|
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snifting Valve
A snifting valve (sometimes snifter valve) is an automatic anti-vacuum valve used in a steam locomotive when coasting. The word ''Snift'' imitates the sound made by the valve. Overview When the driver shuts off the steam to the cylinders of a steam locomotive while it is in motion, the moving pistons could create a partial vacuum in the cylinders. This would give rise to two problems. Firstly, the pumping action would absorb energy and prevent the engine from coasting freely. Secondly, when the exhaust valve opened, soot and cinders from the smokebox could be sucked down the exhaust pipe and into the valve chest or cylinder, causing damage. (The exhaust is open to the smokebox because in normal running the exhaust steam is sent through the blastpipe to draw the fire and eject the combustion products from the chimney.) These problems are avoided by using snifting valves to allow air to be drawn into the cylinder. On railways which did not use snifting valves, drivers were instr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney (or funnel). Early locomotives had no smokebox and relied on a long chimney to provide natural draught for the fire but smokeboxes were soon included in the design for two specific reasons. Firstly and most importantly, the blast of exhaust steam from the cylinders, when directed upwards through an airtight smokebox with an appropriate design of exhaust nozzle, effectively draws hot gases through the boiler tubes and flues and, consequently, fresh combustion air into the firebox. Secondly, the smokebox provides a convenient collection point for ash and cinders ("char") drawn through the boiler tubes, which can be easily cleaned out at the end of a working day. Without a smokebox, all char must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
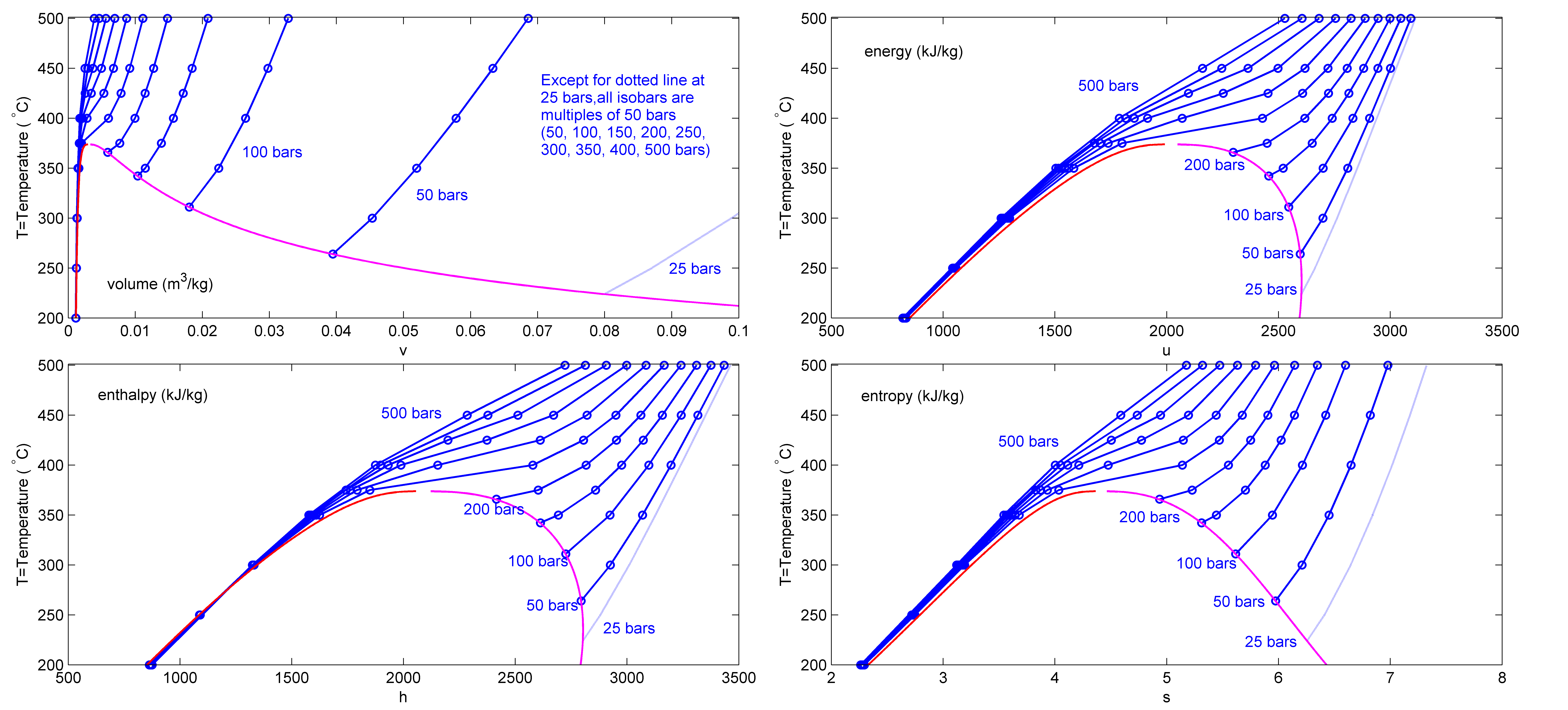
Superheated Steam
Superheated steam is steam at a temperature higher than its vaporization point at the absolute pressure where the temperature is measured. Superheated steam can therefore cool (lose internal energy) by some amount, resulting in a lowering of its temperature without changing state (i.e., condensing) from a gas, to a mixture of saturated vapor and liquid. If unsaturated steam (a mixture which contains both water vapor and liquid water droplets) is heated at constant pressure, its temperature will also remain constant as the vapor quality (think dryness, or percent saturated vapor) increases towards 100%, and becomes dry (i.e., no saturated liquid) saturated steam. Continued heat input will then "super" heat the dry saturated steam. This will occur if saturated steam contacts a surface with a higher temperature. Superheated steam and liquid water cannot coexist under thermodynamic equilibrium, as any additional heat simply evaporates more water and the steam will become saturated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Schmidt (engineer)
Wilhelm Schmidt, known as Hot Steam Schmidt (German: ''Heißdampf-Schmidt'') (1858–1924) was a German engineer and inventor who achieved the breakthrough in the development of superheated steam technology for steam engines. Wilhelm Schmidt was born in Wegeleben in the Prussian Province of Saxony on 18 February 1858. Education At school Wilhelm Schmidt had difficulties with reading, writing and arithmetic, a case of dyslexia. For example, he was unable to recite the alphabet without hesitation all his life. Nor could he memorise poetry or prose. He developed a passion for drawing, however, and for machines. Career Schmidt began his professional career as a machine fitter. He studied at the technical high school in Dresden under Gustav Zeuner. Superheated steam In 1883 he took a post as a civil engineer in Kassel, where he developed superheated steam technology to the point where it could be practically used. In 1908 he transferred his home and the base of his firm to Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LB&SCR I3 Class
The LB&SCR I3 class was a class of 4-4-2 steam tank locomotives designed by D. E. Marsh for suburban passenger service on the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway. History After introducing two unsuccessful designs of 4-4-2 tank locomotive with the I1 and I2 classes, Douglas Earle Marsh learned a lesson and provided a new design with a far larger firebox.The new design was a tank version of Robert Billinton's successful B4 class tender locomotives. At the time of its introduction locomotive engineers were beginning to take an interest in superheating and Marsh therefore ordered two locomotives from Brighton railway works for comparative purposes, one with a traditional saturated boiler and one incorporating the Schmidt superheater. These were built in October 1907 and March 1908 respectively. Several months of trials proved that both locomotives were performing well and reliably, but the LB&SCR Board of Directors were still not convinced that the extra building costs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian S 4
The Prussian S 4's were German superheated express steam locomotives with the Prussian state railways, later grouped as DRG Class 13.5 in the Deutsche Reichsbahn. They were an evolutionary development of the Prussian S 3. The first locomotive was built in 1898 by Vulcan, Stettin as a modified S 3. She was the first superheated locomotive in the world.Rauter and Scheingraber (1991), pp. 84-90. She was initially designated as ''Hannover 74'' and towards the end as the S 4 ''Cassel 401''. Two further trials locomotives appeared in 1899 and 1900 as ''Hannover 86'' and ''Berlin 74'' also classed as S 3's. They were later reclassified as S 4's ''Hannover 401'' and ''Posen 401''. Not until the teething troubles had been resolved was the S 4 put into series production in 1902 in Borsig, from 1906 also in Henschel and Humboldt. Unlike the prototypes the production engines were developed independently of the S 3, and 104 examples were built in the years to 1909 when procurement was halted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D Slide Valve
The slide valve is a rectilinear valve used to control the admission of steam into and emission of exhaust from the cylinder of a steam engine. Use In the 19th century, most steam locomotives used slide valves to control the flow of steam into and out of the cylinders. In the 20th century, slide valves were gradually superseded by piston valves, particularly in engines using superheated steam. There were two reasons for this: * With piston valves, the steam passages can be made shorter. This reduces resistance to the flow of steam and improves efficiency. * It is difficult to lubricate slide valves adequately in the presence of superheated steam. Murdoch's D slide valve The D slide valve, or more specifically Long D slide valve, is a form of slide valve, invented by William Murdoch and patented in 1799. It is named after the hollow central D-sectioned piston. This valve worked by "connecting the upper and lower valves so as to be worked by one rod or spindle, and in makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.jpg)
