|
Suchitra Sebastian
Suchitra Sebastian is a condensed matter physicist at Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge. She is known for her discoveries of exotic quantum phenomena that emerge in complex materials. In particular, she is known for the discovery of unconventional insulating materials which display simultaneous conduction-like behaviour. In 2022 she was awarded the New Horizons in Physics Prize by the Breakthrough Foundation. She was named as one of thirty ''Exceptional Young Scientists'' by the World Economic Forum in 2013, one of ''The Next Big Names in Physics'' by the Financial Times in 2013, and spoke at the World Economic Forum at Davos in 2016. Biography Suchitra Sebastian obtained an undergraduate degree in physics from the Women's Christian College, Chennai. She attended the Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad, where she received an MBA. She received a PhD in Applied Physics from Stanford University. She was a Junior Research Fellow in Physics at Trinity College, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Critical Point
A quantum critical point is a point in the phase diagram of a material where a continuous phase transition takes place at absolute zero. A quantum critical point is typically achieved by a continuous suppression of a nonzero temperature phase transition to zero temperature by the application of a pressure, field, or through doping. Conventional phase transitions occur at nonzero temperature when the growth of random thermal fluctuations leads to a change in the physical state of a system. Condensed matter physics research over the past few decades has revealed a new class of phase transitions called quantum phase transitions which take place at absolute zero. In the absence of the thermal fluctuations which trigger conventional phase transitions, quantum phase transitions are driven by the zero point quantum fluctuations associated with Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. Overview Within the class of phase transitions, there are two main categories: at a ''first-order phase t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Women Physicists
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Women Scientists
This is a list of notable women scientists active in the 21st century. Albania * Mimoza Hafizi (born 1962), Albanian physicist *Laura Mersini-Houghton, cosmology and theoretical physicist * Afërdita Veveçka Priftaj (1948–2017), Albanian physicist Argentina * Sonia Álvarez Leguizamón (born 1954), urban anthropologist studying poverty *Zulma Brandoni de Gasparini (born 1944), Argentine paleontologist and zoologist *Constanza Ceruti (born 1973), Argentine archaeologist and anthropologist * Rachel Chan (graduated 1988), led group of research scientists to create more drought resistant seed in Argentina * Perla Fuscaldo (born 1941), Argentine egyptologist Armenia * Vandika Ervandovna Avetisyan (born 1928), botanist and mycologist; major contributor to knowledge of the flora of her native Armenia * Ninet Sinaii, epidemiologist Australia * Anne Astin (graduated 1976), biochemist active in dairy development *Katherine Belov (born 1973), Australian geneticist, Tasmanian devil c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Condensed Matter Physicists
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Indian Physicists
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University Alumni
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneuriali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP) is a UK-based learned society and professional body that works to advance physics education, research and application. It was founded in 1874 and has a worldwide membership of over 20,000. The IOP is the Physical Society for the UK and Ireland and supports physics in education, research and industry. In addition to this, the IOP provides services to its members including careers advice and professional development and grants the professional qualification of Chartered Physicist (CPhys), as well as Chartered Engineer (CEng) as a nominated body of the Engineering Council. The IOP's publishing company, IOP Publishing, publishes 85 academic titles. History The Institute of Physics was formed in 1960 from the merger of the Physical Society, founded as the Physical Society of London in 1874, and the Institute of Physics, founded in 1918. The Physical Society of London had been officially formed on 14 February 1874 by Frederick Guthrie, following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Physics
The International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP ) is an international non-governmental organization whose mission is to assist in the worldwide development of physics, to foster international cooperation in physics, and to help in the application of physics toward solving problems of concern to humanity. It was established in 1922 and the first General Assembly was held in 1923 in Paris. The Union is domiciled in Geneva, Switzerland. IUPAP carries out this mission by: sponsoring international meetings; fostering communications and publications; encouraging research and education; fostering the free circulation of scientists; promoting international agreements on the use of symbols, units, nomenclature and standards; and cooperating with other organizations on disciplinary and interdisciplinary problems. IUPAP is a member of the International Science Council. IUPAP is the lead organization promoting the adoption of the International Year of Basic Sciences for Sustainab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
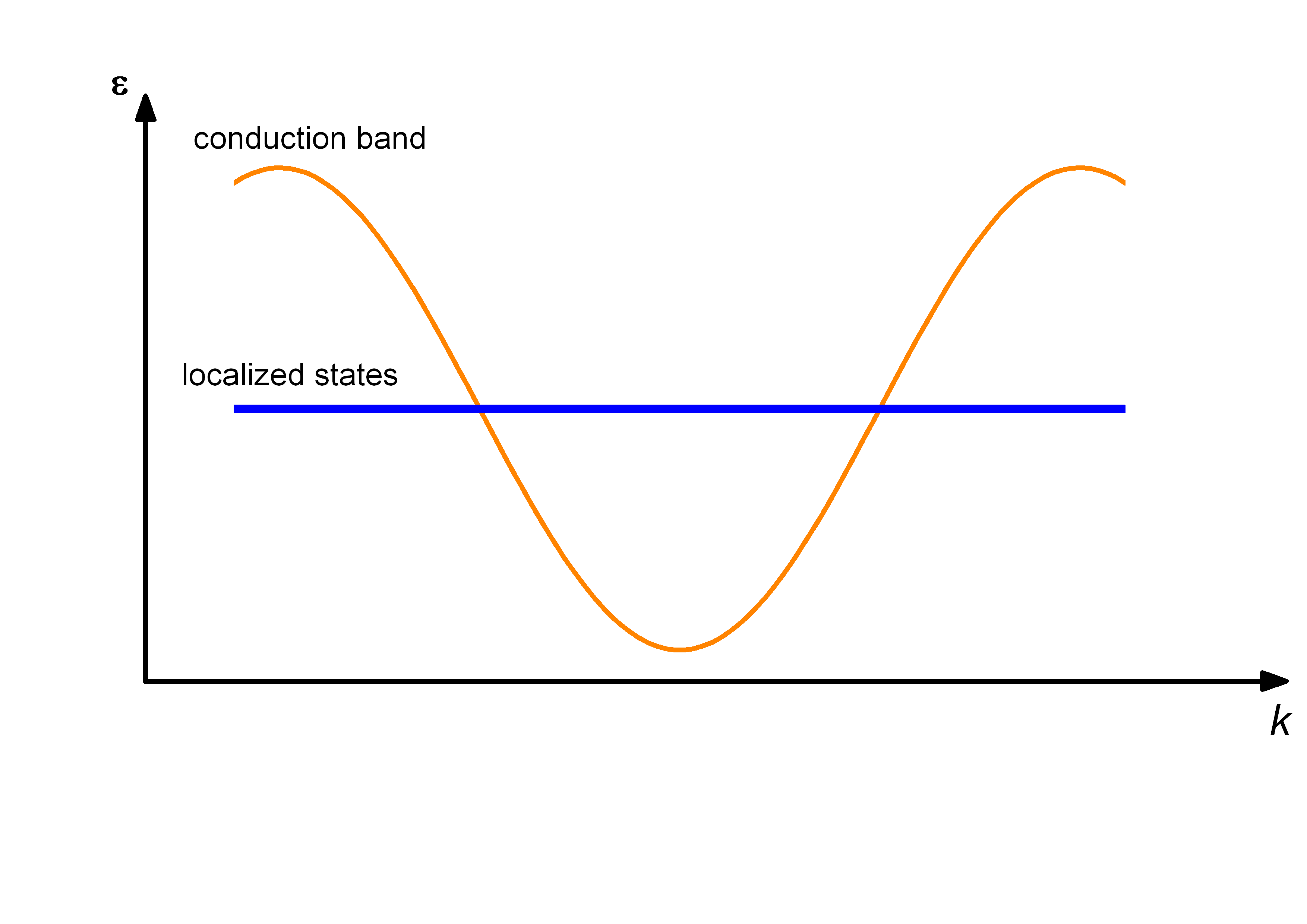
Kondo Insulator
In solid-state physics, Kondo insulators (also referred as Kondo semiconductors and heavy fermion semiconductors) are understood as materials with strongly correlated electrons, that open up a narrow band gap (in the order of 10 meV) at low temperatures with the chemical potential lying in the gap, whereas in heavy fermion materials the chemical potential is located in the conduction band. The band gap opens up at low temperatures due to hybridization of localized electrons (mostly f-electrons) with conduction electrons, a correlation effect known as the Kondo effect. As a consequence, a transition from metallic behavior to insulating behavior is seen in resistivity measurements. The band gap could be either direct or indirect. Most studied Kondo insulators are FeSi, Ce3Bi4Pt3, SmB6, YbB12, and CeNiSn, although there are over a dozen known Kondo insulators. Historical overview In 1969, Menth ''et al.'' found no magnetic ordering in SmB6 down to 0.35 K and a change from metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium Hexaboride
Samarium hexaboride (SmB6) is an intermediate-valence compound where samarium is present both as Sm2+ and Sm3+ ions at the ratio 3:7. It belongs to a class of Kondo insulators. At temperatures above 50 K its properties are typical of a Kondo metal, with metallic electrical conductivity characterized by strong electron scattering, whereas at low temperatures, it behaves as a non-magnetic insulator with a narrow band gap of about 4–14 meV. The cooling-induced metal-insulator transition in SmB6 is accompanied by a sharp increase in thermal conductivity, peaking at about 15 K. The reason for this increase is that electrons do not contribute to thermal conductivity at low temperatures, which is instead dominated by phonons. The decrease in electron concentration reduced the rate of electron-phonon scattering. Some research claims that it may be a topological insulator. Other researchers found no evidence of topological surface states. The increasing electrical resistance with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |