|
Stretch Rule
In classical mechanics, the stretch rule (sometimes referred to as Routh's rule) states that the moment of inertia of a rigid object is unchanged when the object is stretched parallel to an axis of rotation that is a principal axis, provided that the distribution of mass remains unchanged except in the direction parallel to the axis. This operation leaves cylinders oriented parallel to the axis unchanged in radius. This rule can be applied with the parallel axis theorem The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body abo ... and the perpendicular axes rule to find moments of inertia for a variety of shapes. Derivation The (scalar) moment of inertia of a rigid body around the z-axis is given by: : I_z = \int_V d^3 r \, \rho(\mathbf)\,r^2 Where r is the distance of a point from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility). The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Routh
Edward John Routh (; 20 January 18317 June 1907), was an English mathematician, noted as the outstanding coach of students preparing for the Mathematical Tripos examination of the University of Cambridge in its heyday in the middle of the nineteenth century. He also did much to systematise the mathematical theory of mechanics and created several ideas critical to the development of modern control systems theory. Biography Early life Routh was born of an English father and a French-Canadian mother in Quebec, at that time the British colony of Lower Canada. His father's family could trace its history back to the Norman conquest when it acquired land at Routh near Beverley, Yorkshire. His mother's family, the Taschereau family, was well-established in Quebec, tracing their ancestry back to the early days of the French colony. His parents were Sir Randolph Isham Routh (1782–1858) and his second wife, Marie Louise Taschereau (1810–1891). Sir Randolph was Commissary General o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid Object
In physics, a rigid body (also known as a rigid object) is a solid body in which deformation is zero or so small it can be neglected. The distance between any two given points on a rigid body remains constant in time regardless of external forces or moments exerted on it. A rigid body is usually considered as a continuous distribution of mass. In the study of special relativity, a perfectly rigid body does not exist; and objects can only be assumed to be rigid if they are not moving near the speed of light. In quantum mechanics, a rigid body is usually thought of as a collection of point masses. For instance, molecules (consisting of the point masses: electrons and nuclei) are often seen as rigid bodies (see classification of molecules as rigid rotors). Kinematics Linear and angular position The position of a rigid body is the position of all the particles of which it is composed. To simplify the description of this position, we exploit the property that the body is rigid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Axis (mechanics)
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the ''right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through a fixed plane curve in a pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
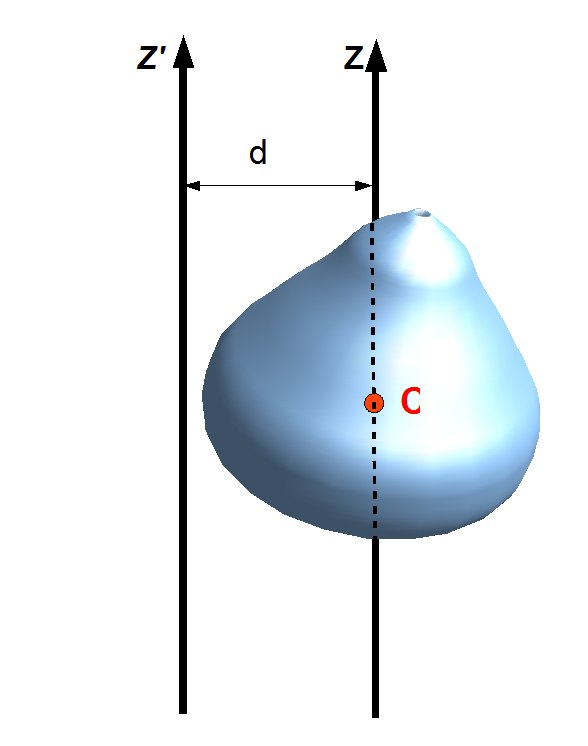
Parallel Axis Theorem
The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body about any axis, given the body's moment of inertia about a parallel axis through the object's center of gravity and the perpendicular distance between the axes. Mass moment of inertia Suppose a body of mass is rotated about an axis passing through the body's center of mass. The body has a moment of inertia with respect to this axis. The parallel axis theorem states that if the body is made to rotate instead about a new axis , which is parallel to the first axis and displaced from it by a distance , then the moment of inertia with respect to the new axis is related to by : I = I_\mathrm + md^2. Explicitly, is the perpendicular distance between the axes and . The parallel axis theorem can be applied with the stretch rule and perpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Axes Rule
The perpendicular axis theorem (or plane figure theorem) states that the moment of inertia of a planar lamina (i.e. 2-D body) about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the lamina is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia of the lamina about the two axes at right angles to each other, in its own plane intersecting each other at the point where the perpendicular axis passes through it. Define perpendicular axes x, y, and z (which meet at origin O) so that the body lies in the xy plane, and the z axis is perpendicular to the plane of the body. Let ''I''''x'', ''I''''y'' and ''I''''z'' be moments of inertia about axis ''x'', ''y'', ''z'' respectively. Then the perpendicular axis theorem states that :I_z = I_x + I_y This rule can be applied with the parallel axis theorem and the stretch rule to find polar moments of inertia for a variety of shapes. If a planar object has rotational symmetry such that I_x and I_y are equal, then the perpendicular axes theorem provides the useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility). The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)