|
Sour Cream
Sour cream (in North American English, Australian English and New Zealand English) or soured cream (British English) is a dairy product obtained by fermenting regular cream with certain kinds of lactic acid bacteria. The bacterial culture, which is introduced either deliberately or naturally, sours and thickens the cream. Its name comes from the production of lactic acid by bacterial fermentation, which is called souring. Crème fraîche is one type of sour cream with a high fat content and less sour taste. Traditional Traditionally, sour cream was made by letting cream that was skimmed off the top of milk ferment at a moderate temperature. It can also be prepared by the souring of pasteurized cream with acid-producing bacterial culture. The bacteria that developed during fermentation thickened the cream and made it more acidic, a natural way of preserving it. Commercial varieties According to US (FDA) regulations, commercially produced sour cream contains no less than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowl Of Chili With Sour Cream And Cheese
A bowl is a typically round dish or container generally used for preparing, serving, or consuming food. The interior of a bowl is characteristically shaped like a spherical cap, with the edges and the bottom forming a seamless curve. This makes bowls especially suited for holding liquids and loose food, as the contents of the bowl are naturally concentrated in its center by the force of gravity. The exterior of a bowl is most often round but can be of any shape, including rectangular. The size of bowls varies from small bowls used to hold a single serving of food to large bowls, such as Punch (drink), punch bowls or salad bowls, that are often used to hold or store more than one portion of food. There is some overlap between bowls, cups, and Plate (dishware), plates. Very small bowls, such as the Chawan, tea bowl, are often called cups, while plates with especially deep wells are often called bowls. In many cultures bowls are the most common kind of vessel used for serving and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrageenan
Carrageenans or carrageenins ( ; ) are a family of natural linear sulfated polysaccharides that are extracted from red edible seaweeds. Carrageenans are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. Their main application is in dairy and meat products, due to their strong binding to food proteins. In recent years, carrageenans have emerged as a promising candidate in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications as they resemble native glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). They have been mainly used for tissue engineering, wound coverage and drug delivery. Carrageenans contain 15-40% ester-sulfate content, which makes them anionic polysaccharides. They can be mainly categorized into three different classes based on their sulfate content. Kappa-carrageenan has one sulfate group per disaccharide, iota-carrageenan has two, and lambda-carrageenan has three. The most well-known and most important red seaweed used for manufacturing the hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locust Bean Gum
Locust bean gum (LBG, carob gum, carob bean gum, carobin, E410) is a galactomannan vegetable gum extracted from the seeds of the carob tree and used as a thickening agent (gelling agent) in food technology. Production Locust bean gum is extracted from the seeds of the carob tree, which is native to the Mediterranean region. In 2016, nearly 75% of global production came from Portugal, Italy, Spain and Morocco. The seeds are contained within long pods that grow on the tree. First, the pods are kibbled to separate the seed from the pulp. Then, the seeds have their skins removed by an acid or heat treatment. Acid treatment yields a lighter coloured gum than heat treatment.:222 the deskinned seed is then split and gently milled. This causes the brittle germ to break up while not affecting the more robust endosperm. The two are separated by sieving. The separated endosperm can then be milled by a roller operation to produce the final locust bean gum powder. Alternatively, the gum ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Sorbate
Potassium sorbate is the potassium salt of sorbic acid, chemical formula CH3CH=CH−CH=CH−CO2K. It is a white salt that is very soluble in water (58.2% at 20 °C). It is primarily used as a food preservative (E number 202). Potassium sorbate is effective in a variety of applications including food, wine, and personal-care products. While sorbic acid occurs naturally in rowan berries, virtually all of the world's supply of sorbic acid, from which potassium sorbate is derived, is manufactured synthetically. Production Potassium sorbate is produced industrially by neutralizing sorbic acid with potassium hydroxide. The precursor sorbic acid is produced in a two-step process via the condensation of crotonaldehyde and ketene. Uses Potassium sorbate is used to inhibit molds and yeasts in many foods, such as cheese, wine, yogurt, dried meats, apple cider, dehydrated fruits, soft drinks and fruit drinks, and baked goods.Erich Lück, Martin Jager and Nico Raczek "Sorbic Acid" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris, and another occurs naturally as the mineral gypsum. It has many uses in industry. All forms are white solids that are poorly soluble in water.Franz Wirsching "Calcium Sulfate" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Calcium sulfate causes permanent hardness in water. Hydration states and crystallographic structures The compound exists in three levels of hydration corresponding to different crystallographic structures and to minerals: * (anhydrite): anhydrous state. The structure is related to that of zirconium orthosilicate (zircon): is 8-coordinate, is tetrahedral, O is 3-coordinate. * (gypsum and selenite (mineral)): dihydrate. * (bassanite): hemihydrate, also known as plaster of Paris. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Citrate
Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citric acid (though most commonly the third): * Monosodium citrate * Disodium citrate * Trisodium citrate The three forms of salt are collectively known by the E number E331. Applications Food Sodium citrates are used as acidity regulators in food and drinks, and also as emulsifiers for oils. They enable cheeses to melt without becoming greasy. It reduces the acidity of food as well. Blood clotting inhibitor Sodium citrate is used to prevent donated blood from clotting in storage. It is also used in a laboratory, before an operation, to determine whether a person's blood is too thick and might cause a blood clot, or if the blood is too thin to safely operate. Sodium citrate is used in medical contexts as an alkalinizing agent in place of sodium bicarbonate, to neutralize excess acid in the blood and urine. Metabolic acidosis It has applications for the treatment of metabolic acidosis and chronic kidney disease. Ferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Phosphate
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salts of sodium (Na+) and phosphate (PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms. Uses Sodium phosphates have many applications in food and for water treatment. For example, sodium phosphates are often used as emulsifiers (as in processed cheese), thickening agents, and leavening agents for baked goods. They are also used to control pH of processed foods. They are also used in medicine for constipation and to prepare the bowel for medical procedures. Moreover, they are used in detergents for softening water, and as an efficient anti rust solution. Adverse effects Sodium phosphates are popular in commerce in part because they are inexpensive and because they are nontoxic at normal levels of consumption. However, oral sodium phosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process Of Sour Cream Manufacturing
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic. Things called a process include: Business and management *Business process, activities that produce a specific service or product for customers *Business process modeling, activity of representing processes of an enterprise in order to deliver improvements *Manufacturing process management, a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. *Process architecture, structural design of processes, applies to fields such as computers, business processes, logistics, project management *Process costing, a cost allocation procedure of managerial accounting *Process management, ensemble of activities of planning and monitoring the performance of a business process or manufacturing processes *Process management (project management), a systematic series of activities directed towards causing an end result in engineerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/ashrae-terminology Refrigeration can be considered an artificial, or human-made, cooling method. Refrigeration refers to the process by which energy, in the form of heat, is removed from a low-temperature medium and transferred to a high-temperature medium. This work of energy transfer is traditionally driven by mechanical means, but can also be driven by heat, magnetism, electricity, laser, or other means. Refrigeration has many applications, including household refrigerators, industrial freezers, cryogenics, and air conditioning. Heat pumps may use the heat output of the refrigeration process, and also may be designed to be reversible, but are otherwise similar to air conditioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermented
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
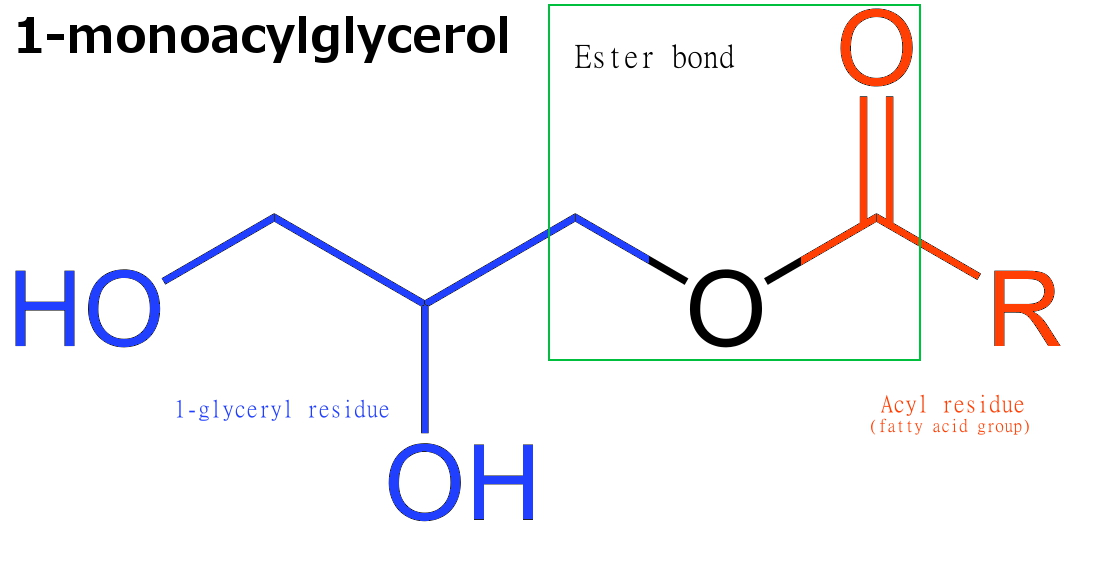
Monoglycerides
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industrial pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene Glycol Alginate
Propylene glycol alginate (PGA) is an emulsifier, stabilizer, and thickener used in food products. It is a food additive with E number E405. Chemically, propylene glycol alginate is an ester of alginic acid, which is derived from kelp. Some of the carboxyl groups are esterified with propylene glycol, some are neutralized with an appropriate alkali, and some remain free. See also *List of food additives, Codex Alimentarius The International Numbering System for Food Additives (INS) is a European-based naming system for food additives, aimed at providing a short designation of what may be a lengthy actual name."Class Names and the International Numbering System for F ... References {{reflist External links What is the "propylene glycol alginate" found in salad dressings?at The Straight Dope Food additives Carboxylate esters E-number additives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |