|
Surge (glacier)
Glacial surges are short-lived events where a glacier can advance substantially, moving at velocities up to 100 times faster than normal. Surging glaciers cluster around a few areas. High concentrations of surging glaciers occur in the Karakoram, Pamir Mountains, Svalbard, the Canadian Arctic islands, Alaska and Iceland, although overall it is estimated that only one percent of all the world's glaciers ever surge. In some glaciers, surges can occur in fairly regular cycles, with 15 to 100 or more surge events per year. In other glaciers, surging remains unpredictable. In some glaciers, however, the period of stagnation and build-up between two surges typically lasts 10 to 200 years and is called the quiescent phase. Dowdeswell, J. A., B. Unwin, A. M. Nuttall and D. J. Wingham. 1999. Velocity structure, flow instability and mass flux on a large Arctic ice cap from satellite radar interferometry. Elsevier Science B.V. During this period the velocities of the glacier are significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between latitudes 35°N and 35°S, glaciers occur o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
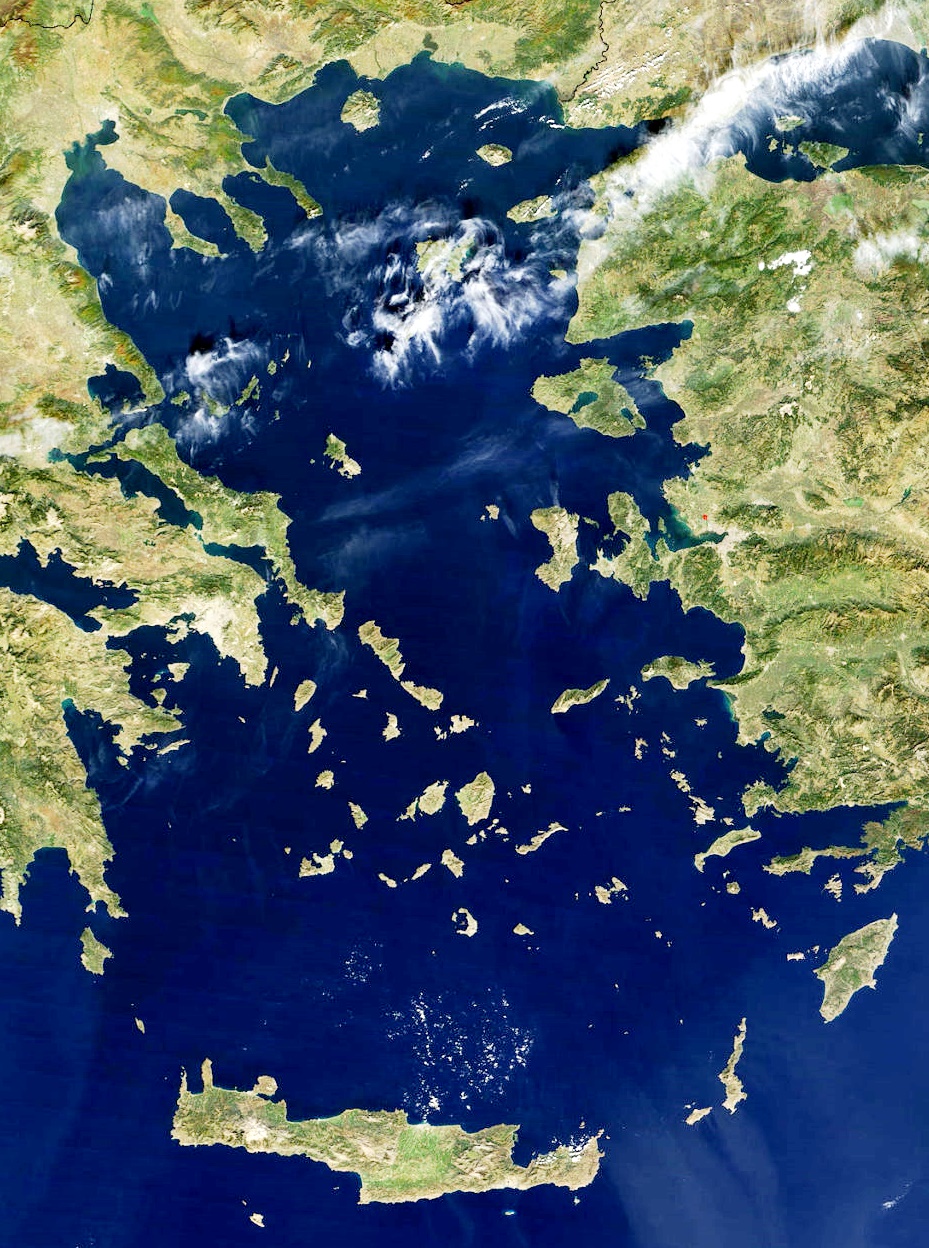
Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the jurisdiction of Gilgit-Baltistan, which is controlled by Pakistan. Its highest peak (and world's second-highest), K2, is located in Gilgit-Baltistan. It begins in the Wakhan Corridor (Afghanistan) in the west, encompasses the majority of Gilgit-Baltistan, and extends into Ladakh (controlled by India) and Aksai Chin (controlled by China). It is the second-highest mountain range in the world and part of the complex of ranges including the Pamir Mountains, the Hindu Kush and the Himalayan Mountains. The Karakoram has eighteen summits over in height, with four exceeding : K2, the second-highest peak in the world at , Gasherbrum I, Broad Peak and Gasherbrum II. The range is about in length and is the most heavily glaciated part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains. Much of the Pamir Mountains lie in the Gorno-Badakhshan Province of Tajikistan. To the south, they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in Badakhshan Province, Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan regions of Pakistan. To the north, they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the east, they extend to the range that includes China's Kongur Tagh, in the "Eastern Pamirs", separated by the Yarkand valley from the Kunlun Mountains. Name and etymology Since Victorian times, they have been known as the " Roof of the World", presumably a translation from Persian. Names In other languages they are called: ps, , ; ky, Памир тоолору, , ; fa, , R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Arctic Islands
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark). Situated in the northern extremity of North America and covering about , this group of 36,563 islands, surrounded by the Arctic Ocean, comprises much of Northern Canada, predominately Nunavut and the Northwest Territories. The archipelago is showing some effects of climate change, with some computer estimates determining that melting there will contribute to the rise in sea levels by 2100. History Around 2500 BCE, the first humans, the Paleo-Eskimos, arrived in the archipelago from the Canadian mainland. Between 1000–1500 CE, they were replaced by the Thule people, who are the ancestors of today's Inuit. British claims on the islands, the British Arctic Territories, were based on the explorations in the 1570s by Martin Frobisher. Canadian sovereignty was originally ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier Retreat
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 affects the availability of fresh water for irrigation and domestic use, mountain recreation, animals and plants that depend on glacier-melt, and, in the longer term, the level of the oceans. Deglaciation occurs naturally at the end of ice ages, but glaciologists find the current glacier retreat is accelerated by the measured increase of atmospheric greenhouse gases—an effect of climate change. Mid-latitude mountain ranges such as the Himalayas, Rockies, Alps, Cascades, Southern Alps, and the southern Andes, as well as isolated tropical summits such as Mount Kilimanjaro in Africa, are showing some of the largest proportionate glacial losses. Excluding peripheral glaciers of ice sheets, the total cumulated global glacial losses over the 26 year period from 1993–2018 were likely 5500 gigatons, or 210 gigatons per yr.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, S.S. Drijfhout, T.L. Edwards, N.R. Golledge, M. Hemer, R.E. Kopp, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
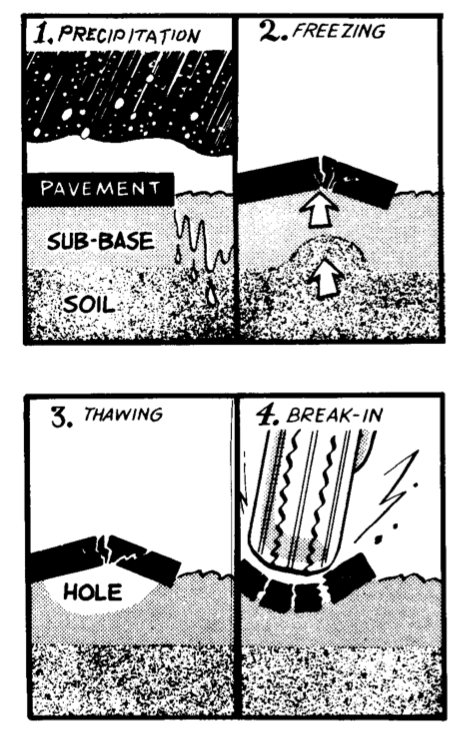
Pothole
A pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area. Water first weakens the underlying soil; traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt surface in the affected area. Continued traffic action ejects both asphalt and the underlying soil material to create a hole in the pavement. Formation According to the US Army Corps of Engineers's Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, pothole formation requires two factors to be present at the same time: water and traffic. Water weakens the soil beneath the pavement while traffic applies the loads that stress the pavement past the breaking point. Potholes form progressively from fatigue of the road surface which can lead to a precursor failure pattern known as crocodile (or alligator) cracking. Eventually, chunks of pavem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands. Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archipelago, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Lakshadweep Islands, the Galápagos Islands, the Japanese archipelago, the Philippine Archipelago, the Maldives, the Balearic Islands, The Bahamas, the Aegean Islands, the Hawaiian Islands, the Canary Islands, Malta, the Azores, the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the British Isles, the islands of the Archipelago Sea, and Shetland. They are sometimes defined by political boundaries. For example, the Gulf archipelago off the northeastern Pacific coast forms part of a larger archipelago that geographically includes Washington state's San Juan Islands; while the Gulf archipelago and San Juan Islands are geographically related, they are not technically included in the same archipelago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Flow
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''. Science * Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure * Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is necessary for health or life, such as a minimum insulin dose * Basal (phylogenetics), a sister group relationship in a phylogenetic tree Places * Basal, Hungary, a village in Hungary * Basal, Pakistan, a village in the Attock District Other * Basal plate (other) * Basal sliding Basal sliding is the act of a glacier sliding over the bed due to meltwater under the ice acting as a lubricant. This movement very much depends on the temperature of the area, the slope of the glacier, the bed roughness, the amount of meltwater f ..., the act of a glacier sliding over the bed before it due to meltwater increasing the water pressure underneath the glacier causing it to be lifted from its bed * Basal conglomerate, see conglomerate (geology) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraglacial Lake
A supraglacial lake is any pond of liquid water on the top of a glacier. Although these pools are ephemeral, they may reach kilometers in diameter and be several meters deep. They may last for months or even decades at a time, but can empty in the course of hours. Lifetime Lakes may be created by surface melting during summer months, or over the period of years by rainfall, such as monsoons. They may dissipate by overflowing their banks, or creating a moulin. Effects on ice masses Lakes of a diameter greater than ~300 m are capable of driving a fluid-filled crevasse to the glacier/bed interface, through the process of hydrofracture. A surface-to-bed connection made in this way is referred to as a moulin. When these crevasses form, it can take a mere 2–18 hours to empty a lake, supplying warm water to the base of the glacier - lubricating the bed and causing the glacier to surge. The rate of emptying such a lake is equivalent to the rate of flow of the Niagara Falls. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |