|
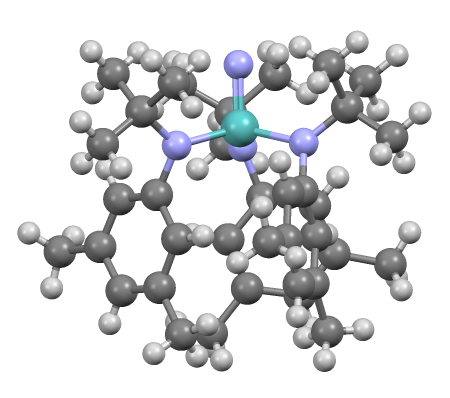
Sulfur Diimide
Sulfur diimides are chemical compounds of the formula S(NR)2. Structurally, they are the diimine of sulfur dioxide. The parent member, S(NH)2, is of only theoretical interest. Other derivatives where R is an organic group are stable and useful reagents. Organic derivatives A particularly stable derivative is di- ''t''-butylsulfurdiimide.Kresze, G.; Wucherpfennig, W., "Organic synthesis with imides of sulfur dioxide", Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1967, volume 6, 149-167. It is prepared by reaction of ''tert''-butylamine with sulfur dichloride to give the intermediate "S(N-''t''-Bu)", which decomposes at 60 °C to give the diimide. A second route to sulfur diimides involve treatment of sulfur tetrafluoride with amines. A third route involves transimidation of disulfonylsulfodiimide: :S(NSO2Ph)2 + 2 RNH2 → S(NR)2 + 2 PhSO2NH2 ''N'',''N-Bis(methoxycarbonyl)sulfur diimide (MeO2C-N=S=N-CO2Me) is obtained from methyl carbamate. Structure, bonding, reactions These com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Structure For ketimines and aldimines, respectively, the five core atoms (C2C=NX and C(H)C=NX, X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29-1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C-N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å, respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E- and Z-isomers of aldimines have been detected. Owing to steric effects, the E isomer is favored. Nomenclature and classification The term "imine" was coine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene ( ) (diolefin ( ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur Diimide
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide is the organosulfur compound with the formula S(NSiMe3)2 (Me = CH3). A colorless liquid, it is a diaza analogue of sulfur dioxide, i.e., a sulfur diimide. It is a reagent in the synthesis of sulfur nitrides. For example, it is a precursor to C2(N2S)2. Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide is prepared by the reaction of thionyl chloride and sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is the organosilicon compound with the formula . This species, usually called NaHMDS (sodium hexamethyldisilazide), is a strong base used for deprotonation reactions or base-catalyzed reactions. Its advantages are ...:{{cite journal, title=Synthese eines siliciumorganischen cyclischen Schwefeldiimids (Synthesis of an Organosilicon Cyclic Sulfur Diimide), journal=Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, year=1970, volume=25B, page=1486-7, doi=10.1515/znb-1970-1240, first1=Otto J., last1=Scherer, last2=Wies, first2=Reinhard, s2cid=93647579, doi-access=free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfur Dinitride
Disulfur dinitride is the chemical compound with the formula . Preparation and reactions Passing gaseous over silver metal wool at 250–300 °C at low pressure (1mm Hg) yields cyclic . The silver reacts with the sulfur produced by the thermal decomposition of the to form , and the resulting catalyzes the conversion of the remaining into the four-membered ring , : : An alternative uses the less explosive . decomposes explosively above 30°C, and is shock sensitive. It readily sublimes, and is soluble in diethyl ether. Traces of water cause it to polymerize into . In the solid state it spontaneously polymerizes forming . It forms adducts with Lewis acids via a nitrogen atom, e.g. , , , . Structure and bonding The molecule is a four-membered ring, with alternating S and N atoms. One S atom has valence 4 and the other S atom has valence 2. Both nitrogen atoms has valence 3. The molecule is almost square and planar. The S–N bond lengths are 165.1pm and 165.7pm and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbodiimide
In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide (systematic IUPAC name: methanediimine) is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. They are exclusively synthetic. A well known carbodiimide is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, which is used in peptide synthesis. Dialkylcarbodiimides are stable. Some diaryl derivatives tend to convert to dimers and polymers upon standing at room temperature, though this mostly occurs with low melting point carbodiimides that are liquids at room temperature. Solid diaryl carbodiimides are more stable, but can slowly undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water over time. Structure and bonding From the perspective of bonding, carbodiimides are isoelectronic with carbon dioxide. Three principal resonance structures describe carbodiimides: :RN=C=NR ↔ RN+≡C-N−R ↔ RN−-C≡N+R The N=C=N core is relatively linear and the C-N=C angles approach 120°. In the case of C(NCHPh2)2, the central N=C=N angle is 170° and the C-N=C angles are within 1° of 126°. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Amide
Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amide ligands have two electron pairs available for bonding. In principle, they can be terminal or bridging. In these two examples, the dimethylamido ligands are both bridging and terminal: File:Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer.png, Tris(dimethylamino)aluminium dimer File:Tris(dimethylamino)gallium dimer.png, Tris(dimethylamino)gallium dimer File:Ti(NMe2)4.png, Tetrakis(dimethylamino)titanium File:Ta(NMe2)5.png, Pentakis(dimethylamido)tantalum In practice, bulky amide ligands have a lesser tendency to bridge. Amide ligands may participate in metal-ligand π-bonding giving a complex with the metal center being co-planar with the nitrogen and substituents. Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides form a significant subcategory of metal amide compounds. These compounds tend to be discrete and soluble in organic solvents. Alkali metal am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are widely used. Sulfites are substances that naturally occur in some foods and the human body. They are also used as regulated food additives. When in food or drink, sulfites are often lumped together with sulfur dioxide.SeREGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL/ref> Structure The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent resonance structures. In each resonance structure, the sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom with a formal charge of zero (neutral), and sulfur is singly bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, which each carry a formal charge of −1, together accounting for the −2 charge on the anion. There is also a non-bonded lone pair on the sulfur, so the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
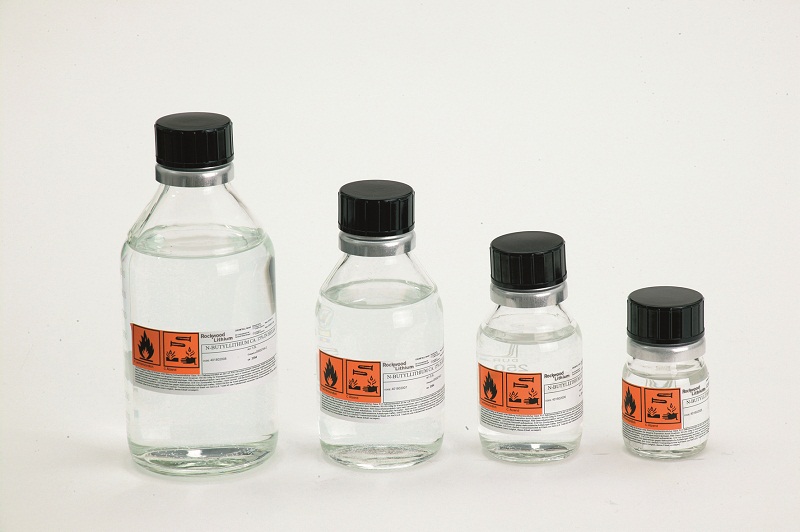
Organolithium Reagent
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric. History and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diels–Alder Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene derivative. It is the prototypical example of a pericyclic reaction with a concerted mechanism. More specifically, it is classified as a thermally-allowed +2cycloaddition with Woodward–Hoffmann symbol π4s_+_π2s.html" ;"title="sub>π4s + π2s">sub>π4s + π2s It was first described by Otto Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928. For the discovery of this reaction, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. Through the simultaneous construction of two new carbon–carbon bonds, the Diels–Alder reaction provides a reliable way to form six-membered rings with good control over the regio- and stereochemical outcomes. Consequently, it has served as a powerful and widely applied tool for the introduction of chemical complexity in the synthesis of natural products and new materials. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
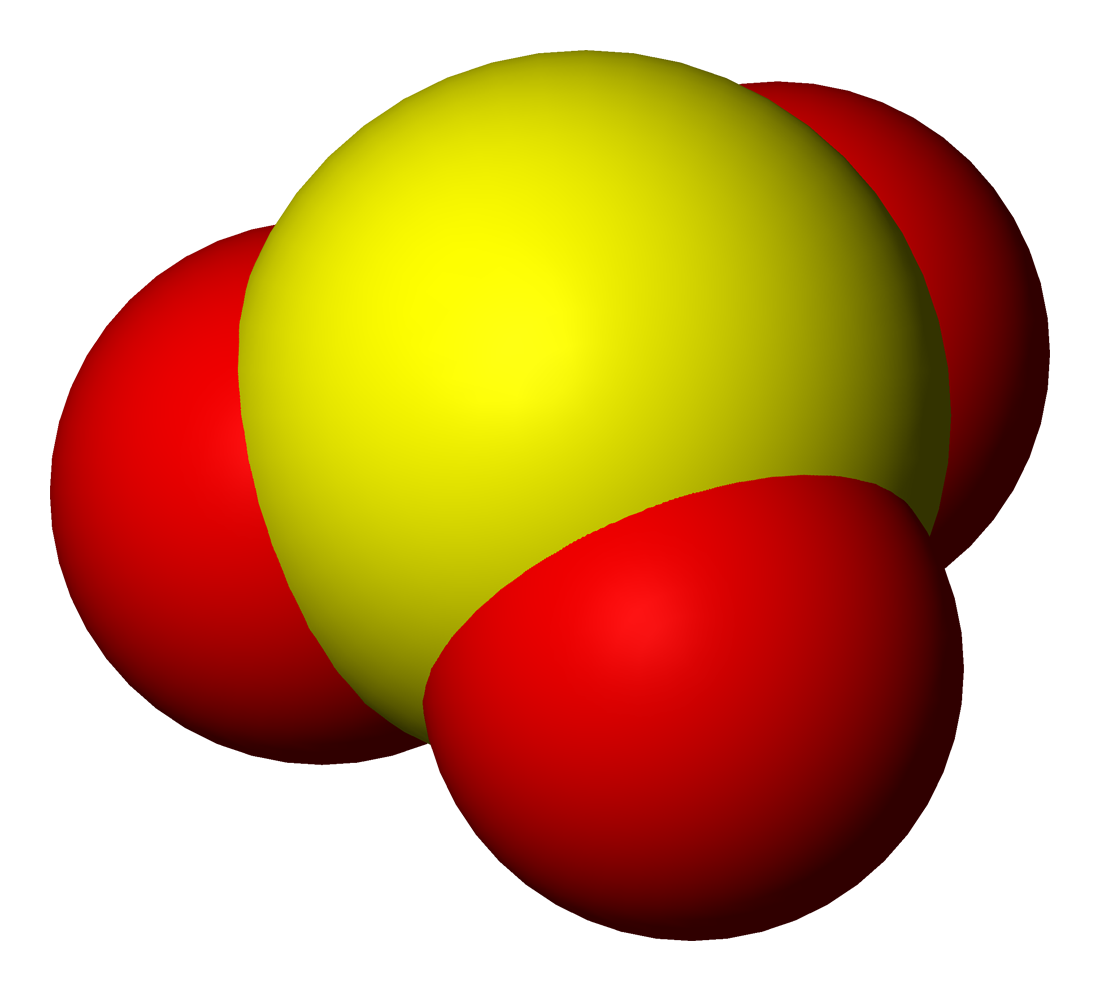
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through addition and substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in organic syntheses include cations such as H+ and NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as Cl2 and Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and radicals, and some Lewis acids such as BH3 and DIBAL. Organic chemistry Addition of halogens These occur between alkenes and electrophiles, often halogens as in halogen addition reactions. Common reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E–Z Notation
''E''–''Z'' configuration, or the ''E''–''Z'' convention, is the IUPAC preferred method of describing the absolute stereochemistry of double bonds in organic chemistry. It is an extension of ''cis''–''trans'' isomer notation (which only describes ''relative stereochemistry'') that can be used to describe double bonds having two, three or four substituents. Following the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules (CIP rules), each substituent on a double bond is assigned a priority, then positions of the higher of the two substituents on each carbon are compared to each other. If the two groups of higher priority are on opposite sides of the double bond (''trans'' to each other), the bond is assigned the configuration ''E'' (from ''entgegen'', , the German word for "opposite"). If the two groups of higher priority are on the same side of the double bond (''cis'' to each other), the bond is assigned the configuration ''Z'' (from ''zusammen'', , the German word for "together" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |