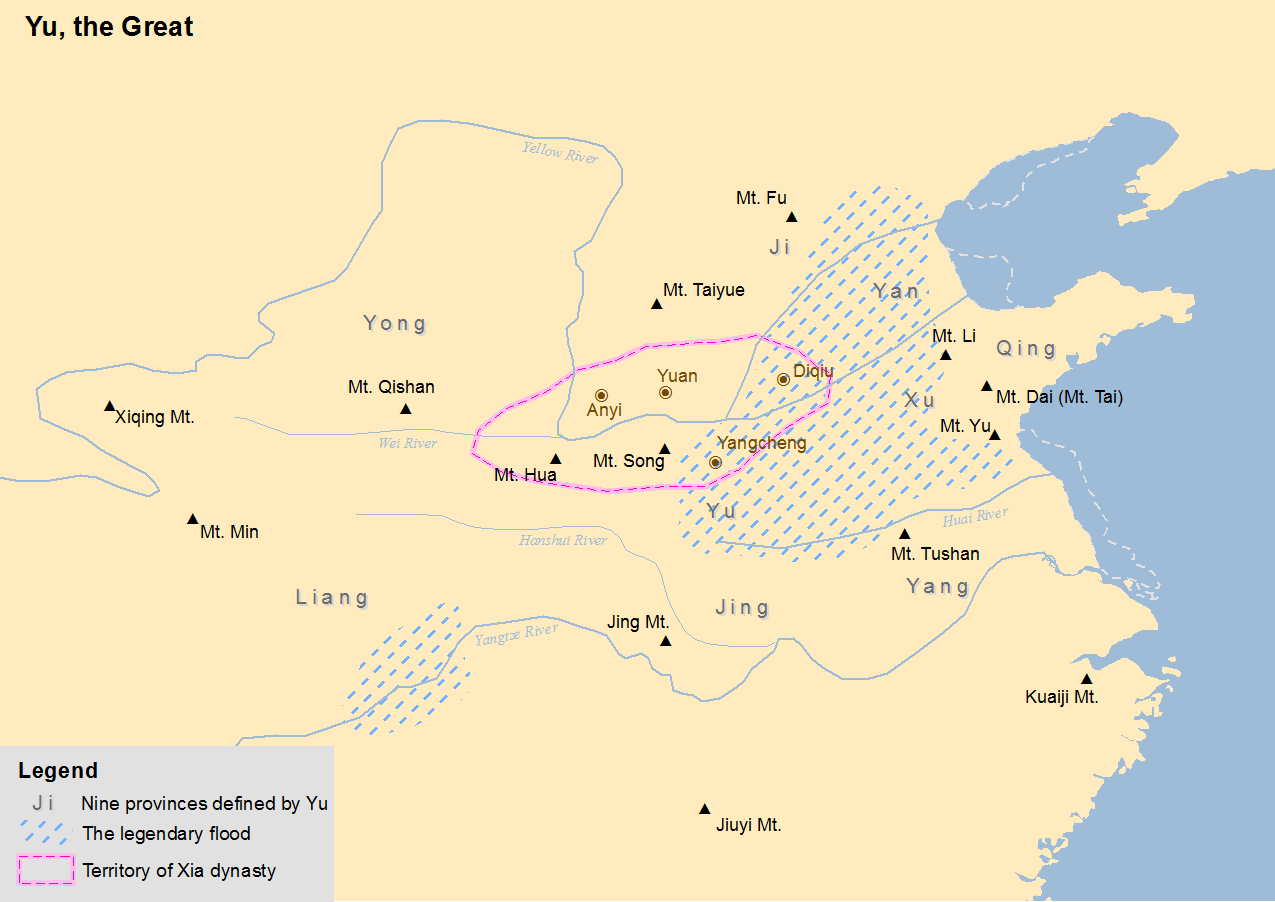
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongbieocheonga
''Yongbieocheonga'', literally ''Songs of the Dragons Flying to Heaven'', was the first work written in Hangul. The book was published in 1447 and written by Jeong Inji (정인지, 鄭麟趾), An Ji (안지, 安止), and Kwon Jae (권제, 權踶). The preface was written by Seong Sam-mun (성삼문, 成三問) and Pak Paengnyeon (박팽년, 朴彭年). The book was written on the Joseon dynasty and its ancestral heritage. Today, the Songs provide insight into the development of Joseon, the Korean people, and the history of neighboring ethnicities in Northeast Asia such as the Jurchens (Manchus) who would later establish the Qing dynasty of China. The songs, in the form of 125 cantos, were composed through the efforts of a committee of Confucian philologists and literati. This compilation was the first Korean writing to be recorded in hangul (in addition to hanja). Previously, Korea had a long history of recording texts using Chinese characters exclusively. Several important the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shūjīng'', earlier ''Shu King'') or ''Classic of History'', also known as the ''Shangshu'' (“Venerated Documents”), is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, and served as the foundation of Chinese political philosophy for over 2,000 years. The ''Book of Documents'' was the subject of one of China's oldest literary controversies, between proponents of different versions of the text. A version was preserved from Qin Shi Huang's burning of books and burying of scholars by scholar Fu Sheng, in 29 sections (''pian'' 篇). This group of texts were referred to as "Modern Script" ''jinwen'' 今文, because written with the script in use at the beginning of the Western Han dyansty. According to Western Han dynasty documents, new textual material was discovered in the wall of Confucius' family estate in Qufu by his descendant Kong Anguo in the late 2nd c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Of Xia
Xiang () is the name of a king of the semi-legendary Xia dynasty who is said to have reigned during the 3rd millennium BC. He was the fifth king of the Xia dynasty. Biography Xiang had been preceded on the throne of Xia by his father Zhong Kang, and before that by his uncle Tai Kang.''The Shape of the Turtle: Myth, Art, and Cosmos in Early China'' by Sarah Allan Reign according to the ''Bamboo Annals'' Xiang got his throne in the year of Wuxu and set his capital in Shangqiu. In the first year of his reign, he sent troops against the Huai Barbarians and Fei Barbarians (畎夷, aka ''Quanyi''). In the third year, he sent troops to the Feng Barbarians and Huang Barbarians. In his 7th year, "the hordes of Yu came to make their submission", while in the 8th year, the warlord Han Zhuo killed Hou Yi. Han Zhuo also sent his son Jiao against Ge. In his 9th year, Xiang moved his court to Zhenguan. In the 15th year, Xiang's vassal, Xiangshi duke of Shang, "prepared carriages and hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhong Kang Of Xia
Zhong Kang () was the fourth king of the Xia Dynasty, the first dynasty in traditional Chinese history. Family Zhong Kang was a son of king Qi of Xia and thus the younger brother of Tai Kang. He was the father of Xiang of Xia. Reign According to the ''Bamboo Annals'', Zhong Kang took the throne in the year of ''Jichou'' (''己丑''). His capital was at Zhenxun. On the day of ''gengwu(庚戌)'', the 9th month in the 5th year of his reign, there was a solar eclipse. Since the royal astronomers at that time were licentious and drunk, they failed to predict this eclipse, resulting in confusion and panic among the common people. Zhong Kang sent the nobleman Yin to punish the Ministers of Astronomy for thus neglecting their duties. This is described more fully in the document known as the ''Punitive Expedition of Yin(胤征)'' in the Book of Documents. In the Bamboo Annals, this was reflected as nobleman Yin conquering Xihe, which is the god of astronomy. In the 6th year of Zhong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lushi (book)
The ''Lushi'' (, ''Grand History''), formerly known as the ''Lopi'', is an unofficial history of China written by Southern Song The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. ... Dynasty scholar Luo Mi or Luo Bi (; 1131 – c. 1189), with key assistance from his son Luo Ping (). As ''Lushi'' mixes historical facts with legends and folklore, its reliability has been disputed by historians. However, it is a valuable work for the study of ancient Chinese mythology. The extant version of ''Lushi'' was assembled by the later scholars based on Luo's work. Notes References {{reflist, 30em Song dynasty literature 12th-century Chinese books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo River (Henan)
The Luo River () is a tributary of the Yellow River in China. It rises in the southeast flank of Mount Hua in Shaanxi province and flows east into Henan province, where it eventually joins the Yellow River at the city of Gongyi. The river's total length is . Although not a major river by most standards, it flows through an area of great archaeological significance in the early history of China. Principal cities or prefectures located on the river include Lushi, Luoning, Yiyang, Luoyang, Yanshi, and Gongyi. The Luo's main tributary is the Yi River, which joins it at Yanshi, after which the river is called the Yiluo River. See also * Lo Shu Square * Peiligang culture The Peiligang culture was a Neolithic culture in the Luo River (Henan), Yi-Luo river basin (in modern Henan, Henan Province, China) that existed from 7000 to 5000 BC. Over 100 sites have been identified with the Peiligang culture, nearly all o ... External links Confluence of the Luo and Yellow Rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi Of Xia
Qi () was a Chinese king, the son of Yu the Great and the second sovereign of the Xia dynasty. He ruled for roughly nine to ten years.戴逸, 龔書鐸. 002(2003) 中國通史. 史前 夏 商 西周. Intelligence press. . p. 40. Biography Family Qi's father, Yu the Great, also the founder of the Xia dynasty, married Nu Jiao and had Qi. Qi was not to be the next king but due to public pressure Qi was chosen as Yu's successor, starting the dynastic tradition. Later, Qi had a son named Tài Kāng who also became the next king. Reign Yu died 45 years into his reign. After Qi's rule, Qi's son Tai Kang succeeded him as king. According to the historian Sima Qian, Yu did not want his son to become king and intended to give the throne to Gao Yao, his Minister of Justice, but when Gao died Yu designated as his heir Yi (also known as Boyi), his former companion for thirteen years fighting the flood and his current Minister of Animal Husbandry. But due to Yu's great influence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhenxun
Zhenxun () was the last capital for the pre historical Chinese Xia dynasty. There is a consensus among many Chinese scholars that the Erlitou site about 20 km east of central Luoyang Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the ... is identified as Zhenxun. References Ancient Chinese capitals {{Portal, China, History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |