|
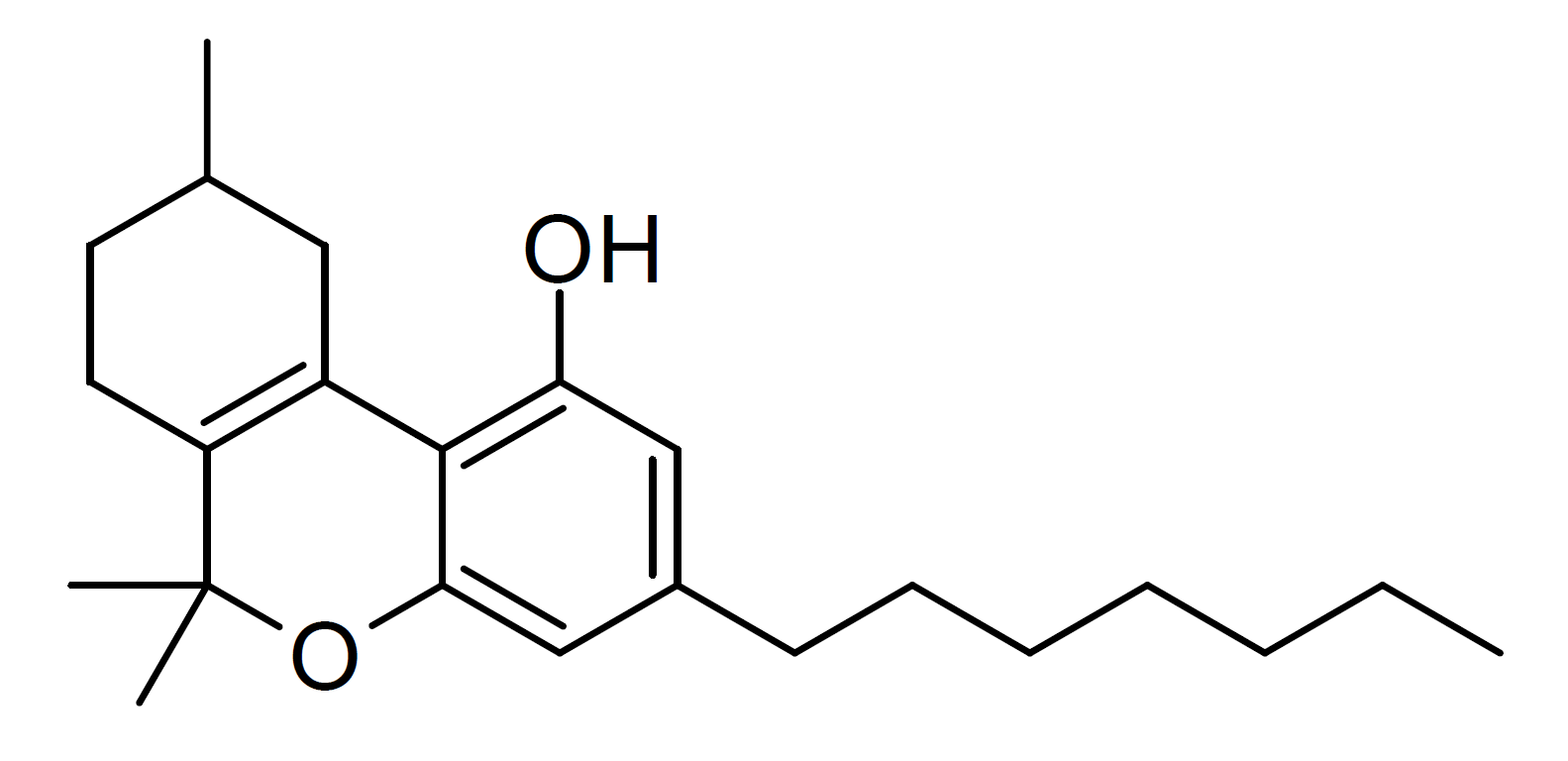
THCP
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ... which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabis sativa''. It is structurally similar to Δ9-THC, the main active component of cannabis, but with the pentyl side chain extended to heptyl. Since it has a longer side chain, its cannabinoid effects are "far higher than Δ9-THC itself." Tetrahydrocannabiphorol has a reported binding affinity approximately 33 times that of Delta-9-THC. Isomers Delta-3-THCP ] The Δ3/Δ6a(10a) isomer Δ3-THCP was synthesised in 1941, and was found to have around the same potency as Delta-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ3-THC, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV, O-4394, GWP42004) is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of a pentyl (5-carbon) group on the molecule, which makes it produce very different effects from THC. Natural occurrence THCV is prevalent in certain central Asian and southern African strains of ''Cannabis''. Chemistry Similar to THC, THCV has 7 possible double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Tetrahydrocannabinol#Isomerism). The alternative isomer Δ8-THCV is known as a synthetic compound with a code number of O-4395, but it is not known to have been isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material. ] Description Plants with elevated levels of propyl cannabinoids (including THCV) have been found in populations of ''Cannabis sativa'' L. ssp. ''indica'' (= ''Cannabis indica'' Lam.) from China, India, Nepal, Thailand, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, as well as southern and western Africa. THCV levels up to 53.7% of total cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JWH-138
JWH-138 (THC-Octyl, Δ8-THC-C8) is a synthetic cannabinoid first synthesised by John W. Huffman, with a Ki of 8.5nM at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Isomers The Δ3/Δ6a(10a) isomer was synthesised in 1941, but was found to be slightly less active than Δ3-THC itself. The alternate isomer Δ9-THC-C8 has also been synthesised, but has not been identified as a natural product. See also * Cannabicyclohexanol * Parahexyl * Tetrahydrocannabihexol * THCP Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to ... References {{cannabinoid-stub Xanthenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the Cannabis, cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in Cannabis (drug), cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis Sativa
''Cannabis sativa'' is an annual herbaceous flowering plant indigenous to Eastern Asia, but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to widespread cultivation. It has been cultivated throughout recorded history, used as a source of industrial fiber, seed oil, food, recreation, religious and spiritual moods and medicine. Each part of the plant is harvested differently, depending on the purpose of its use. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The word ''sativa'' means "things that are cultivated." Plant physiology The flowers of ''Cannabis sativa'' are unisexual and plants are most often either male or female. It is a short-day flowering plant, with staminate (male) plants usually taller and less robust than pistillate (female or male) plants. The flowers of the female plant are arranged in racemes and can produce hundreds of seeds. Male plants shed their pollen and die several weeks prior to seed ripening on the female plants. Under typical conditions with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists Receptors can be activated by either agonists (such as[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CB1 Receptor Agonists
{{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ...
CB1 may refer to: * CB1, a postcode district in the CB postcode area * Cannabinoid receptor 1, a receptor for cannabinoids in the brain * ''Crash Bandicoot'' (video game), the first game in the ''Crash Bandicoot'' series * Manhattan Community Board 1 The Manhattan Community Board 1 is a New York City community board encompassing the neighborhoods of Battery Park City, the Financial District, the South Street Seaport, and TriBeCa in Lower Manhattan in the borough of Manhattan as well as Liber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabicyclohexanol
Cannabicyclohexanol (CCH, CP 47,497 dimethyloctyl homologue, (C8)-CP 47,497) is a cannabinoid receptor agonist drug, developed by Pfizer in 1979. On 19 January 2009, the University of Freiburg in Germany announced that an analog of CP 47,497 was the main active ingredient in the herbal incense product ''Spice'', specifically the 1,1-dimethyloctyl homologue of CP 47,497, which is now known as cannabicyclohexanol. The 1,1-dimethyloctyl homologue of CP 47,497 is in fact several times more potent than the parent compound, which is somewhat unexpected as the 1,1-dimethylheptyl is the most potent substituent in classical cannabinoid compounds such as HU-210. Enantiomers Cannabicyclohexanol has four enantiomers, which by analogy with other related cannabinoid compounds can be expected to have widely varying affinity for cannabinoid receptors, and consequently will show considerable variation in potency. While the (-)-''cis'' enantiomer (-)-cannabicyclohexanol discovered in the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMHP
Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP, 3-(1,2-dimethylheptyl)-Δ6a(10a)-THC, 1,2-dimethylheptyl-Δ3-THC, A-40824, or EA-2233) is a synthetic analog of THC, which was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of ''Cannabis''. DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents. Effects DMHP is similar in structure to THC, differing only in the position of one double bond, and the replacement of the 3-pentyl chain with a 3-(1,2-dimethylheptyl) chain. It produces similar activity to THC, such as sedative effects, but is considerably more potent, especially having much stronger analgesic and anticonvulsant effects than THC, although comparatively weaker psychological effects. It is thought to act as a CB1 agonist, in a similar manner to other cannabinoid derivatives. While DMHP itself has been subject to relatively little study since the characterization of the cannabino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-1871
O-1871 is a potent cannabinoid agonist which was invented by Billy R Martin and Raj K Razdan at Organix Inc in 2002. It has a CB1 receptor affinity of 2.0nM and a CB2 receptor affinity of 0.3nM. Structurally, O-1871 is a cyclohexylphenol derivative related to CP 47,497, and so is illegal in some jurisdictions where CP 47,497 and its derivatives are banned. However the 3,3-dimethylcyclohexyl substituent of O-1871 can be replaced by various other groups, producing other potent compounds such as the cycloheptyl derivative O-1656 and the 2-adamantyl derivative O-1660, as well as the corresponding 3,5-dichlorophenyl derivative, which are not cyclohexylphenol derivatives. ] ] See also * CP 55,940 * Cannabidiol * Cannabicyclohexanol * Cannabinor Cannabinor (PRS-211,375) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist. It is classed as a "nonclassical" cannabinoid with a chemical structure similar to that of cannabidiol. It has a CB2 affinity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabihexol
Tetrahydrocannabihexol (Δ9-THCH, Δ9-Parahexyl, n-Hexyl-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid, the hexyl homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was first isolated from '' Cannabis'' plant material in 2020 along with the corresponding hexyl homologue of cannabidiol, though it had been known for several decades prior to this as an isomer of the synthetic cannabinoid parahexyl. Another isomer Δ8-THCH is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code number JWH-124, though it is unclear whether this occurs naturally in ''Cannabis'', but likely is due to Delta-8-THC itself being a degraded form of Delta-9-THC. ] ] See also * Cannabidiphorol * Tetrahydrocannabiorcol * Tetrahydrocannabivarin * Tetrahydrocannabutol * Tetrahydrocannabiphorol Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from '' Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |