|
Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate ENSI
The Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (german: Eidgenössisches Nuklearsicherheitsinspektorat (ENSI)) is Switzerland's regulatory supervisory authority for nuclear safety and for the security of nuclear installations; it supervises the nuclear power plants at Beznau, Gösgen, Leibstadt and Mühleberg, the research reactors at the Paul Scherrer Institute, the University of Basel and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne), as well as the Swiss national central interim storage facility for radioactive waste ( ZWILAG). ENSI's headquarters are located in Brugg in the Canton of Aargau. For its part, ENSI is supervised by the ENSI Board: this body is elected by the Swiss Federal Council, to which it reports directly. History Until the end of 2008, the Principal Nuclear Safety Division (HSK) within the Swiss Federal Office for Energy (SFOE) was the technical supervisory body responsible for nuclear plants in Switzerland. Its headq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Administration Of Switzerland
The federal administration of Switzerland (german: Bundesverwaltung, french: Administration fédérale, it, Amministrazione federale, rm, Administraziun federala) is the ensemble of agencies that constitute, together with the Swiss Federal Council, the executive branch of the Swiss federal authorities. The administration is charged with executing federal law and preparing draft laws and policy for the Federal Council and the Federal Assembly. The administration consists of seven federal departments and the Federal Chancellery. The departments are roughly equivalent to the ministries of other states, but their scope is generally broader. Each department consists of several federal offices, which are headed by a director, and of other agencies. The much smaller Federal Chancellery, headed by the Federal Chancellor, operates as an eighth department in most respects. Federal Council The administration in its entirety is directed by the Swiss Federal Council, and the Fede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
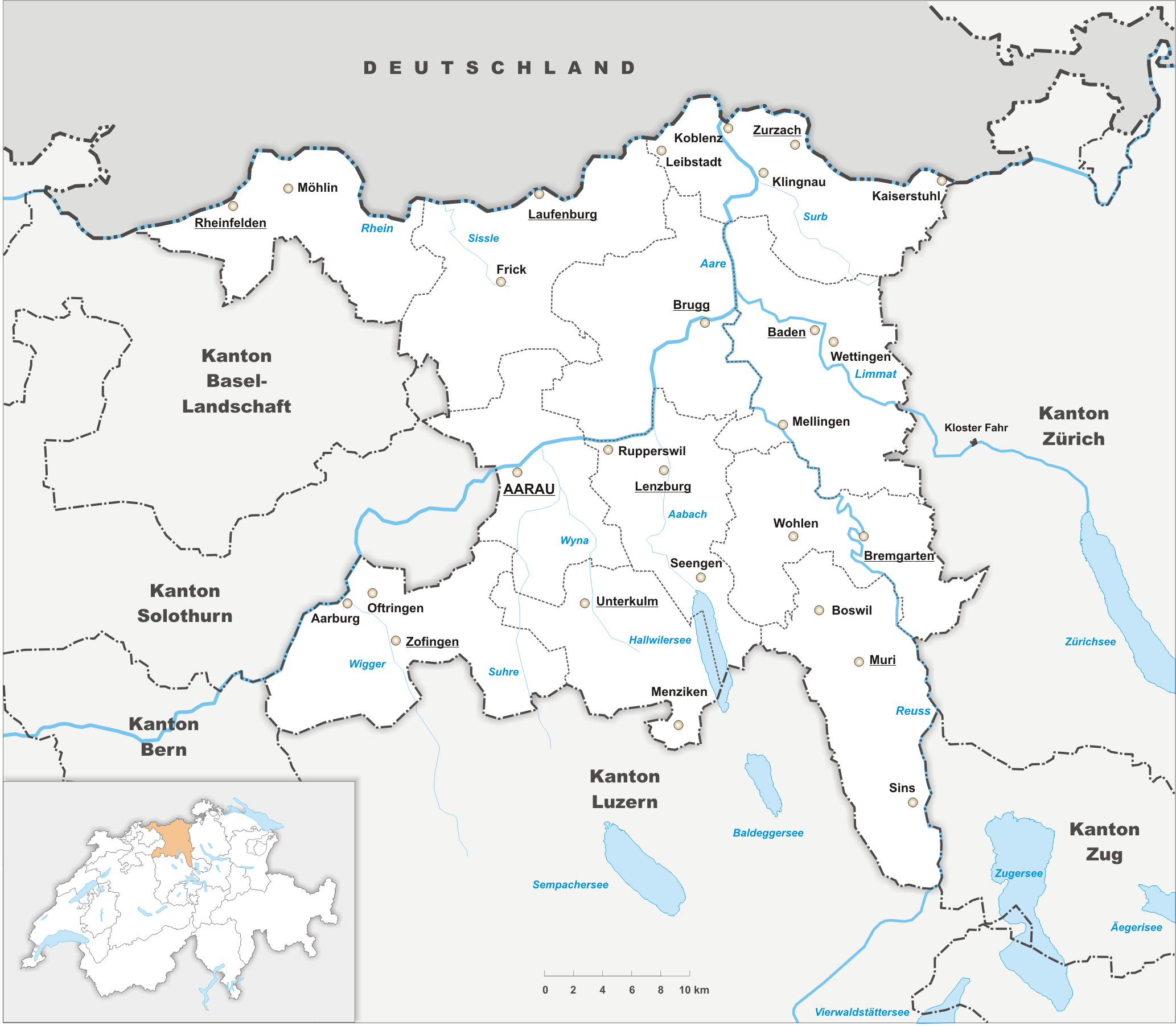
Brugg
, neighboring_municipalities = Gebenstorf, Habsburg, Hausen, Holderbank, Lupfig, Riniken, Rüfenach, Schinznach, Untersiggenthal, Villigen, Villnachern, Veltheim, Windisch , twintowns = Rottweil (Germany) , website = www.stadt-brugg.ch Brugg (sometimes written as Brugg AG in order to distinguish it from other ''Brugg''s) is a Swiss municipality and a town in the canton of Aargau and is the seat of the district of the same name. The town is located at the confluence of the Aare, Reuss, and Limmat, with the Aare flowing through its medieval part. It is located approximately from the cantonal capital of Aarau; from Zürich; and about from Basel. Brugg is the Swiss German term for bridge (german: Brücke). This is an allusion to the purpose of the medieval town's establishment under the Habsburgs, as the town is located at the narrowest point on the Aare in the Swiss midlands. The Habsburgs’ oldest known residence is located in the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
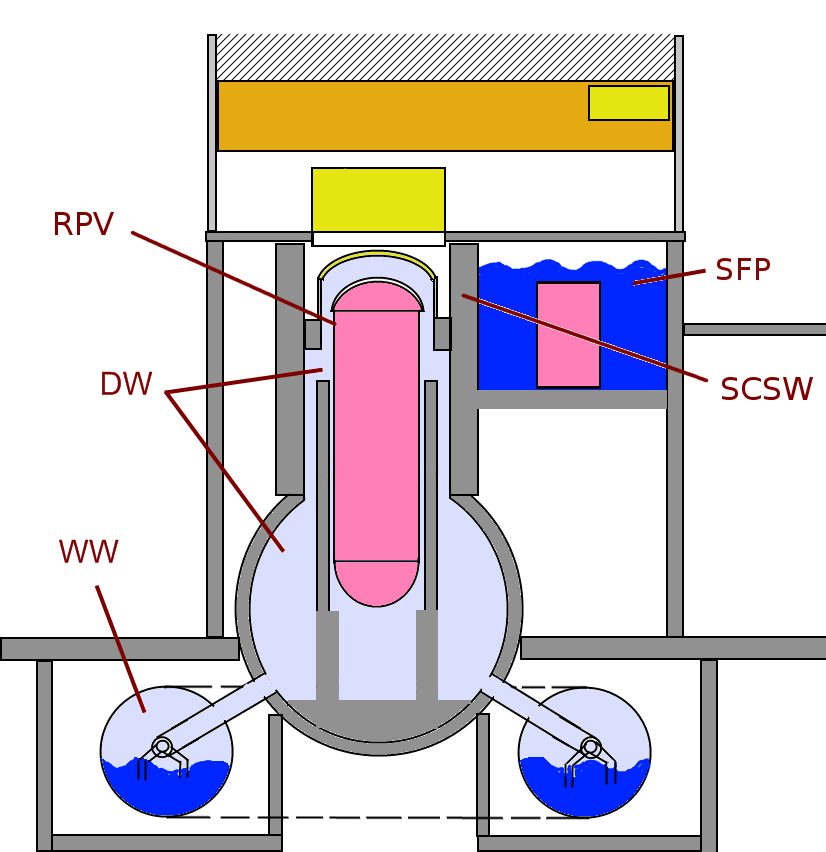
Mühleberg Nuclear Power Plant
The Mühleberg Nuclear Power Plant (german: Kernkraftwerk Mühleberg, KKM) is a formerly operational nuclear power plant in the Mühleberg municipality in the Canton of Berne, Switzerland. Operated by BKW FMB Energie AG, the plant generated power from 6 November 1972 until 20 December 2019. Nuclear decommissioning of the plant began January 2020 and is currently forecasted to be completed by 2034. History Mühleberg 1 In parallel with the planning of Beznau 1, the then Bernische Kraftwerke AG decided to build a second nuclear power plant in the canton of Berne. Mühleberg was identified as possible location and the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) approved this choice on 21 July 1965. Two years later, on 21 March 1967, a first partial construction permit was issued, followed on 7 March 1968 by the final one. The reactor entered criticality in March 1971 but, due to a fire in the turbine housing, the plant had to be shut down for repairs. It started commercial operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Scherrer Institute
The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is a multi-disciplinary research institute for natural and engineering sciences in Switzerland. It is located in the Canton of Aargau in the municipalities Villigen and Würenlingen on either side of the River Aare, and covers an area over 35 hectares in size. Like ETH Zurich and EPFL, PSI belongs to the Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology Domain of the Swiss Confederation. The PSI employs around 2,100 people. It conducts basic and applied research in the fields of matter and materials, human health, and energy and the environment. About 37% of PSI's research activities focus on material sciences, 24% on life sciences, 19% on general energy, 11% on nuclear energy and safety, and 9% on particle physics. PSI develops, builds and operates large and complex research facilities and makes them available to the national and international scientific communities. In 2017, for example, more than 2,500 researchers from 60 different countries came to PS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Basel
The University of Basel (Latin: ''Universitas Basiliensis'', German: ''Universität Basel'') is a university in Basel, Switzerland. Founded on 4 April 1460, it is Switzerland's oldest university and among the world's oldest surviving universities. The university is traditionally counted among the leading institutions of higher learning in the country. The associated Basel University Library is the largest and among the most important libraries in Switzerland. The university hosts the faculties of theology, law, medicine, humanities and social sciences, science, psychology, and business and economics, as well as numerous cross-disciplinary subjects and institutes, such as the Biozentrum for biomedical research and the Institute for European Global Studies. In 2020, the university had 13,139 students and 378 professors. International students accounted for 27 percent of the student body. In its over 500-year history, the university has been home to Erasmus of Rotterdam, Parac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Polytechnique Fédérale De Lausanne , a Japanese video-games developer/publisher
{{disambiguation, geo ...
École may refer to: * an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée) * École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France * École, Savoie, a French commune * École-Valentin, a French commune in the Doubs département * Grandes écoles, higher education establishments in France * The École, a French-American bilingual school in New York City Ecole may refer to: * Ecole Software This is a list of Notability, notable video game companies that have made games for either computers (like PC or Mac), video game consoles, handheld or mobile devices, and includes companies that currently exist as well as now-defunct companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Council (Switzerland)
The Federal Council (german: Bundesrat; french: Conseil fédéral; it, Consiglio federale; rm, Cussegl federal) is the executive body of the federal government of the Swiss Confederation and serves as the collective head of state and government of Switzerland. It meets in the west wing of the Federal Palace in Bern. While the entire Federal Council is responsible for leading the federal administration of Switzerland, each Councillor heads one of the seven federal executive departments. The position of President of the Swiss Confederation rotates among the seven Councillors on a yearly basis, with one year's Vice President of Switzerland becoming the next year's President of Switzerland. Ignazio Cassis has been the incumbent officeholder since 1 January 2022. An election of the entire Federal Council occurs every four years; voting is restricted to the 246 members of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland. There is no mechanism for recall after election. Incumbents are almost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention On Nuclear Safety
The Convention on Nuclear Safety is a 1994 International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) treaty that governs safety rules at nuclear power plants in state parties to the convention. The convention creates obligations on state parties to implement certain safety rules and standards at all civil facilities related to nuclear energy. These include issues of site selection; design and construction; operation and safety verification; and emergency preparedness. The convention was adopted in Vienna, Austria, at an IAEA diplomatic conference on 17 June 1994. It was opened for signature on 20 September 1994 and has been signed by 65 states; it entered into force on 24 October 1996 after it had been ratified by 22 signatories. As of July 2015, there are 78 state parties to the Convention plus the European Atomic Energy Community. The states that have signed the treaty but have not ratified it include Algeria, Cuba, Egypt, Ghana, Iceland, Israel, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Monaco, Morocco, Nicaragua, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 as an autonomous organization within the United Nations system; though governed by its own founding treaty, the organization reports to both the General Assembly and the Security Council of the United Nations, and is headquartered at the UN Office at Vienna, Austria. The IAEA was created in response to growing international concern toward nuclear weapons, especially amid rising tensions between the foremost nuclear powers, the United States and the Soviet Union. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower's " Atoms for Peace" speech, which called for the creation of an international organization to monitor the global proliferation of nuclear resources and technology, is credited with catalyzing the formation of the IAEA, whose treaty came into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Nuclear Disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13–14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl (335,000 people evacuated) and Fukushima (154,000 evacuate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)