|
TFET Lateral Structure
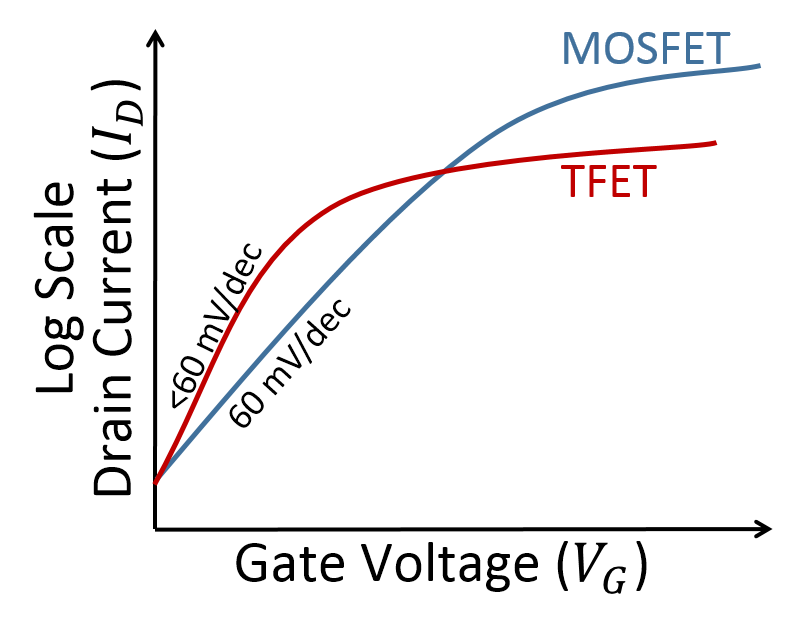
The tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) is an experimental type of transistor. Even though its structure is very similar to a metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), the fundamental switching mechanism differs, making this device a promising candidate for low power electronics. TFETs switch by modulating quantum tunneling through a barrier instead of modulating thermionic emission over a barrier as in traditional MOSFETs. Because of this, TFETs are not limited by the thermal Maxwell–Boltzmann tail of carriers, which limits MOSFET drain current subthreshold swing to about 60 mV/decade of current at room temperature. TFET studies can be traced back to Stuetzer who in 1952 published first investigations of a transistor containing the basic elements of the TFET, a gated p-n junction. The reported surface conductivity control was, however, not related to tunneling. The first TFET was reported in 1965. Joerg Appenzeller and his colleagues at IBM were the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in watt.html" ;"title="amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFET Lateral Structure
The tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) is an experimental type of transistor. Even though its structure is very similar to a metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), the fundamental switching mechanism differs, making this device a promising candidate for low power electronics. TFETs switch by modulating quantum tunneling through a barrier instead of modulating thermionic emission over a barrier as in traditional MOSFETs. Because of this, TFETs are not limited by the thermal Maxwell–Boltzmann tail of carriers, which limits MOSFET drain current subthreshold swing to about 60 mV/decade of current at room temperature. TFET studies can be traced back to Stuetzer who in 1952 published first investigations of a transistor containing the basic elements of the TFET, a gated p-n junction. The reported surface conductivity control was, however, not related to tunneling. The first TFET was reported in 1965. Joerg Appenzeller and his colleagues at IBM were the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carver Mead
Carver Andress Mead (born May 1, 1934) is an American scientist and engineer. He currently holds the position of Gordon and Betty Moore Professor Emeritus of Engineering and Applied Science at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), having taught there for over 40 years. He taught Deborah Chung, the first female engineering graduate of Caltech. He advised the first female electrical engineering student at Caltech, Louise Kirkbride. His contributions as a teacher include the classic textbook ''Introduction to VLSI Systems'' (1980), which he coauthored with Lynn Conway. A pioneer of modern microelectronics, he has made contributions to the development and design of semiconductors, digital chips, and silicon compilers, technologies which form the foundations of modern very-large-scale integration chip design. In the 1980s, he focused on electronic modelling of human neurology and biology, creating " neuromorphic electronic systems." Mead has been involved in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunnel Diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode that has effectively " negative resistance" due to the quantum mechanical effect called tunneling. It was invented in August 1957 by Leo Esaki, Yuriko Kurose, and Takashi Suzuki when they were working at Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo, now known as Sony. In 1973, Esaki received the Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Brian Josephson, for discovering the electron tunneling effect used in these diodes. Robert Noyce independently devised the idea of a tunnel diode while working for William Shockley, but was discouraged from pursuing it. Tunnel diodes were first manufactured by Sony in 1957, followed by General Electric and other companies from about 1960, and are still made in low volume today. Tunnel diodes have a heavily doped positive-to-negative (P-N) junction that is about 10 nm (100 Å) wide. The heavy doping results in a broken band gap, where conduction band electron states on the N-side are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunnel Junction
In electronics/spintronics, a tunnel junction is a barrier, such as a thin insulating layer or electric potential, between two electrically conducting materials. Electrons (or quasiparticles) pass through the barrier by the process of quantum tunnelling. Classically, the electron has zero probability of passing through the barrier. However, according to quantum mechanics, the electron has a non-zero wave amplitude in the barrier, and hence it has some probability of passing through the barrier. Tunnel junctions serve a variety of different purposes. Multijunction photovoltaic cell In multijunction photovoltaic cells, tunnel junctions form the connections between consecutive p-n junctions. They function as an ohmic electrical contact in the middle of a semiconductor device. Magnetic tunnel junction In magnetic tunnel junctions, electrons tunnel through a thin insulating barrier from one magnetic material to another. This can serve as a basis for a magnetic detector. Superconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Antimonide
Gallium antimonide (GaSb) is a semiconducting compound of gallium and antimony of the III-V family. It has a lattice constant of about 0.61 nm. It has a band gap of 0.67 eV. History The intermetallic compound GaSb was first prepared in 1926 by Victor Goldschmidt, who directly combined the elements under an inert gas atmosphere and reported on GaSb's lattice constant, which has since been revised. Goldschmidt also synthesized gallium phosphide and gallium arsenide. The Ga-Sb phase equilibria was investigated in 1955 by Koster and by Greenfield.Greenfield, I. G.; Smith, R. L., ''Trans. AIME'' 203, 351 (1955). Applications GaSb can be used for Infrared detectors, infrared LEDs and lasers and transistors, and thermophotovoltaic Thermophotovoltaic (TPV) energy conversion is a direct conversion process from heat to electricity via photons. A basic thermophotovoltaic system consists of a hot object emitting thermal radiation and a photovoltaic cell similar to a solar cell bu ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Arsenide
Indium arsenide, InAs, or indium monoarsenide, is a narrow-bandgap semiconductor composed of indium and arsenic. It has the appearance of grey cubic crystals with a melting point of 942 °C. Indium arsenide is similar in properties to gallium arsenide and is a direct bandgap material, with a bandgap of 0.35 eV at room temperature. Indium arsenide is used for construction of infrared detectors, for the wavelength range of 1–3.8 µm. The detectors are usually photovoltaic photodiodes. Cryogenically cooled detectors have lower noise, but InAs detectors can be used in higher-power applications at room temperature as well. Indium arsenide is also used for making of diode lasers. InAs is well known for its high electron mobility and narrow energy bandgap. It is widely used as terahertz radiation source as it is a strong photo-Dember emitter. The optoelectronic properties and phonon vibrations are slightly changed under the effect of temperature over the range form 0 K t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Well
A quantum well is a potential well with only discrete energy values. The classic model used to demonstrate a quantum well is to confine particles, which were initially free to move in three dimensions, to two dimensions, by forcing them to occupy a planar region. The effects of quantum confinement take place when the quantum well thickness becomes comparable to the de Broglie wavelength of the carriers (generally electrons and holes), leading to energy levels called "energy subbands", i.e., the carriers can only have discrete energy values. A wide variety of electronic quantum well devices have been developed based on the theory of quantum well systems. These devices have found applications in lasers, photodetectors, modulators, and switches for example. Compared to conventional devices, quantum well devices are much faster and operate much more economically and are a point of incredible importance to the technological and telecommunication industries. These quantum well devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-gate
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) and the GAAFET (gate-all-around field-effect transistor), which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors. Multi-gate transistors are one of the several strategies being developed by MOS semiconductor manufacturers to create ever-smaller microprocessors and memory cells, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's law (in its narrow, specific version concerning density scaling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals interactions in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFET Band Diagram
The tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) is an experimental type of transistor. Even though its structure is very similar to a metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), the fundamental switching mechanism differs, making this device a promising candidate for low power electronics. TFETs switch by modulating quantum tunneling through a barrier instead of modulating thermionic emission over a barrier as in traditional MOSFETs. Because of this, TFETs are not limited by the thermal Maxwell–Boltzmann tail of carriers, which limits MOSFET drain current subthreshold swing to about 60 mV/decade of current at room temperature. TFET studies can be traced back to Stuetzer who in 1952 published first investigations of a transistor containing the basic elements of the TFET, a gated p-n junction. The reported surface conductivity control was, however, not related to tunneling. The first TFET was reported in 1965. Joerg Appenzeller and his colleagues at IBM were the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Band
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature, while the conduction band is the lowest range of vacant electronic states. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the Fermi level, while the conduction band is located above it. The distinction between the valence and conduction bands is meaningless in metals, because conduction occurs in one or more partially filled bands that take on the properties of both the valence and conduction bands. Band gap In semiconductors and insulators the two bands are separated by a band gap, while in semimetals the bands overlap. A band gap is an energy range in a solid where no electron states can exist due to the quantizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |