|
St Blazey Engine Shed
St Blazey engine shed is located in Par, Cornwall, United Kingdom, although it is named after the adjacent village of St Blazey. It was built in 1874 as the headquarters of the Cornwall Minerals Railway but for many years was a depot of the Great Western Railway. The current depot operator (in 2016) is DB Cargo and the depot TOPS code is BZ. History St Blazey engine shed dates from the opening of the Cornwall Minerals Railway on 1 June 1874. This line linked Fowey and Newquay via Par in Cornwall. The engineer was Sir Morton Peto and he built workshops for the railway on the north side of Par, close to the adjoining town of St Blazey. The workshops included a distinctive roundhouse engine shed of nine 70 feet long roads around a turntable. Each shed road had a 58 feet long pit between the rails for servicing engines. The area also boasted an erecting and repair shop, a fitting shop, a smithy, boiler house and a 2,500 gallon water tower. Because of their location, the engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Par, Cornwall
Par ( kw, An Porth, meaning ''creek'' or ''harbour''Henry Jenner, ''A Handbook of the Cornish Language: Chiefly in Its Latest Stages, with Some Account of its History and Literature'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1904 reprinted 2012, ) is a village and fishing port with a harbour on the south coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is situated in the civil parish of Tywardreath and Par, although West Par and the docks lie in the parish of St Blaise. Par is approximately east of St Austell. Par has a population of around 1,600 (in 2012). It became developed in the second quarter of the 19th century when the harbour was developed, to serve copper mines and other mineral sites in and surrounding the Luxulyan Valley; china clay later became the dominant traffic as copper working declined, and the harbour and the china clay dries remain as distinctive features of the industrial heritage; however the mineral activity is much reduced. Par Harbour and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex Trains
Wessex Trains was a train operating company in the United Kingdom owned by National Express that operated the Wessex Trains franchise from October 2001 until March 2006, when the franchise was merged with the Great Western and Thames Valley franchises to form the Greater Western franchise. History In October 1996, Wales & West commenced operating the South West & Wales franchise in Wales and the West Country. It also operated services to Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Birmingham International, Southampton Central, Brighton and London Waterloo. In 2001 the Strategic Rail Authority decided to re-organise the Valley Lines and Wales & West franchises, both being operated by National Express. Wales & West became Wessex Trains from October 2001. Wessex Trains retained the West Country services with the Welsh services transferred to Wales & Borders although Wessex Trains operated services to Cardiff. Services Wessex Trains ran the majority of local trains in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff Canton TMD
Cardiff Canton TMD ( cy, Depo Cynnal a Chadw Treganna Caerdydd) is a diesel locomotive traction maintenance depot in Cardiff, Wales. Its depot code is CF. It is operated by Transport for Wales. The depot is used by Transport for Wales fleet and some Cross Country Class 170s. In steam days the depot was called Cardiff Canton and its shed code was 86C. It was built in 1882 as the main maintenance base for the South Wales Railway and the major Welsh engineering base for the Great Western Railway (GWR). After nationalisation in 1948 it was a heavy overhaul base for British Railways. After privatisation in the mid-1990s the depot became a joint Arriva Trains Wales and English Welsh & Scottish facility. The EWS depot closed as a maintenance centre from 10 December 2005, but EWS' successor DB Cargo UK still uses the depot for long-term storage and occasional stabling. History Steam Cardiff Canton was opened in June 1882 as a six road, -long shed, built to replace Long Dyke, ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Cargo UK
DB Cargo UK (formerly DB Schenker Rail UK and English, Welsh & Scottish Railway (EWS)), is a British rail freight company headquartered in Doncaster, England. The company was established in early 1995 as ''North & South Railways'', successfully acquiring and merging five of the six freight companies that were sold during the privatisation of British Rail,The sixth rail freight company created during privatisation, Freightliner, was privatised through a management buyout. On 25 April 1996, the EWS brand was revealed and implemented over successive months. By the end of March 1997, it controlled 90% of the UK rail freight market, operated a fleet of 900 locomotives and 19,000 wagons, and had 7,000 employees. During the late 1990s, EWS invested heavily into rolling stock renewal, procuring a large number of British Rail Class 66 diesel locomotives, headcount was also reduced. It also acquired National Power's open-access freight operator in April 1998. During January 2001, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penzance TMD
Penzance TMD, also known as Long Rock TMD, is a railway traction maintenance depot situated in the village of Long Rock east of Penzance, Cornwall, England, and is the most westerly and southerly rail depot in the country. The depot operator is Great Western Railway (train operating company), Great Western Railway. The depot code is PZ. Description The depot is beside the Cornish Main Line, where it runs as a single track on the southern side and terminates at Penzance railway station, half a mile west of the depot. The depot is small, with six long sidings to store British Rail Class 253, High Speed Trains and British Rail Class 220, Voyagers, and four smaller sidings. If the longer sidings are all used up, trains are stored at Laira TMD, Plymouth, and then make their way to Penzance railway station in the morning. The depot also has a fuel lane, a single-tracked modern maintenance shed, and a small carriage washer. A few years ago, facilities at Penzance TMD were expanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenfordbridge
Wenfordbridge, or Wenford Bridge, is a hamlet some north of Bodmin and on the western flank of Bodmin Moor, in Cornwall, England, UK. It takes its name from an old granite bridge over the River Camel, and lies on the border between the parishes of St Breward and St Tudy. Wenford Bridge was the terminus of a former railway line from Wadebridge that was originally built by the Bodmin and Wadebridge Railway in 1834. The line was built in order to facilitate the transport of sea sand for agricultural use from the estuary of the Camel to the local farms, and never carried passengers. Other traffic included granite and china clay from local quarries, and the line survived to carry the latter until 1983. Today the route of the line forms part of the Camel Trail, a recreational route for walkers, cyclists and horse riders. Pottery The influential studio potter Michael Cardew purchased the inn at Wenford in 1939 and converted it to a pottery where he produced earthenware and stonewar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 1000 Class
The Great Western Railway 1000 Class or County Class was a class of 4-6-0 steam locomotive. Thirty examples were built between 1945 and 1947, but all were withdrawn and scrapped in the early 1960s. A replica locomotive is under construction. Background These locomotives were the final and most powerful development of the two-cylinder Saint Class introduced in 1901 and included several features that had already been used on the successful Modified Hall class. The Chief Mechanical Engineer of the GWR Frederick W. Hawksworth had hoped to design a new 4-6-2 (Pacific) express locomotive for post war traffic, when he took up office in 1941 but had been prevented by the war from doing so. This scheme was not entirely dead in 1945 when he was given the authority to build another batch of mixed-traffic 4-6-0s. Rather than build more examples of existing designs, Hawksworth introduced the County Class as a testbed for a number of the ideas he hoped to incorporate into the Pacific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 1400 Class
The GWR 1400 Class is a class of steam locomotive designed by the Great Western Railway for branch line passenger work. It was originally classified as the 4800 Class when introduced in 1932, and renumbered in 1946. Although credited to Charles Collett, the design dated back to 1868 with the introduction of the George Armstrong 517 class. Precursors Like the 48xx/14xx, the 517 Class was a lightweight loco for branchline work; it was built at Wolverhampton Works between 1868 and 1885. In this period evolutionary changes included: * 517-570 – with wheelbase, inside bearings to trailing wheels, and saddle tanks built 1868-1869. * 571-576 – with wheelbase, outside bearings and side tanks built 1869-1870 * 826-836, 838-849, 1154–1165, 202-05, 215-222, 1421–1432, 1433–1444, 1465-1482 – all with wheelbase with side tanks built 1873-1883 * 1483-1488 – with wheelbase and side tanks built 1884-1885 Later gradual changes included: Belpaire fireboxes, boilers rated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 455 Class
The GWR 455 Class, also called the "Metropolitan" or "Metro" Tanks, was a series of 140 locomotives built for the Great Western Railway, originally for their London suburban services, including running on the underground section of the Metropolitan Railway, the source of their nickname. Later on the class was seen on many other parts of the GWR system. Sixty "Metro" Tanks were built, from 1868 onwards, during the lifetime of their designer, Joseph Armstrong. His successor William Dean regarded the class so highly that he would add a further 80, the final 20 examples appearing as late as 1899. The "Metros" were all built at Swindon Works, in nine lots of ten or 20 engines each. Numbering Variations The first two batches had inside frames on all axles, but subsequently the leading wheels had outside axleboxes. The original 20 engines had a shorter coupled wheelbase than all the others, rather than . Nos. 455–470 were partially rebuilt with longer wheelbases when first reboil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
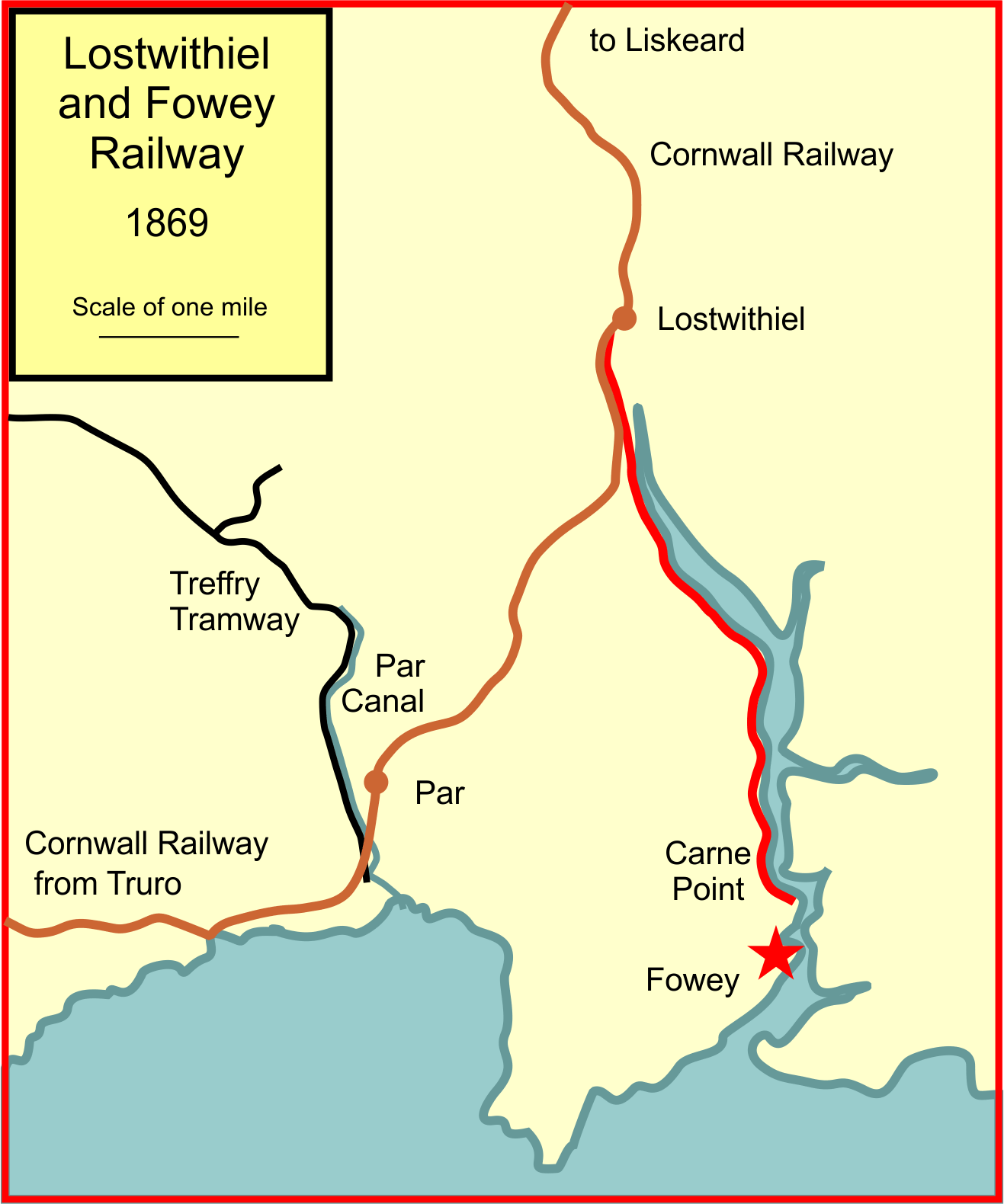
Lostwithiel And Fowey Railway
The Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway opened in 1869 as a broad gauge railway linking the port of Fowey in Cornwall with the Cornish Main Line at Lostwithiel. Its main traffic was china clay. The company ran into financial difficulties and closed in 1880, but the line was purchased by the Cornwall Minerals Railway and reopened in 1895. A passenger service operated, but it was withdrawn in 1965, and the line reverted to the conveyance of china clay; it remains open for that traffic at the present day. Chronology * 1862 Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway Act * 1869 Line opened * 1874 Cornwall Minerals Railway opens from Par to Fowey * 1880 Service suspended * 1892 Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway Company dissolved * 1895 Reopened by Cornwall Minerals Railway * 1968 Par to Fowey line closed History Promoters of an independent company conducted negotiations with the Cornwall Railway in 1861, regarding the construction of a branch line from that railway at Lostwithiel to a location at Caffa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BZ Steam Allocations
BZ may refer to: Chemistry * Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction, example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics * 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate, an odorless military incapacitating agent with NATO code BZ * Benzimidazole, an aromatic compound and parasiticide * Benzodiazepines, a class of psychoactive drugs * Benzoyl, group (Bz), C6H5-CO-, a functional group: acyl derived from benzoic acid * Bronze, an alloy consisting of ( Cu) Copper and ( Sn) tin Entertainment * B'z, a Japanese musical group * Blue Zone (band), credited as "B.Z." for the 1998 cover of the song "Jackie" by Joanne Accom * ''Beyond Zork'', a computer game released by Infocom in 1987 * ''Border Zone'' (video game) Periodicals * ''Badische Zeitung'', Freiburg(Germany) * ''Braunschweiger Zeitung'', Braunschweig * ''B.Z.'' (newspaper), Berlin * Berliner Zeitung, also Berlin * Berner Zeitung, Bern * Byzantinische Zeitschrift, a German academic journal Places * Bautzen, Germany (vehicle registration code BZ) * Belize (ISO 3166 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)