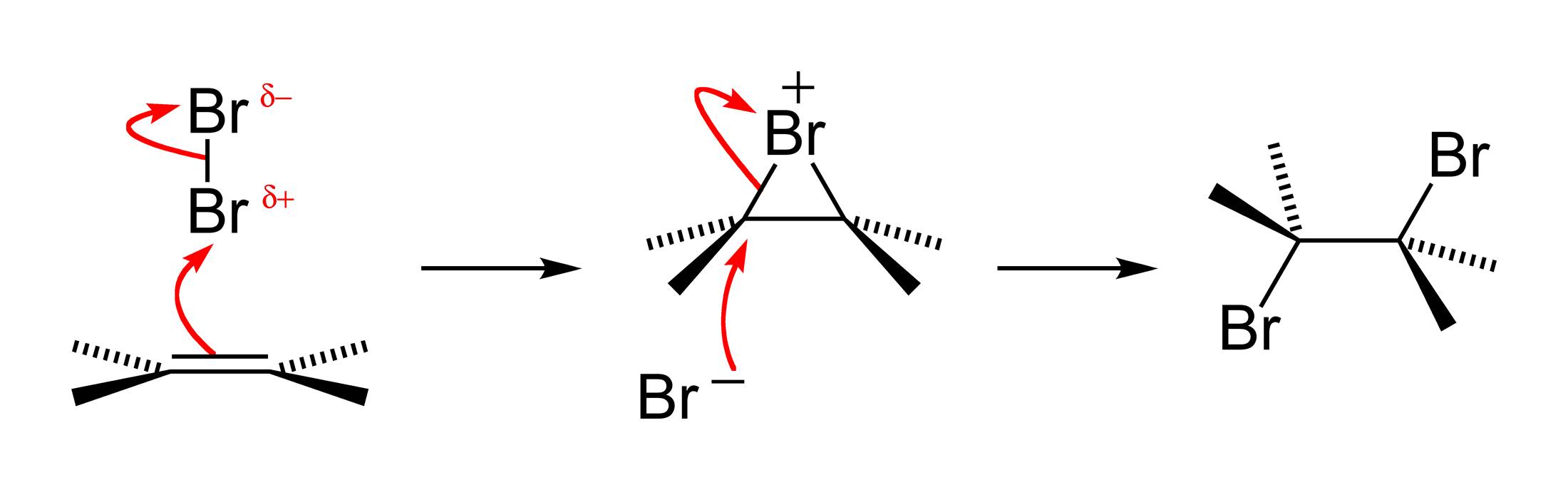|
Electrophilic
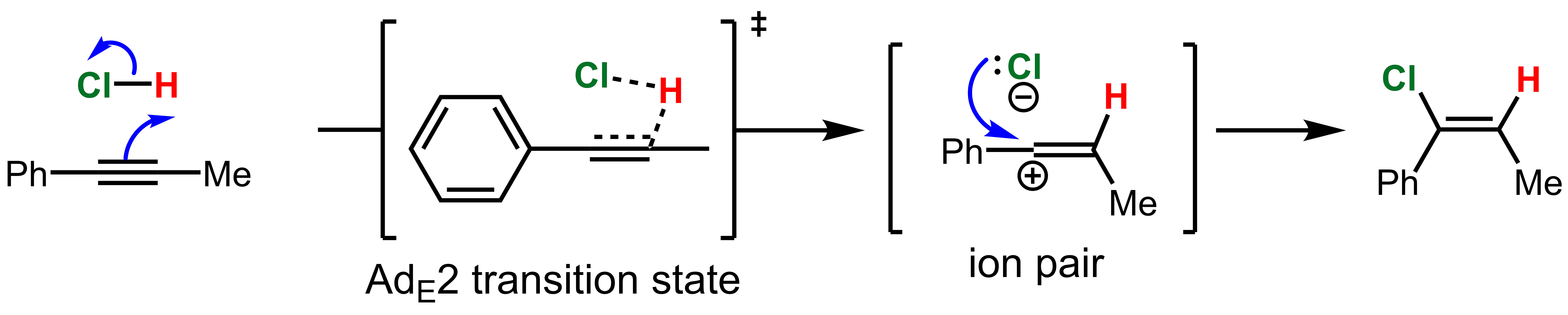
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through addition and substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in organic syntheses include cations such as H+ and NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as Cl2 and Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and radicals, and some Lewis acids such as BH3 and DIBAL. Organic chemistry Addition of halogens These occur between alkenes and electrophiles, often halogens as in halogen addition reactions. Common re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophilic Addition Of Br2
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with Nucleophile, nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively Electric charge, charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through Addition reaction, addition and Substitution reaction, substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in Organic synthesis, organic syntheses include cations such as Hydrogen ion, H+ and nitrosonium, NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as hydrogen chloride, HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as chlorine, Cl2 and bromine, Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and Radical (chemistry), radicals, and some Lewis acids such as Boran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Reaction
A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions are of prime importance in organic chemistry. Substitution reactions in organic chemistry are classified either as electrophilic or nucleophilic depending upon the reagent involved, whether a reactive intermediate involved in the reaction is a carbocation, a carbanion or a free radical, and whether the substrate is aliphatic or aromatic. Detailed understanding of a reaction type helps to predict the product outcome in a reaction. It also is helpful for optimizing a reaction with regard to variables such as temperature and choice of solvent. A good example of a substitution reaction is halogenation. When chlorine gas (Cl2) is irradiated, some of the molecules are split into two chlorine radicals (Cl•), whose free electrons are strongl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Compound
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peracid
A peroxy acid (often spelled as one word, peroxyacid, and sometimes called peracid) is an acid which contains an acidic –OOH group. The two main classes are those derived from conventional mineral acids, especially sulfuric acid, and the peroxy derivatives of organic carboxylic acids. They are generally strong oxidizers. Inorganic peroxy acids Peroxymonosulfuric acid (Caro's acid) is probably the most important inorganic peracid, at least in terms of its production scale. It is used for the bleaching of pulp and for the detoxification of cyanide in the mining industry. It is produced by treating sulfuric acid with hydrogen peroxide. Peroxymonophosphoric acid (H3PO5) is prepared similarly. Organic peracids Several organic peroxyacids are commercially useful. They can be prepared in several ways. Most commonly, peracids are generated by treating the corresponding carboxylic acid with hydrogen peroxide: :RCO2H + H2O2 RCO3H + H2O A related reaction involves treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogen Addition Reaction
A halogen addition reaction is a simple organic reaction where a halogen molecule is added to the carbon–carbon double bond of an alkene functional group. The general chemical formula of the halogen addition reaction is: :C=C + X2 → X−C−C−X (X represents the halogens bromine or chlorine, and in this case, a solvent could be CH2Cl2 or CCl4). The product is a vicinal dihalide. This type of reaction is a halogenation and an electrophilic addition. Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism for an alkene bromination can be described as follows. In the first step of the reaction, a bromine molecule approaches the electron-rich alkene carbon–carbon double bond. The bromine atom closer to the bond takes on a partial positive charge as its electrons are repelled by the electrons of the double bond. The atom is electrophilic at this time and is attacked by the pi electrons of the alkene arbon–carbon double bond It forms for an instant a single sigma bond to ''both'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosonium
The nitrosonium ion is , in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to an oxygen atom with a bond order of 3, and the overall diatomic species bears a positive charge. It can be viewed as nitric oxide with one electron removed. This ion is usually obtained as the following salts: , ( nitrosylsulfuric acid, more descriptively written ) and . The and salts are slightly soluble in acetonitrile . NOBF4 can be purified by sublimation at 200–250 °C and . is isoelectronic with CO, and . It arises via protonation of nitrous acid: :HONO + H+ NO+ + H2O Chemical properties Hydrolysis reacts readily with water to form nitrous acid: : For this reason, nitrosonium compounds must be protected from water or even moist air. With base, the reaction generates nitrite: : As a diazotizing agent reacts with aryl amines, , to give diazonium salts, . The resulting diazonium group is easily displaced (unlike the amino group) by a variety of nucleophiles. As an oxidizing agent , e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borane
Trihydridoboron, also known as borane or borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula . The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated the likely existence of the borane molecule. However, the molecular species BH3 is a very strong Lewis acid. Consequently, it is highly reactive and can only be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen. Structure and properties BH3 is a trigonal planar molecule with D3h symmetry. The experimentally determined B–H bond length is 119 pm. In the absence of other chemical species, it reacts with itself to form diborane. Thus, it is an intermediate in the preparation of diborane according to the reaction: :BX3 +BH4− → HBX3− + (BH3) (X=F, Cl, Br, I) :2 BH3 → B2H6 The standard enthalpy of dimerization of BH3 is esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. The term "carbene" may also refer to the specific compound , also called methylene, the parent hydride from which all other carbene compounds are formally derived. Carbenes are classified as either singlets or triplets, depending upon their electronic structure. Most carbenes are very short lived, although persistent carbenes are known. One well-studied carbene is dichlorocarbene , which can be generated ''in situ'' from chloroform and a strong base. Structures and bonding The two classes of carbenes are singlet and triplet carbenes. Singlet carbenes are spin-paired. In the language of valence bond theory, the molecule adopts an sp2 hybrid structure. Triplet carbenes have two unpaired electrons. Most carbenes have a nonlinear triplet ground state, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimer (chemistry), dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and methylene radical, triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, Plasma (ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |