|
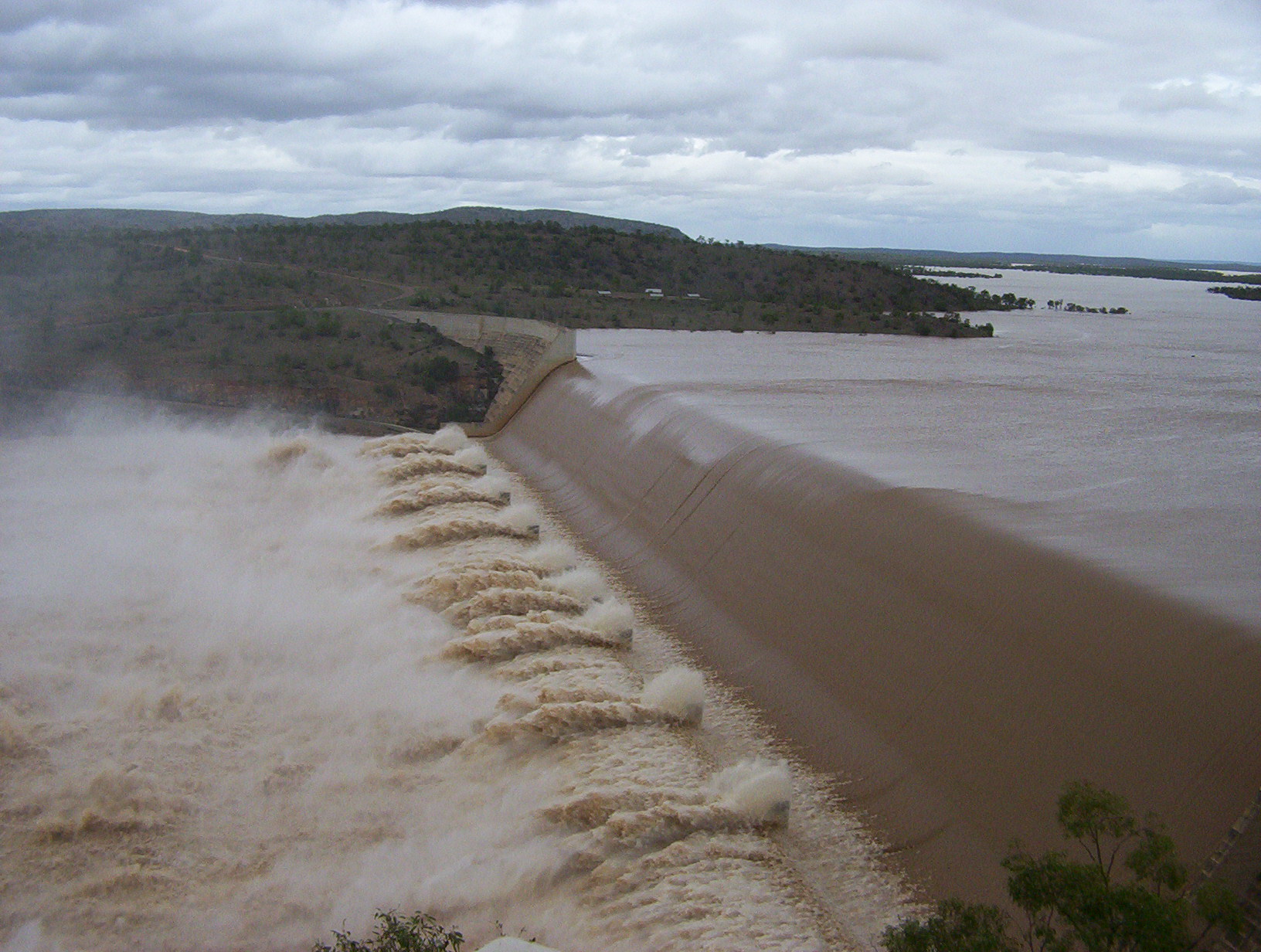
Supercritical Flow
A supercritical flow is a flow whose velocity is larger than the wave velocity. The analogous condition in gas dynamics is supersonic speed. According to the website Civil Engineering Terms, supercritical flow is defined as follows: The flow at which depth of the channel is less than critical depth, velocity of flow is greater than critical velocity and slope of the channel is also greater than the critical slope is known as supercritical flow. Information travels at the wave velocity. This is the velocity at which waves travel outwards from a pebble thrown into a lake. The flow velocity is the velocity at which a leaf in the flow travels. If a pebble is thrown into a supercritical flow then the ripples will all move down stream whereas in a subcritical flow some would travel up stream and some would travel down stream. It is only in supercritical flows that hydraulic jumps ( bores) can occur. In fluid dynamics, the change from one behaviour to the other is often describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow (fluid)
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a ''traveling wave''; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. Waves are often described by a ''wave equation'' (standing wave field of two opposite waves) or a one-way wave equation for single wave propagation in a defined direction. Two types of waves are most commonly studied in classical physics. In a '' mechanical wave'', stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Dynamics
Compressible flow (or gas dynamics) is the branch of fluid mechanics that deals with flows having significant changes in fluid density. While all flows are compressible, flows are usually treated as being incompressible when the Mach number (the ratio of the speed of the flow to the speed of sound) is smaller than 0.3 (since the density change due to velocity is about 5% in that case).Anderson, J.D., ''Fundamentals of Aerodynamics'', 4th Ed., McGraw–Hill, 2007. The study of compressible flow is relevant to high-speed aircraft, jet engines, rocket motors, high-speed entry into a planetary atmosphere, gas pipelines, commercial applications such as abrasive blasting, and many other fields. History The study of gas dynamics is often associated with the flight of modern high-speed aircraft and atmospheric reentry of space-exploration vehicles; however, its origins lie with simpler machines. At the beginning of the 19th century, investigation into the behaviour of fired bullets led to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic Speed
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2. Sounds are traveling vibrations in the form of pressure waves in an elastic medium. Objects move at supersonic speed when the objects move faster than the speed at which sound propagates through the medium. In gases, sound travels longitudinally at different speeds, mostly depending on the molecular mass and temperature of the gas, and pressure has little effect. Since air temperature and composition varies significantly with altitude, the speed of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Jump
A hydraulic jump is a phenomenon in the science of hydraulics which is frequently observed in open channel flow such as rivers and spillways. When liquid at high velocity discharges into a zone of lower velocity, a rather abrupt rise occurs in the liquid surface. The rapidly flowing liquid is abruptly slowed and increases in height, converting some of the flow's initial kinetic energy into an increase in potential energy, with some energy irreversibly lost through turbulence to heat. In an open channel flow, this manifests as the fast flow rapidly slowing and piling up on top of itself similar to how a shockwave forms. It was first observed and documented by Leonardo da Vinci in the 1500s. The mathematics were first described by Giorgio Bidone of Turin University when he published a paper in 1820 called ''Experiences sur le remou et sur la propagation des ondes''. The phenomenon is dependent upon the initial fluid speed. If the initial speed of the fluid is below the critical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Bore
{{disambiguation ...
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide. Tidal may also refer to: * ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple * Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim * TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music * Tidal (service), a music streaming service * Tidal, Manitoba, Canada ** Tidal station, Tidal, Manitoba See also * Tidal flow (traffic), the flow of traffic thought of as an analogy with the flow of tides * Tidal force, a secondary effect of the force of gravity and is responsible for the tides * Tide (other) A tide is the rise and fall of a sea level caused by the Moon's gravity and other factors. Tide may also refer to: Media * ''The Tide'' (Nigeria), a newspaper * ''Tide'' (TV series), 2019 Irish/Welsh/Scottish documentary series * WTKN, a radio s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Quantity
A dimensionless quantity (also known as a bare quantity, pure quantity, or scalar quantity as well as quantity of dimension one) is a quantity to which no physical dimension is assigned, with a corresponding SI unit of measurement of one (or 1), ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. which is not explicitly shown. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in many fields, such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering, and economics. Dimensionless quantities are distinct from quantities that have associated dimensions, such as time (measured in seconds). Dimensionless units are dimensionless values that serve as units of measurement for expressing other quantities, such as radians (rad) or steradians (sr) for plane angles and solid angles, respectively. For example, optical extent is defined as having units of metres multiplied by steradians. History Quantities having dimension one, ''dimensionless quantities'', regularly occur in sciences, and are formally treated within the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
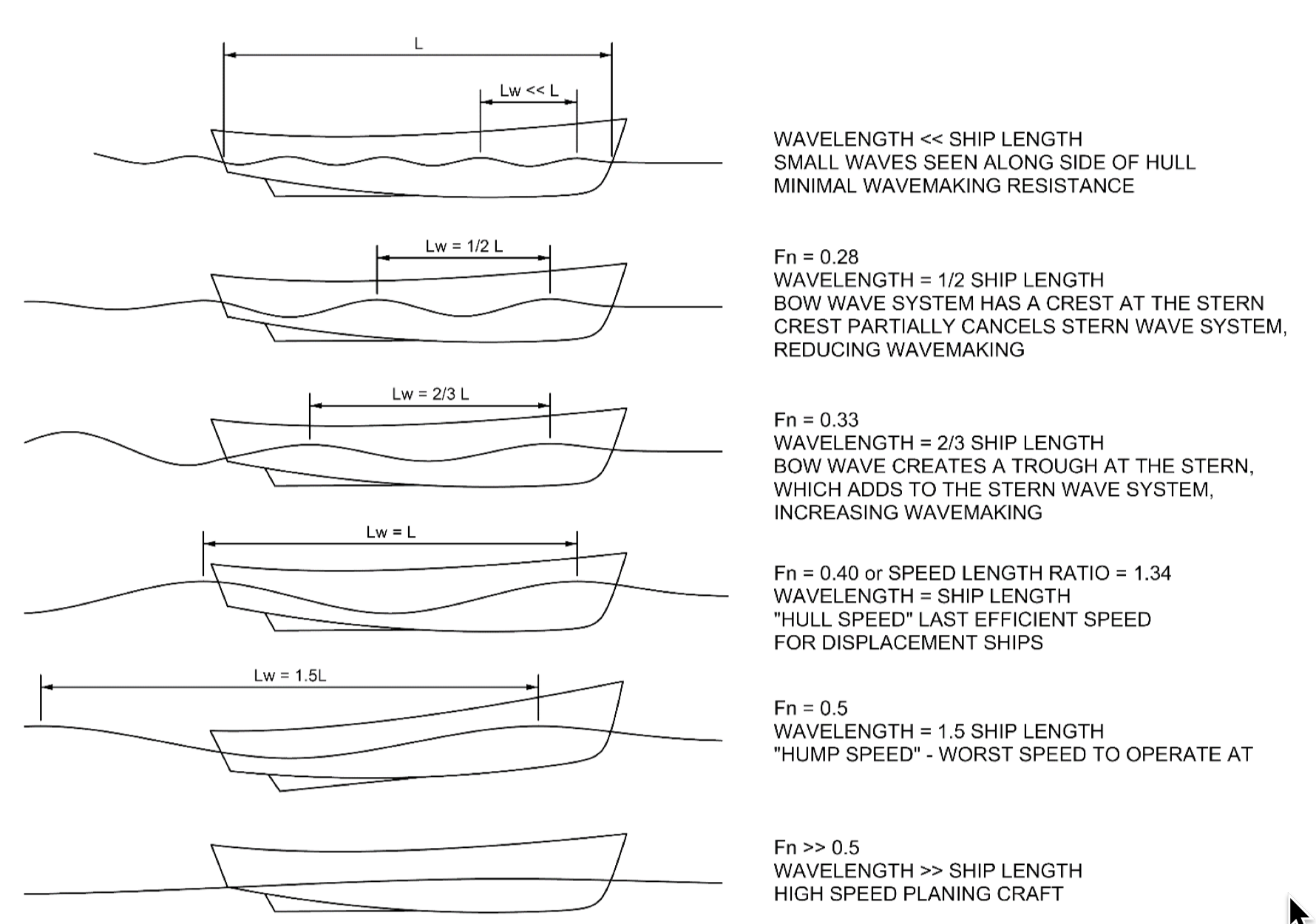
Froude Number
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity, is the local external field, and is a characteristic length. The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open channel flows, introduced first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point (chemistry), critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can Effusion, effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCF are much superior to gases in their ability to Solvation, dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Also, near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned". Supercritical fluids occur in the atmospheres of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, the terrestrial planet Venus, and probably in those of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Supercritical water is found on Earth, such as the water issuing from black smokers, a type of underwater hydrothermal vent. They are used as a sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum–depth Relationship In A Rectangular Channel
In fluid mechanics and hydraulics, open-channel flow is a type of liquid flow within a conduit with a free surface, known as a channel. The other type of flow within a conduit is pipe flow. These two types of flow are similar in many ways but differ in one important respect: open-channel flow has a free surface, whereas pipe flow does not. Classifications of flow Open-channel flow can be classified and described in various ways based on the change in flow depth with respect to time and space. The fundamental types of flow dealt with in open-channel hydraulics are: * Time as the criterion ** ''Steady flow'' *** The depth of flow does not change over time, or if it can be assumed to be constant during the time interval under consideration. ** ''Unsteady flow'' *** The depth of flow does change with time. * Space as the criterion ** ''Uniform flow'' *** The depth of flow is the same at every section of the channel. Uniform flow can be steady or unsteady, depending on whether or no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2. Sounds are traveling vibrations in the form of pressure waves in an elastic medium. Objects move at supersonic speed when the objects move faster than the speed at which sound propagates through the medium. In gases, sound travels longitudinally at different speeds, mostly depending on the molecular mass and temperature of the gas, and pressure has little effect. Since air temperature and composition varies significantly with altitude, the speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |