|
TKM-Ebola
TKM-Ebola was an experimental antiviral drug for Ebola disease that was developed by Arbutus Biopharma (formerly Tekmira Pharmaceuticals Corp.) in Vancouver, Canada. The drug candidate was formerly known as Ebola-SNALP. TKM-Ebola is a combination of small interfering RNAs targeting three of the seven proteins in Ebola virus: Zaire Ebola L polymerase, Zaire Ebola membrane-associated protein (VP24), and Zaire Ebola polymerase complex protein (VP35).David Kroll for Forbes. 7 August 201FDA Moves On Tekmira's Ebola Drug While Sarepta's Sits Unused/ref> By down-regulating these three proteins, TKM-Ebola inhibits virus replication and eliminates the infection. The drug was effective in rhesus monkeys infected with Ebola. After the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, the new variant responsible for it was isolated from several Ebola virus families and the specific genomic sequence was determined. The company re-designed TKM-Ebola and renamed it as "TKM-Ebola-Guinea". In January 2014, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbutus Biopharma
Arbutus Biopharma Corporation is a publicly traded Canadian (NASDAQ: ABUS) biopharmaceutical company with an expertise in liposomal drug delivery and RNA interference, and is developing drugs for hepatitis B infection. It is headquartered in Vancouver, British Columbia and has research facilities in Warminster, Pennsylvania. The company was formerly known as Tekmira, which was spun out of Inex Pharmaceuticals in 2007. History Tekmira, as the company was formerly called, was formed as a wholly owned subsidiary of Inex Pharmaceuticals in 2005 after that company began collapsing after its regulatory and partnering strategy failed in 2004. Tekmira was fully spun out in 2007 and Tekmira absorbed the assets of Inex, which had been founded in 1992. Inex had been developing liposomal formulations of off-patent cancer drugs, and licensed them to Talon Pharmaceuticals in 2005; Talon was acquired by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals in 2013, and three former Inex/Tekmira products reached the mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZMapp
ZMapp is an experimental biopharmaceutical drug comprising three chimeric monoclonal antibodies under development as a treatment for Ebola virus disease. Two of the three components were originally developed at the Public Health Agency of Canada's National Microbiology Laboratory (NML), and the third at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases; the cocktail was optimized by Gary Kobinger, a research scientist at the NML and underwent further development under license by Mapp Biopharmaceutical. ZMapp was first used on humans during the 2014 West Africa Ebola virus outbreak, having only been previously tested on animals and not yet subjected to a randomized controlled trial. The NIH ran a clinical trial starting in January 2015 with subjects from Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia aiming to enroll 200 people, but the epidemic waned and the trial closed early, leaving it too statistically underpowered to give a meaningful result about whether ZMapp worked. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from viricides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural viricides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
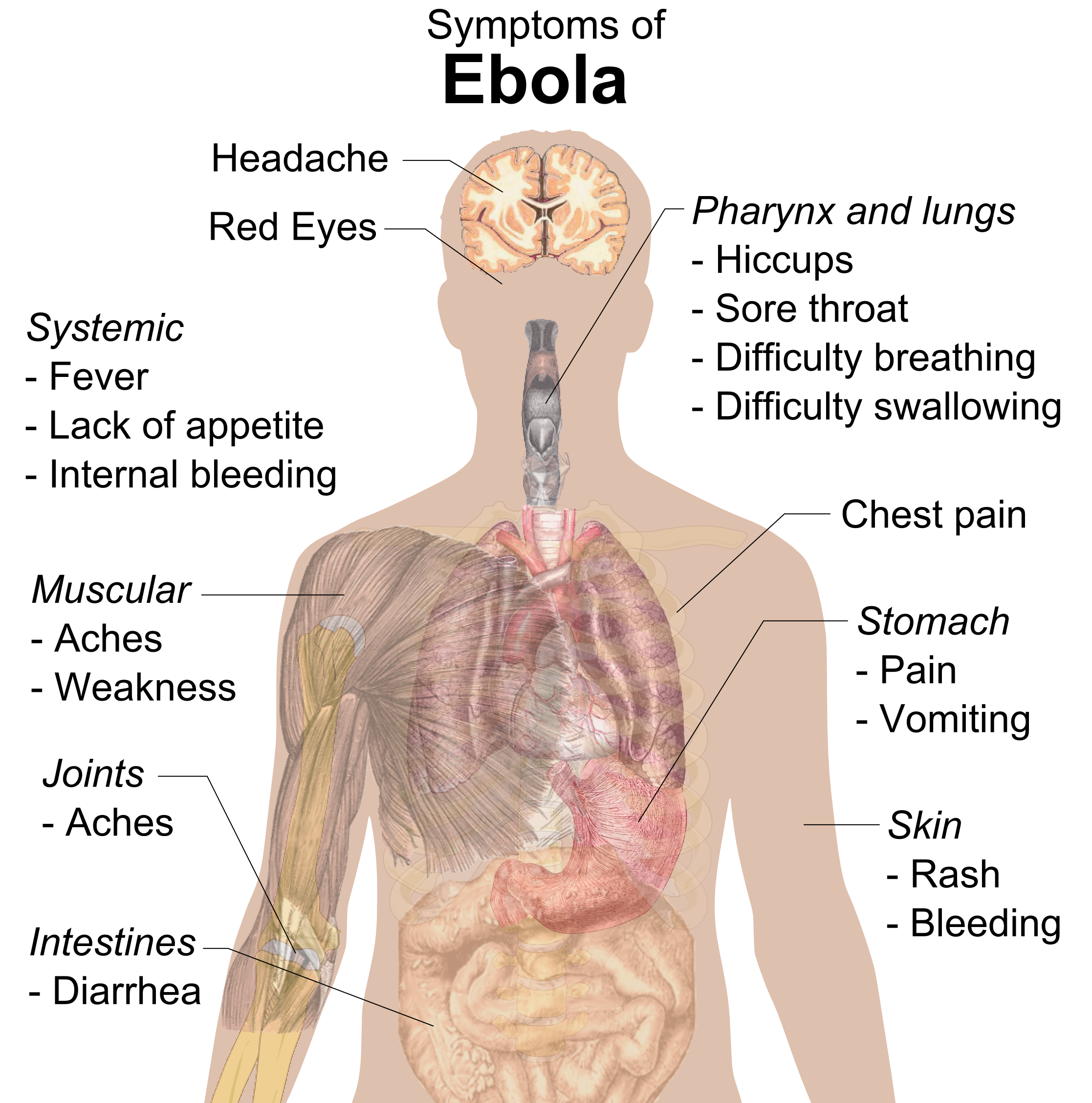
Ebola Disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Interfering RNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-24 (normally 21) base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading mRNA after transcription, preventing translation. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Structure Naturally occurring siRNAs have a well-defined structure that is a short (usually 20 to 24- bp) double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) with phosphorylated 5' ends and hydroxylated 3' ends with two overhanging nucleotides. The Dicer enzyme catalyzes production of siRNAs from long dsRNAs and small hairpin RNAs. siRNAs can also be introduced into cells by transfection. Since in principle any gene can be knocked down by a syntheti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expanded Access
Expanded access or compassionate use is the use of an unapproved drug or medical device under special forms of investigational new drug applications (IND) or IDE application for devices, outside of a clinical trial, by people with serious or life-threatening conditions who do not meet the enrollment criteria for the clinical trial in progress. These programs go under various names, including early access, special access, or managed access program, compassionate use, compassionate access, named-patient access, temporary authorization for use, cohort access, and pre-approval access. In general the person and their doctor must apply for access to the investigational product, the company has to choose to cooperate, and the medicines regulatory agency needs to agree that the risks and possible benefits of the drug or device are understood well enough to determine if putting the person at risk has sufficient potential benefit. In some countries the government will pay for the drug or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Disease Despite there being a vaccine to prevent Hepatitis B, HBV remains a global health problem. Hepatitis B can be acute and later become chronic, leading to other diseases and health conditions. In addition to causing hepatitis, infection with HBV can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Roles in disease Viral infection by ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) causes many hepatocyte changes due to the direct action of a protein encoded by the virus, HBx, and to indirect changes due to a large increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) after infection. HBx appears to dysregulate a number of cellular pathways. HBx causes dysregulation in part by binding to genomic DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab
Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab, sold under the brand name Inmazeb, is a fixed-dose combination of three monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of ''Zaire ebolavirus'' (Ebola virus). It contains atoltivimab, maftivimab, and odesivimab-ebgn and was developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. The most common side effects include fever, chills, tachycardia (fast heart rate), tachypnea (fast breathing), and vomiting; however, these are also common symptoms of Ebola virus infection. Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab is the first FDA-approved treatment for ''Zaire ebolavirus''. Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab was approved for medical use in the United States in October 2020. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab is indicated for the treatment of infection caused by ''Zaire ebolavirus''. Contraindications People who receive atoltivimab/maftivimab/odesivimab should avoid the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaire Ebolavirus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Favipiravir
Favipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative. It is being developed and manufactured by Toyama Chemical (a subsidiary of Fujifilm) and was approved for medical use in Japan in 2014. In 2016, Fujifilm licensed it to Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co. It became a generic drug in 2019. Medical use Favipiravir has been approved to treat influenza in Japan. It is, however, only indicated for novel influenza (strains that cause more severe disease) rather than seasonal influenza. As of 2020, the probability of resistance developing appears low. Side effects There is evidence that use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Teratogenic and embryotoxic effects were shown on four animal species. Mechanism of actio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from viricides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural viricides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)