|
TL-1238
TL-1238 (Substance 3393) is an extremely potent carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It has been shown to be more potent than neostigmine. See also * Miotine *Neostigmine *T-1123 T-1123 is a carbamate-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It was investigated as a chemical warfare agent starting in 1940. It does not go through the blood-brain barrier due to the charge on quaternary nitrogen. The antidote is atropine. T-112 ... * T-1152 * T-1194 * TL-599 References Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Aromatic carbamates Quaternary ammonium compounds Phenol esters Carbamate nerve agents {{Ester-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miotine
Miotine is an anticholinesterase drug. Miotine was the first synthetic carbamate that was used clinically. Unlike the miotine analog neostigmine, it doesn't have a quaternary ammonium group to give it a permanent positive charge. It can exist as an uncharged free base which could allow it to cross the blood–brain barrier and cause unwanted central nervous system (CNS) side effects. : See also *Neostigmine *T-1123 *TL-1238 TL-1238 (Substance 3393) is an extremely potent carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It has been shown to be more potent than neostigmine. See also * Miotine *Neostigmine *T-1123 T-1123 is a carbamate-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitor ... * TMTFA References Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Aromatic carbamates Phenol esters {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-1123
T-1123 is a carbamate-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It was investigated as a chemical warfare agent starting in 1940. It does not go through the blood-brain barrier due to the charge on quaternary nitrogen. The antidote is atropine. T-1123 is a quaternary ammonium ion. A phenyl carbamate ester is bonded in the meta position to the nitrogen on a diethylmethyl amine. The chloride and methylsulfate salt of T-1123 is TL-1299 and TL-1317, respectively. Synthesis T-1123 can be produced from m-diethylaminophenol, methyl isocyanate and methyl iodide. First, m-diethylaminophenol is reacted with methyl isocyanate to produce a methylcarbamate. The resulting methylcarbamate is then reacted with methyl iodide to produce T-1123. See also * Miotine *Neostigmine Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-1152
T-1152 is a quaternary carbamate anticholinesterase. It is synthesized by reaction of m-dimethylaminophenol with methyl isocyanate, followed by quaternization with methyl iodide. Since T-1152 is toxic by ingestion, it was patented as a rodenticide in 1932. The chloride and methylsulfate salt of T-1152 is T-1690 (TL-1226) and AR-13, respectively. See also *Neostigmine *T-1123 * T-1194 * TL-599 *TL-1238 TL-1238 (Substance 3393) is an extremely potent carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It has been shown to be more potent than neostigmine. See also * Miotine *Neostigmine *T-1123 T-1123 is a carbamate-based acetylcholinesterase inhibitor ... References {{Rodenticides Carbamate nerve agents Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Aromatic carbamates Phenol esters Quaternary ammonium compounds Iodides Rodenticides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-1194
T-1194, also known as TL-1323, is an extremely toxic carbamate nerve agent. T-1194 is the methylcarbamate ester of edrophonium. The bromide salt of T-1194 is AR-14. See also *T-1123 *T-1152 * TL-599 *TL-1238 *Neostigmine *Miotine Miotine is an anticholinesterase drug. Miotine was the first synthetic carbamate that was used clinically. Unlike the miotine analog neostigmine, it doesn't have a quaternary ammonium group to give it a permanent positive charge. It can exist as ... References Carbamate nerve agents Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Quaternary ammonium compounds Iodides Phenol esters Aromatic carbamates {{Neurotoxin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TL-599
TL-599, also known as SB-8, is an extremely potent carbamate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. See also *Neostigmine *Miotine *T-1123 *T-1152 *T-1194 *TL-1238 *Physostigmine Physostigmine (also known as eserine from ''éséré'', the West African name for the Calabar bean) is a highly toxic parasympathomimetic alkaloid, specifically, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. It occurs naturally in the Calabar bean a ... References Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Aromatic carbamates Quaternary ammonium compounds Phenol esters Isopropyl compounds Iodides Carbamate nerve agents {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
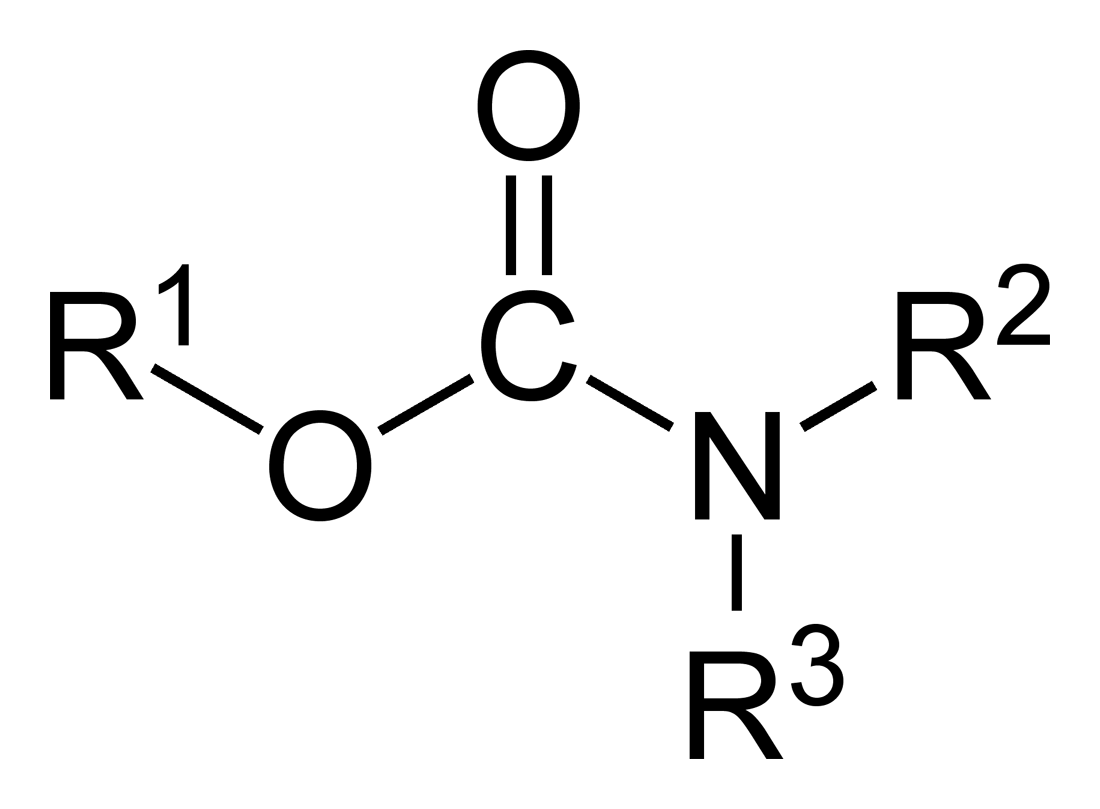
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking medication. It is given by injection either into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours. Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine. Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The term is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neostigmine
Neostigmine, sold under the brand name Bloxiverz, among others, is a medication used to treat myasthenia gravis, Ogilvie syndrome, and urinary retention without the presence of a blockage. It is also used in anaesthesia to end the effects of non-depolarising neuromuscular blocking medication. It is given by injection either into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. After injection effects are generally greatest within 30 minutes and last up to 4 hours. Common side effects include nausea, increased saliva, crampy abdominal pain, and slow heart rate. More severe side effects include low blood pressure, weakness, and allergic reactions. It is unclear if use in pregnancy is safe for the baby. Neostigmine is in the cholinergic family of medications. It works by blocking the action of acetylcholinesterase and therefore increases the levels of acetylcholine. Neostigmine was patented in 1931. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The term is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like TEPP and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature two important sites, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Carbamates
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic (ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-benz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)