|
TYROBP
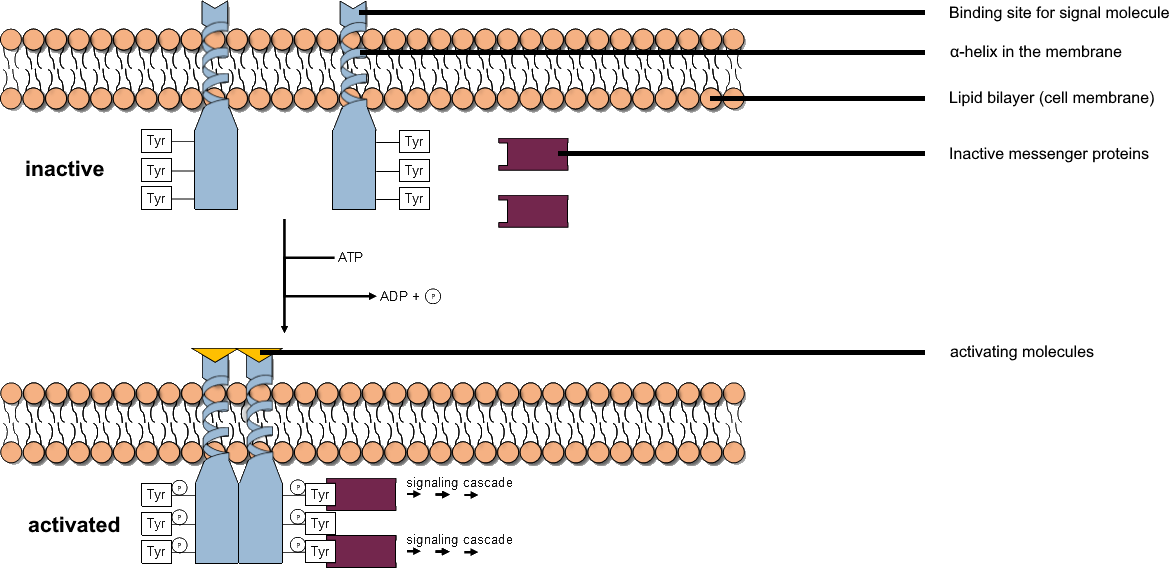
TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein is an adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TYROBP'' gene. Function This gene encodes a transmembrane signaling polypeptide which contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) in its cytoplasmic domain. The encoded protein may associate with the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family of membrane glycoproteins and may act as an activating signal transduction element. This protein may bind zeta-chain associated protein kinase 70 kDa (ZAP-70) and spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) and play a role in signal transduction, bone modeling, brain myelination, and inflammation Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' .... Mutations within this gene have been associated with polycystic lip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TREM2
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TREM2'' gene. TREM2 is expressed on macrophages, immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells, osteoclasts, and microglia, which are immune cells in the central nervous system. In the liver, TREM2 is expressed by several cell types, including macrophages, that respond to injury. In the intestine, TREM2 is expressed by myeloid-derived dendritic cells and macrophage. TREM2 is overexpressed in many tumor types and has anti-inflammatory activities. It might therefore be a good therapeutic target. Gene The TREM2' gene lies on the sixth chromosome in humans, specifically in location 6p21.1. The gene has 5 coding exon regions. Alternative splicing of the ''TREM2'' mRNA transcript leads to different isoforms of the protein being produced upon translation. Specifically, ''TREM2'' mRNA has 3 different isoforms containing 3 consistent exons, and 2 that vary between the isoforms. ''TREM2' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Lipomembranous Osteodysplasia With Sclerosing Leukoencephalopathy
Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy also known as Nasu–Hakola disease is a rare disease characterised by early-onset dementia and multifocal bone cysts. It is caused by autosomal recessive loss of function mutations in either the ''TREM2'' or ''TYROBP'' gene that are found most frequently in the Finnish and Japanese populations. Signs and symptoms Symptoms appear in four stages over the course of the disease. The first (latent stage) is asymptomatic and lasts up to the early 20s. The second stage (osseous stage) is characterized by persistent bone pain, usually accompanied by pathological fractures of these bones. Bones of the hands, feet, wrists, and ankles are typically affected first, then followed by the arms and legs. The third stage (early neurologic) is marked by the onset of symptoms typical of a frontal lobe syndrome (euphoria, lack of concentration, loss of judgment and social inhibitions) with memory loss. Epilepsy may occur du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIRPB1
Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SIRPB1'' gene. SIRPB1 has also recently been designated CD172B (cluster of differentiation 172B). The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the signal-regulatory-protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. This protein was found to interact with TYROBP/DAP12, a protein bearing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. This protein was also reported to participate in the recruitment of tyrosine kinase SYK. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. Interactions SIRPB1 has been shown to interact with TYROBP TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein is an adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TYROBP'' gene. Function This gene encodes a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif
An immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) is a conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated twice in the cytoplasmic tails of non-catalytic tyrosine-phosphorylated receptors, cell-surface proteins found mainly on immune cells. Its major role is being an integral component for the initiation of a variety of signaling pathway and subsequently the activation of immune cells, although different functions have been described, for example an osteoclast maturation. Structure The motif contains a tyrosine separated from a leucine or isoleucine by any two other amino acids, giving the signature YxxL/I. Two of these signatures are typically separated by between 6 and 8 amino acids in the cytoplasmic tail of the molecule (YxxL/Ix(6-8)YxxL/I). However, in various sources, this consensus sequence differs, mainly in the number of amino acids between individual signatures. Apart from ITAMs which have the structure described above, there is also a variety of proteins c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptor
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), are a family of type I transmembrane glycoproteins expressed on the plasma membrane of natural killer (NK) cells and a minority of T cells. In humans, they are encoded in the leukocyte receptor complex (LRC) on chromosome 19q13.4; the KIR region is approximately 150 kilobases and contains 14 loci, including 7 protein-coding genes (some duplicated) and 2 pseudogenes. They regulate the killing function of these cells by interacting with major histocompatibility (MHC) class I molecules, which are expressed on all nucleated cell types. KIR receptors can distinguish between MHC I allelic variants, which allows them to detect virally infected cells or transformed cells. KIRs are paired receptors, meaning some have activating and others have inhibitory functions; most KIRs are inhibitory: their recognition of MHC molecules suppresses the cytotoxic activity of their NK cell. A limited number of KIRs are activating: their recognition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand (biochemistry), ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a Cell signaling#Signaling pathways, signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription (biology), transcription or translation (biology), translation of genes, and post-translational modification, post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZAP-70
ZAP-70 (Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70) is a protein normally expressed near the surface membrane of Lymphocyte, lymphocytes (T cells, natural killer cells, and a subset of B cell, B cells). It is most prominently known to be recruited upon antigen binding to the T cell receptor (TCR), and it plays a critical role in T cell signaling. ZAP-70 was initially discovered in TCR-stimulated Jurkat cells, an immortal line of human T lymphocytes, in 1991. Its molecular weight is 70 kDa, and it is a member of the protein-tyrosine kinase family and is a paralog, close homolog of Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK, SYK. SYK and ZAP70 share a common evolution, evolutionary origin and split from a Most recent common ancestor, common ancestor in the jawed vertebrates. The importance of ZAP-70 in T cell activation was determined when comparing ZAP-70 expression in patients with SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency). ZAP-70 deficient individuals were found to have no functioning T cells in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine-protein Kinase SYK
Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK, also known as spleen tyrosine kinase, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''SYK'' gene. Function SYK, along with ZAP70, is a member of the Syk family of tyrosine kinases. These cytoplasmic non-receptor tyrosine kinases share a characteristic dual SH2 domain separated by a linker domain. However, activation of SYK relies less on phosphorylation by Src family kinases than ZAP70. SYK and ZAP70 share a common evolutionary origin and split from a common ancestor in the jawed vertebrates. While Syk and ZAP70 are primarily expressed in hematopoietic tissues, a variety of tissues express Syk. Within B and T cells, respectively, Syk and ZAP70 transmit signals from the B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor. Syk plays a similar role in transmitting signals from a variety of cell surface receptors including CD74, Fc receptor, and integrins. Function during development Mice that lack Syk completely (Syk−/−, Syk-knockout) die during embryonic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Modeling
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialised connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralisation of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralised matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |