|
Syracuse Lake
Syracuse Lake is a natural lake bordering Syracuse in Kosciusko County, Indiana, United States. Location Syracuse Lake is bordered on the west by N. Front Street, Pickwick Road and the B&O Railroad on the south. On the east it is bordered by E. Shore Drive and on the north by E. Northshore Drive. It connects to Lake Wawasee by a channel on the south end. Hydrology Syracuse Lake is classified as a Trophic Class 1 lake, having a eutrophication index value of 10. The lake is typical in structure of natural lakes of the glaciated portions of the upper Midwest. The lake is presently healthy and has a balanced aquatic ecosystem (WAW 1995). It has a surface area of with a maximum depth of and an average depth of . History Pre-glaciation Around 1 million years ago, just prior to the Pleistocene epoch, northern Indiana was covered by the Teays River system, which flowed northwest out of Virginia, West Virginia, and Ohio, entering Indiana at Adams County and flowing about 49 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosciusko County, Indiana
Kosciusko County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. At the 2020 United States Census, its population was 80,240. The county seat (and only incorporated city) is Warsaw. The county was organized in 1836. It was named for the Polish general Tadeusz Kościuszko who served in the American Revolutionary War and then returned to Poland. The county seat is named for Warsaw, the capital of Poland. History The Indiana State Legislature passed an omnibus county bill on 7 February 1835 that authorized the creation of thirteen counties in northeast Indiana, including Kosciusko. The county government was organized beginning in 1836. The county's boundary lines have remained unchanged since 1835. Geographical features Kosciusko County terrain consists of low rolling hills dotted with bodies of water and drainages, with all available area devoted to agriculture or urban development. Its highest point (1025'/312 meters ASL) is a hill NE of Dewart Lake. The Tippecanoe River flows west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platygonus
''Platygonus'' ("flat head" in reference to the straight shape of the forehead) is an extinct genus of herbivorous peccaries of the family Tayassuidae, endemic to North and South America from the Miocene through Pleistocene epochs (10.3 million to 11,000 years ago), existing for about . ''P. compressus'' stood 2.5 feet (0.75 meters) tall. Description Most ''Platygonus'' species were similar in size to modern peccaries especially giant peccary, at around in body length, and had long legs, allowing them to run well. They also had a pig-like snout and long tusks which were probably used to fend off predators. Taxonomy While long thought to be the sister-lineage to the Chacoan peccary based on morphological similarities, a 2017 ancient DNA study which recovered mitochondrial DNA from ''Platygonus'' found that all living peccaries are more closely related to each other than they are to ''Platygonus''. The estimated divergence between ''Platygonus'' and all living peccaries was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castoroides
''Castoroides'' (Latin: "beaver" (castor), "like" (oides)), or giant beaver, is an extinct genus of enormous, bear-sized beavers that lived in North America during the Pleistocene. Two species are currently recognized, ''C. dilophidus'' in the Southeastern US and ''C. ohioensis'' in the rest of its range. ''C. leiseyorum'' was previously described from the Irvingtonian of Florida, but is now regarded as an invalid name. All specimens previously described as ''C. leiseyorum'' are considered to belong to ''C. dilophidus''. Description Species of ''Castoroides'' were much larger than modern beavers. Their average length was approximately , and they could grow as large as . The weight of the giant beaver could vary from to . This makes it the largest known rodent in North America during the Pleistocene and the largest known beaver. Recent analyses suggest that they weighed less, closer to , but this is disputable. The hind feet of the giant beaver were much larger than in modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. The term is used to refer to all extinct sloths because of the large size of the earliest forms discovered, compared to existing tree sloths. The Caribbean ground sloths, the most recent survivors, lived in the Antilles, possibly until 1550 BCE. However, radiocarbon dating suggests an age of between 2819 and 2660 BCE for the last occurrence of ''Megalocnus'' in Cuba. Ground sloths had been extinct on the mainland of North and South America for 10,000 years or more. They survived 5,000–6,000 years longer in the Caribbean than on the American mainland, which correlates with the later colonization of this area by humans. Much ground sloth evolution took place during the late Paleogene and Neogene of South America, while the continent was isolated. At their earliest appearance in the fossil record, the ground sloths were already distinct at the family level. The presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dire Wolf
The dire wolf (''Aenocyon dirus'' ) is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor ''Smilodon''. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene epochs (125,000–9,500 years ago). The species was named in 1858, four years after the first specimen had been found. Two subspecies are recognized: ''Aenocyon dirus guildayi'' and ''Aenocyon dirus dirus''. The largest collection of its fossils has been obtained from the Rancho La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles. Dire wolf remains have been found across a broad range of habitats including the plains, grasslands, and some forested mountain areas of North America, the arid savanna of South America, and the steppes of eastern Asia. The sites range in elevation from sea level to . Dire wolf fossils have rarely been found north of 42°N latitude; there have been only five unconfirmed reports above this latitude. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctodus
''Arctodus'' is an extinct genus of short-faced bear that inhabited North America during the Pleistocene (~2.5 Mya until 12,000 years ago). There are two recognized species: the lesser short-faced bear (''Arctodus pristinus'') and the giant short-faced bear (''Arctodus simus''). Both species are relatively rare in the fossil record- ''A. pristinus'' was largely restricted to the Early Pleistocene of the eastern United States, whereas ''A. simus'' had a cosmopolitan range, with most finds being from the Late Pleistocene of the US, Mexico and Canada. ''A. simus'' evolved from ''A. pristinus'', but both species likely overlapped in the Middle Pleistocene. Of these species, ''A. simus'' was larger, is known from more complete remains, and is considered one of the most charismatic of North America's megafauna. Today considered to be an enormous omnivore, ''Arctodus simus'' is believed to be one of the largest known terrestrial mammalian carnivorans that has ever existed. However, ''Arct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastodon
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of the Pleistocene 10,000 to 11,000 years ago. They lived in herds and were predominantly forest-dwelling animals. They generally had a browsing diet, distinct from that of the contemporary Columbian mammoth, which tended towards grazing. ''M. americanum'', the American mastodon, and ''M. pacificus'', the Pacific mastodon, are the youngest and best-known species of the genus. Mastodons disappeared from North America as part of a mass extinction of most of the Pleistocene megafauna, widely believed to have been caused by a combination of climate changes at the end of the Pleistocene and overexploitation by Paleo-Indians. History A Dutch tenant farmer found the first recorded remnant of ''Mammut'', a tooth some in weight, in the village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saber-toothed Cat
Machairodontinae is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the family Felidae (true cats). They were found in Asia, Africa, North America, South America, and Europe from the Miocene to the Pleistocene, living from about 16 million until about 11,000 years ago. The Machairodontinae contain many of the extinct predators commonly known as "saber-toothed cats", including the famed genus ''Smilodon'', as well as other cats with only minor increases in the size and length of their maxillary canines. The name means "dagger-tooth", from Greek μάχαιρα (''machaira''), sword. Sometimes, other carnivorous mammals with elongated teeth are also called saber-toothed cats, although they do not belong to the felids. Besides the machairodonts, other saber-toothed predators also arose in the nimravids, barbourofelids, machaeroidines, hyaenodonts and even in two groups of metatherians (the thylacosmilid sparassodonts and the deltatheroideans). Evolution Family Felidae The Mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
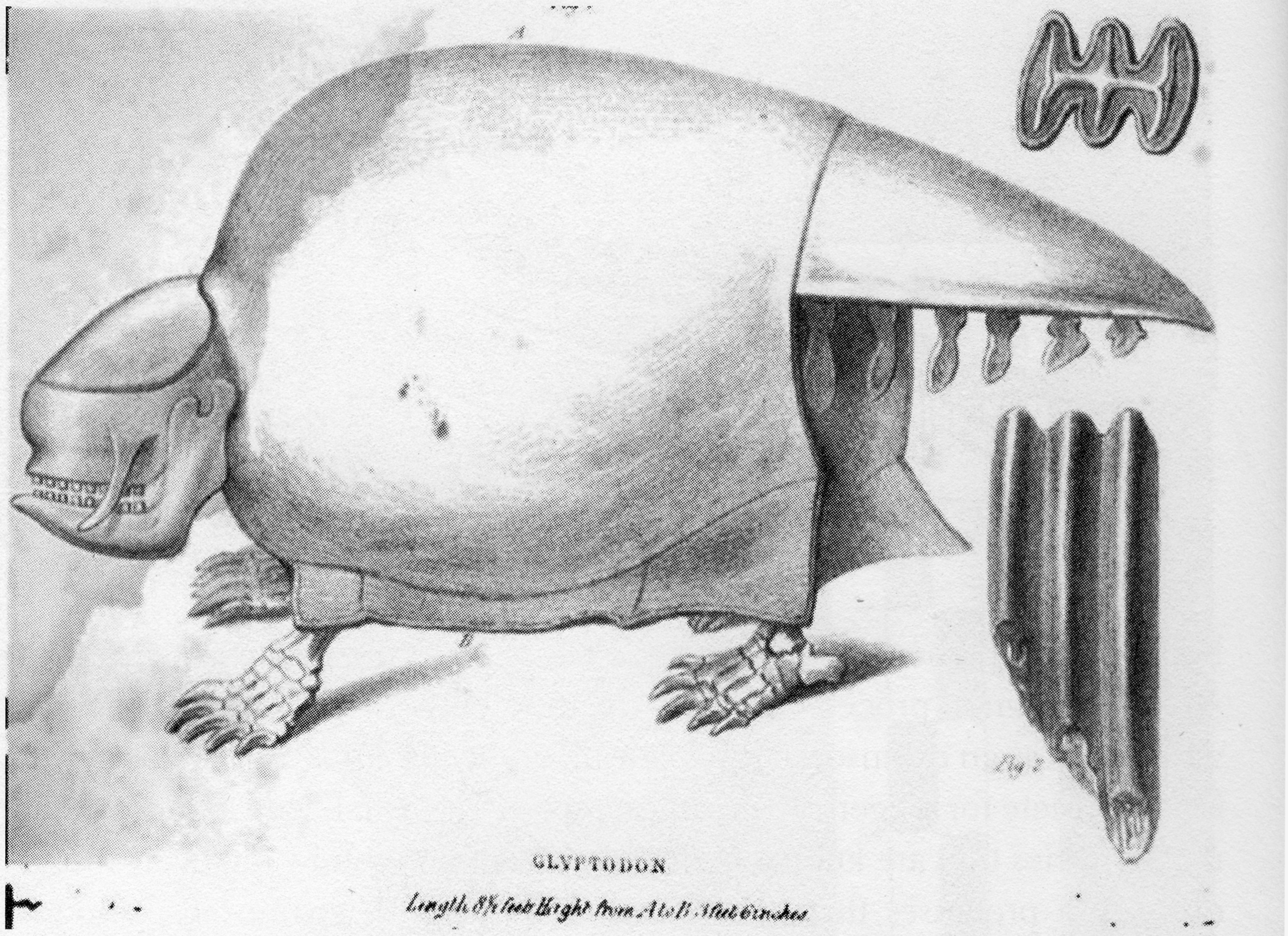
Glyptodon
''Glyptodon'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved tooth': γλυπτός 'sculptured' and ὀδοντ-, ὀδούς 'tooth') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Pleistocene, around 2.5 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia. It was the first named extinct cingulate and is the type genus of Glyptodontinae, and, or, Glyptodontinae. Many species have been named for the genus, though few are considered valid, and it is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. Hundreds of specimens have been referred to the genus, but the holotype, or name specimen, of the type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle, 800–840 kg (1,760–1,850 lb). With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superfic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexico, and two to four are native to Canada. A number of hickory species are used for products like edible nuts or wood. Hickories are temperate forest trees with pinnately compound leaves and large nuts. Hickory flowers are small, yellow-green catkins produced in spring. They are wind-pollinated and self-incompatible. The fruit is a globose or oval nut, long and diameter, enclosed in a four-valved husk, which splits open at maturity. The nut shell is thick and bony in most species, and thin in a few, notably the pecan (''C. illinoinensis''); it is divided into two halves, which split apart when the seed germinates. Etymology The name "hickory" derives from a Native American word in an Algonquian language (perhaps Powhatan). It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balsam Poplar
''Populus balsamifera'', commonly called balsam poplar, bam, bamtree, eastern balsam-poplar, hackmatack, tacamahac poplar, tacamahaca, is a tree species in the balsam poplar species group in the poplar genus, ''Populus.'' The genus name ''Populus'' is from the Latin for poplar, and the specific epithet ''balsamifera'' from Latin for "balsam-bearing". ''Populus balsamifera'' is the northernmost North American hardwood, growing transcontinentally on boreal and montane upland and flood plain sites, and attaining its best development on flood plains. It is a hardy, fast-growing tree which is generally short lived, but some trees as old as 200 years have been found. The tree is known for its strong, sweet fragrance, which emanates from its sticky, resinous buds. The smell has been compared to that of the balsam fir tree. Taxonomy The black cottonwood, ''Populus trichocarpa'', is sometimes considered a subspecies of ''P. balsamifera'' and may lend its common name to this species, alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(white_background).jpg)