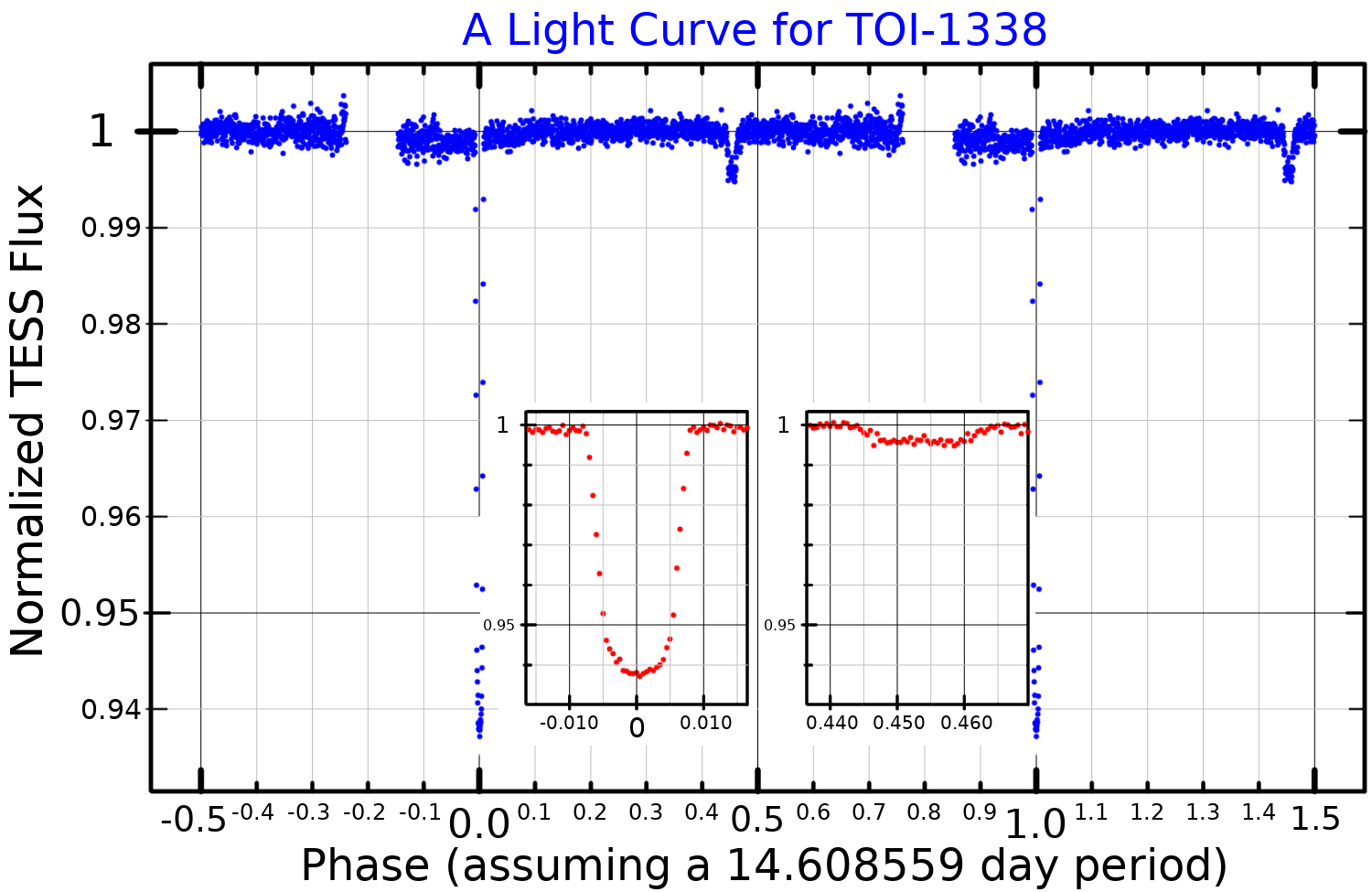
|
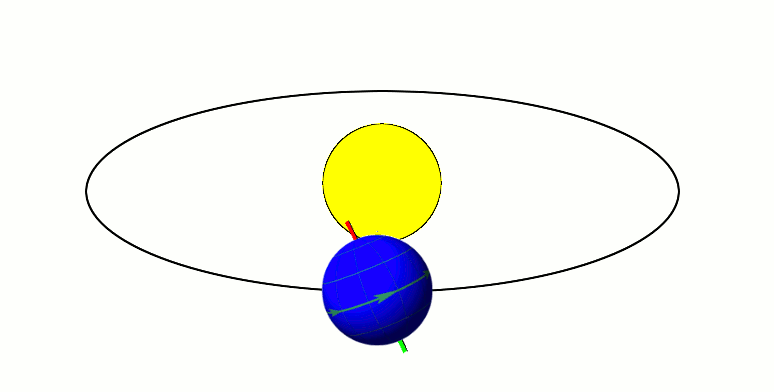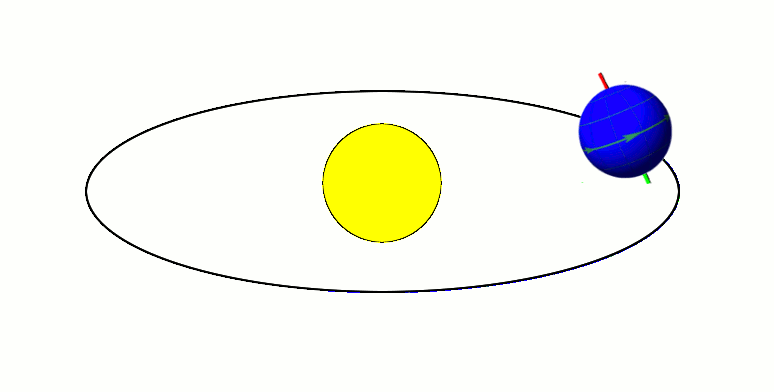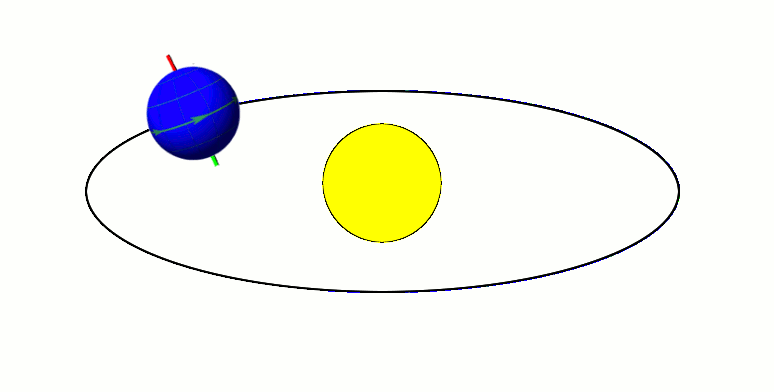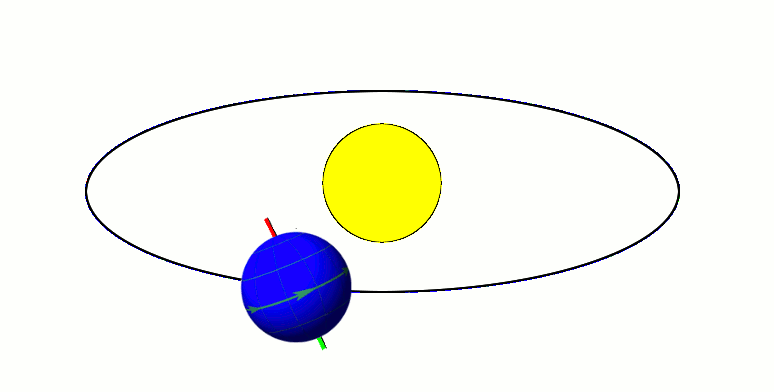
TOI 1338
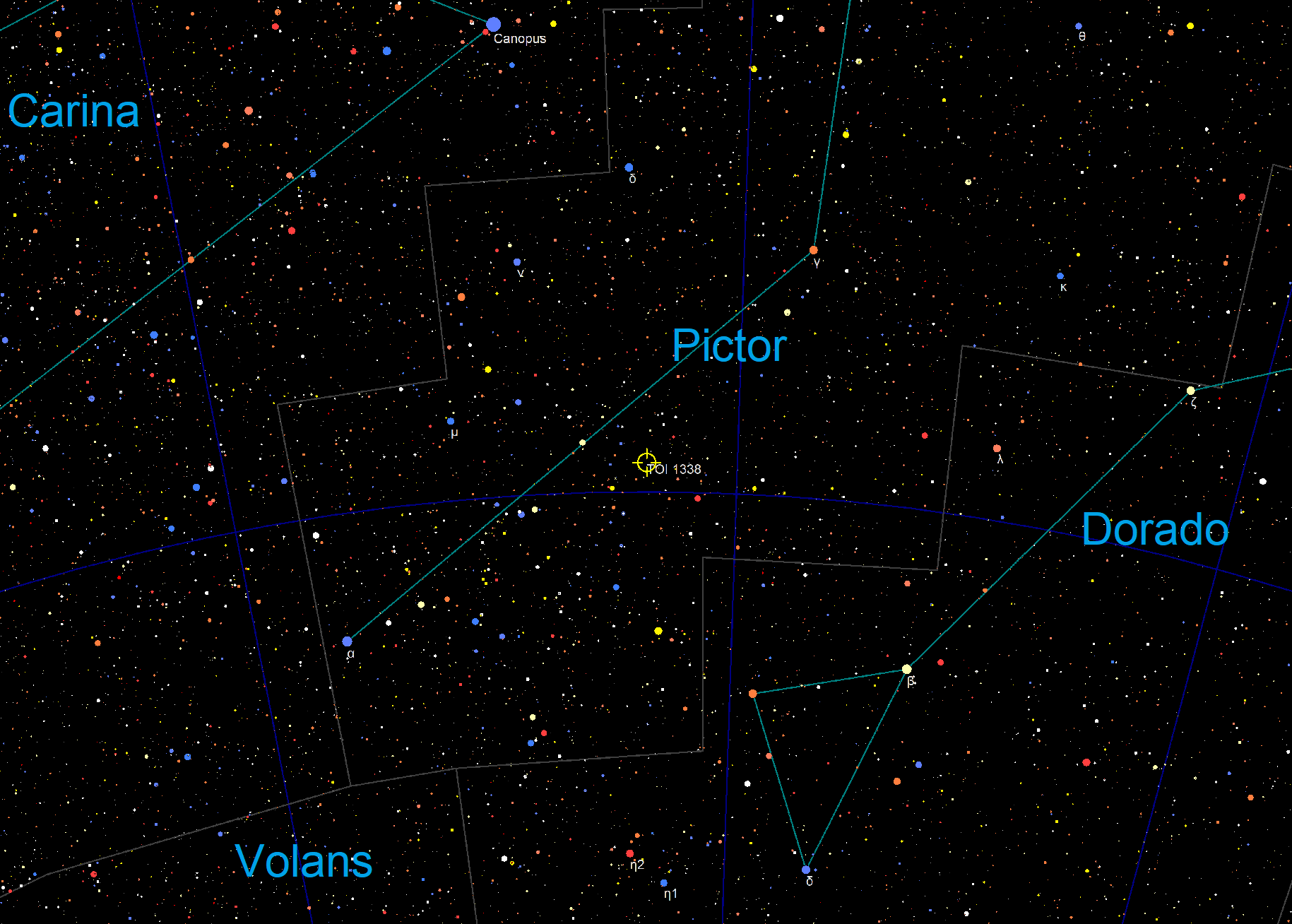
TOI 1338 is a binary star system located in the constellation Pictor, about 1,320 light-years from Earth. It is orbited by the circumbinary planet TOI 1338 b, discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Nomenclature and history The acronym TOI stands for "TESS Objects of Interest." The planet was found by Wolf Cukier, a 17-year-old attending Scarsdale High School in New York at the time, who joined the Goddard Space Flight Center as a summer intern. He looked through light curves that were flagged as eclipsing binaries by volunteers of the Planet Hunters citizen science project. Cukier and six of the Planet Hunter volunteers are co-authors of the publication regarding the newly-discovered planet. Cukier currently attends Princeton University as an undergraduate student in the Department of Astrophysical Sciences. Cukier was not given an opportunity to name the planet. In February 2021, a petition calling for the planet TOI 1338 b in the system to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopic Binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit (astronomy), transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
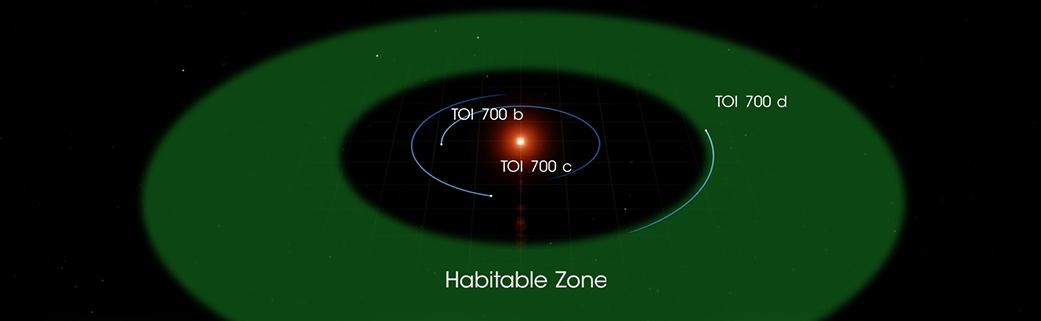
TOI 700
TOI-700 is a red dwarf 101.4 light-years away from Earth located in the Dorado constellation that hosts TOI-700 d, the first Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Nomenclature and history The acronym "TOI" refers to stars and exoplanets studied by TESS, and is short for: "Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite Object of Interest". Stellar characteristics TOI-700 is a red dwarf of spectral class M (much redder, cooler, and dimmer than the sun) that is 40% the mass, 40% the radius and 55% of the temperature of the Sun. The star is bright with low levels of stellar activity. Over the 11 sectors observed with TESS, the star does not show a single white-light flare. The low rotation rate is also an indicator of low stellar activity. Planetary system Four exoplanets have been detected by TESS to be orbiting the host star TOI-700. All four exoplanets may be tidally locked to TOI-700. Three papers desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstellar Disc
A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place, and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways. Young star According to the widely accepted model of star formation, sometimes referred to as the nebular hypothesis, a young star (protostar) is formed by the gravitational collapse of a pocket of matter within a giant molecular cloud. The infalling material possesses some amount of angular momentum, which results in the formation of a gaseous protoplanetary disc around the young, rotating star. The former is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-16
Kepler-16 is an eclipsing binary star system in the constellation of Cygnus that was targeted by the Kepler spacecraft. Both stars are smaller than the Sun; the primary, Kepler-16A, is a K-type main-sequence star and the secondary, Kepler-16B, is an M-type red dwarf. They are separated by 0.22 AU, and complete an orbit around a common center of mass every 41 days. The system is host to one known extrasolar planet in circumbinary orbit: the Saturn-sized Kepler-16b. Eclipses The Kepler-16 system is almost edge-on to Earth and the two stars eclipse each other as they orbit. The larger and brighter primary star is partially eclipsed by the secondary for about six hours and the brightness drops by about 0.15 magnitudes. The secondary star is completely occulted by the primary star for about two hours, but the overall brightness only drops by about 0.02 magnitudes. There are also shallow eclipses caused by a large exoplanet. When this transits across the primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossiter–McLaughlin Effect
The Rossiter–McLaughlin effect is a spectroscopic phenomenon observed when an object moves across the face of a star. Description The Rossiter–McLaughlin effect is a spectroscopic phenomenon observed when either an eclipsing binary's secondary star or an extrasolar planet is seen to transit across the face of the primary or parent star. As the main star rotates on its axis, one quadrant of its photosphere will be seen to be coming towards the viewer, and the other visible quadrant to be moving away. These motions produce blueshifts and redshifts, respectively, in the star's spectrum, usually observed as a broadening of the spectral lines. When the secondary star or planet transits the primary, it blocks part of the latter's disc, preventing some of the shifted light from reaching the observer. That causes the observed mean redshift of the primary star as a whole to vary from its normal value. As the transiting object moves across to the other side of the star's disc, the red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Earth's obliquity oscillates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees on a 41,000-year cycle. Based on a continuously updated formula (here Laskar, 1986, though since 2006 the IMCCE and the IAU recommend the P03 model), Earth's mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coplanarity
In geometry, a set of points in space are coplanar if there exists a geometric plane that contains them all. For example, three points are always coplanar, and if the points are distinct and non-collinear, the plane they determine is unique. However, a set of four or more distinct points will, in general, not lie in a single plane. Two lines in three-dimensional space are coplanar if there is a plane that includes them both. This occurs if the lines are parallel, or if they intersect each other. Two lines that are not coplanar are called skew lines. Distance geometry provides a solution technique for the problem of determining whether a set of points is coplanar, knowing only the distances between them. Properties in three dimensions In three-dimensional space, two linearly independent vectors with the same initial point determine a plane through that point. Their cross product is a normal vector to that plane, and any vector orthogonal to this cross product through the initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOI 1338b
TOI-1338 is a binary star system located in the constellation Pictor, about 1,320 light-years from Earth. It is orbited by two known circumbinary planets, TOI-1338 b, discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and BEBOP-1c, discovered by the Binaries Escorted By Orbiting Planets project. Discovery and nomenclature The circumbinary planet TOI-1338 b was found in the summer of 2019 by Wolf Cukier, a 17-year-old attending Scarsdale High School in New York at the time, who joined the Goddard Space Flight Center as a summer intern. The acronym TOI stands for "TESS Objects of Interest." Cukier studied data provided by volunteers of the Planet Hunters citizen science project, looking through data that had been flagged as an eclipsing binary. Cukier and six of the Planet Hunter volunteers are co-authors of the publication regarding the planet. Cukier currently attends Princeton University as an undergraduate student in the Department of Astrophysical Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occulted
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks from view (occults) an object in the background. In this general sense, occultation applies to the visual scene observed from low-flying aircraft (or computer-generated imagery) when foreground objects obscure distant objects dynamically, as the scene changes over time. If the closer body does not entirely conceal the farther one, the event is called a ''transit''. Both transit and occultation may be referred to generally as ''occlusion''; and if a shadow is cast onto the observer, it is called an eclipse. The symbol for an occultation, and especially a solar eclipse, is file:Occultation symbol.svg (U+1F775 🝵). Occultations by the Moon The term occultation is most frequently used to describe lunar occultations, those relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a syzygy. Apart from syzygy, the term eclipse is also used when a spacecraft reaches a position where it can observe two celestial bodies so aligned. An eclipse is the result of either an occultation (completely hidden) or a transit (partially hidden). The term eclipse is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into the shadow of another moon. A binary star system can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_effect.gif)