|
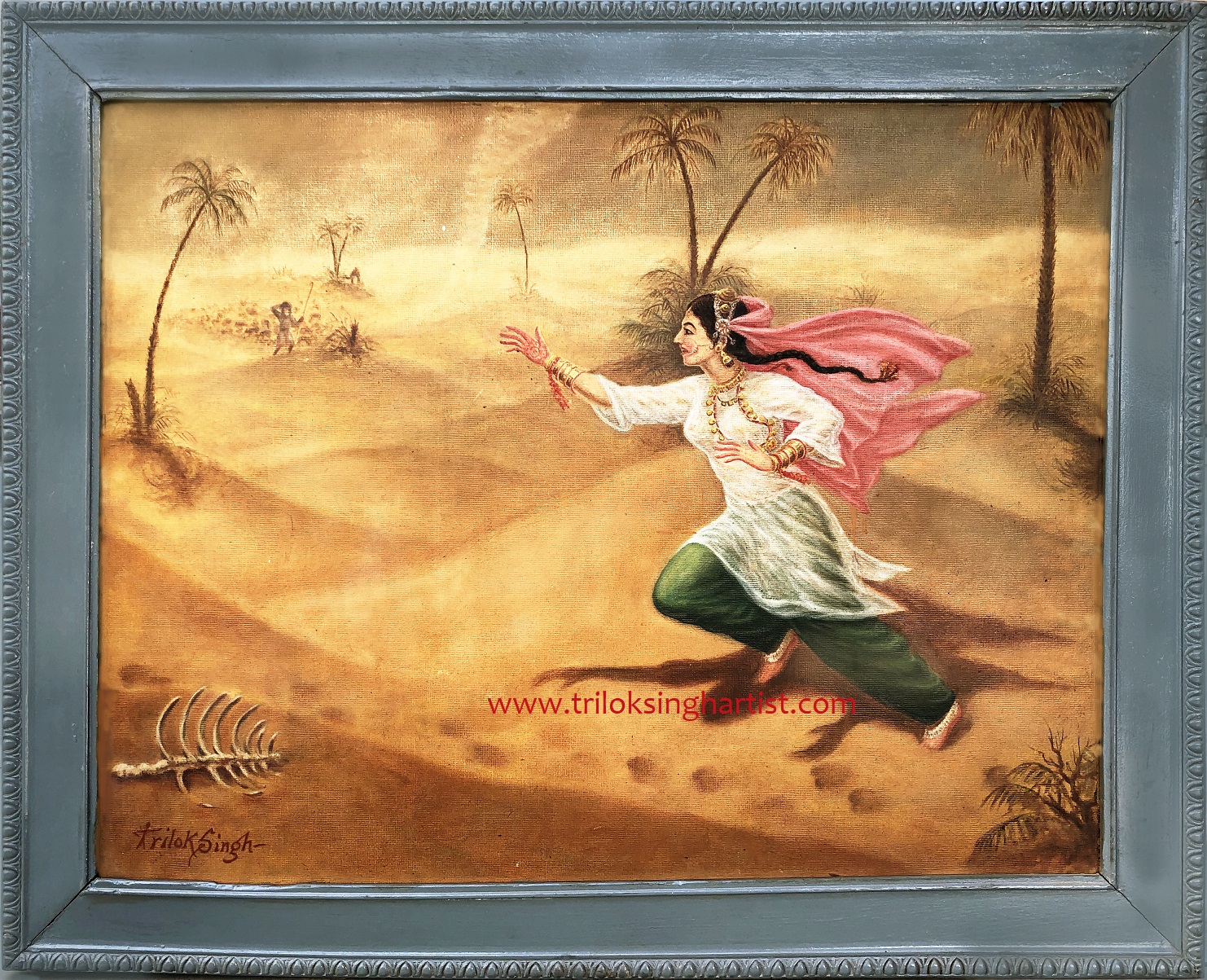
Sorath Rai Diyach
Sorath Rai Diyach ( sd, سورٺ راءِ ڏياچ) is one of the historical romantic tales from Sindh, Pakistan. The story also appears in Shah Jo Risalo and forms part of seven popular tragic romances from Sindh, Pakistan. The other six tales are ''Umar Marvi'', ''Sassui Punnhun'', ''Sohni Mahiwal, Sohni Mehar'', ''Lilan Chanesar'', ''Noori Jam Tamachi'' and ''Momal Rano'' commonly known as the Seven Queens of Sindh, or the Seven heroines of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai. Story Sorath was the queen of King Rai Diyach alias of Raja Dhaj, Ror Kumar of Girnar, Junagadh now in Gujarat who sacrificed herself for the sake of her love for husband. Diyach gave his head to wandering minstrel and followed him to the world of dead. Highly pleased with the songs of minstrel, Bijal, Diyach offered him to ask for anything he liked to have. As the intrigues of fate would have it, his son asked for his head. The kind and generous king gave it. Now the song resounded in Sorath's head. She bid farewell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab to the north. It shares International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province. The economy of Sindh is the second-largest in Pakistan after the province of Punjab; its provincial capital of Karachi is the most populous city in the country as well as its main financial hub. Sindh is home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Punjwani
Ram Prataprai Panjwani (1911-1987) was an Indian writer, folk singer and educationist, known for his contributions to Sindhi literature. Panjwani was born at Larkana in the Sindh province of erstwhile British India (presently in Pakistan). on 20 November 1911 He graduated from Mumbai University in 1934 and started his career as a teacher at the D. J. Sindh Government Science College, Karachi. After Indian independence in 1947, he relocated to Mumbai and started working as a member of faculty of Jai Hind College, Mumbai in their Sindhi department. Later, he moved to Mumbai University as the reader in Sindhi department and headed the department from 1974 to 1976. Panjwani published several literary works in Sindhi language, starting with his debut novel, ''Padma'' (1939) which preceded works like ''Qaidy'', ''Sharmila'', ''Asanjo Ghar'', ''Ahe Na ahe'' and ''Shall Dhiaru Na Jaman''. He also acted in four films, ''Jhulelal'', ''Ladlee'', ''Hojmalo'' and ''Shall Dhiaru Na Jaman'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistani Folklore
Pakistani folklore ( ur, ) encompasses the mythology, poetry, songs, dances and puppetry from Pakistan's various ethnic groups. Origins Both Indo-Aryan mythology and Iranic mythology evolved from the earlier ''Indo-Iranic'' mythology, have played an instrumental role in the development of various Pakistani folklore. Despite linguistic and religious differences at one time, the folklore from across the country seem to revolve around the themes of love, war, historical events or the supernatural. Generally, folklore from the southern regions tend to be based upon historical events, such as a peasant uprising or a tragic love story. In contrast, folklore from the northern regions appear be based on the supernatural, such as on ''Deos'' (giants) and '' Pichal Peri'' (fairies). Types Sindhi folklore Sindhi folklore ( sd, لوڪ ادب) are folk traditions which have developed in Sindh over a number of centuries. Sindh abounds with folklore, in all forms, and colors from such obv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistani Literature
Pakistani literature ( ur, ) is a distinct literature that gradually came to be defined after Pakistan gained nationhood status in 1947, emerging out of literary traditions of the South Asia. The shared tradition of Urdu literature and English literature of British India was inherited by the new state. Over a big time of period a body of literature unique to Pakistan has emerged in nearly all major Pakistani languages, including Urdu, English, Punjabi, Seraiki, Balochi, Pushto and Sindhi."Prolegomena to the Study of Pakistani English and Pakistani Literature in English" (1989), Alamgir Hashmi, ''Pakistani Literature'' (Islamabad), 2:1 1993. History The nature of Pakistani literature soon after independence aroused controversy among writers due to its being centred heavily on the negative events related to the independence movement. According to Gilani Kamran ( GC University), Pakistani literature was expected to take a new direction along with the new state of Pakistan at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Sindh
The Culture of Sindhi ( sd, سنڌ جي ثقافت) has its roots in the Indus Valley civilization. Sindh has been shaped by the largely desert region, the natural resources it had available, and continuous foreign influence. The Indus or Sindhu River that passes through the land, and the Arabian Sea (that defines its borders) also supported the seafaring traditions among the local people. The local climate also reflects why the Sindhis have the language, folklore, traditions, customs and lifestyle that are so different from the neighboring regions. The Sindhi culture is also practiced by the Sindhi diaspora. History The roots of Sindhi culture go back to the distant past. Archaeological research during 19th and 20th centuries showed the roots of social life, religion and culture of the people of the Sindh: their agricultural practices, traditional arts and crafts, customs and tradition and other parts of social life, going back to a mature Indus Valley Civilization of the thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Folklore
Sindhi folklore ( sd, لوڪ ادب) Sindhi Folklore is the folk tradition which has developed in Sindh over a number of centuries. Sindh abounds with folklore, in all forms, and colors from such obvious manifestations as the traditional Watayo Faqir tales, the legend of Moriro, epic poetry tale of Dodo Chanesar, to the heroic character of Marui which distinguishes it among the contemporary folklores of the region. The love story of Sassui, who pines for her lover Punhu, is known and sung in every Sindhi settlement. Other examples of the folklore of Sindh include the stories of Umar Marui and Suhuni Mehar ( Sohni Mahiwal in Punjab region).Kalyan Adwani, ed. ''Shah Jo Risalo''. Jamshoro: Sindhi Adabi Board, 2002. Sindhi folk Singers and women play a vital role to transmit the Sindhi folklore. They sang the folktales of Sindh in songs with passion in every village of Sindh. Sindhi folklore has been compiled in a series of forty volumes under Sindhi Adabi Board's project of Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassui Punhun
Sassi Punnuh or Sassui Punhun ( sd, سَسُئيِ پُنهوُن) is a love story from Punjabi, Sindhi, and Balochi folklore. The story is about a faithful lover who will endure any difficulty while seeking her beloved husband who was separated from her by rivals. The story also appears in Shah Jo Risalo and forms part of seven popular tragic romances from Sindh, Pakistan. The other six tales are ''Umar Marvi'', ''Sohni Mehar'', ''Lilan Chanesar'', ''Noori Jam Tamachi'', '' Sorath Rai Diyach'', and '' Momal Rano'' commonly known as the Seven Queens of Sindh, or the Seven heroines of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai. Punnu Mir Punnhun Khan (Mir Dostein) was the son of Mir Aalii or Ari, a baloch king of Kech, Balochistan. Sassi Sassi was the daughter of the Raja of Bhambore in Sindh (now in Pakistan). Upon Sassi's birth, astrologers predicted that she was a bane on the royal family's honour. The Raja ordered that the child be put in a wooden box and thrown in the Sindhu. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohni Mehar
Sohni Mahiwal or Suhni Mehar ( pa, , ਸੋਹਣੀ ਮਹੀਂਵਾਲ is one of the four popular tragic romances of Punjab including Sindh. In Sindh Sohni's shrine is in Shahdadpur Town of Sangar District. The others are Sassi Punnun, Mirza Sahiba, and Heer Ranjha. Sohni Mahiwal is a tragic love story which inverts the classical motif of Hero and Leander. The heroine Sohni, unhappily married to a man she despises, swims every night across the river using an earthenware pot to keep afloat in the water, to where her beloved Mehar herds buffaloes. One night her sister-in-law replaces the earthenware pot with a vessel of unbaked clay, which dissolves in water and she dies in the whirling waves of the river. The story also appears in Shah Jo Risalo and is one of seven popular tragic romances from Sindh. The other six tales are Umar Marui, Sassui Punhun, Lilan Chanesar, Noori Jam Tamachi, Sorath Rai Diyach and Momal Rano commonly known as ''Seven Heroines'' ( sd, ست سورم ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umar Marui
Umar Marvi or Marui ( sd, عمر مارئي, ur, ), is a folktale from Sindh, Pakistan about a village girl Marvi Maraich, who resists the overtures of a powerful King and the temptation to live in the palace as a queen, preferring to be in simple rural environment with her own village folk. The story also appears in Shah Jo Risalo and forms part of seven popular tragic romances from Sindh, Pakistan. The other six tales are ''Sassui Punnhun'', ''Sohni Mehar'', ''Lilan Chanesar'', ''Noori Jam Tamachi'', ''Sorath Rai Diyach'' and '' Momal Rano'' commonly known as the Seven Queens of Sindh, or the Seven heroines of Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai. Folklore The story of Umar Marvi is that Marvi was a young Thari girl abducted by then-ruler of Amarkot, Umar, who wanted to marry her because of her beauty. Upon her refusal she was imprisoned in the historic Umerkot Fort for several years. Because of her courage, Marvi is regarded as a symbol of love for one's soil and homeland. In popular cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvind Joshi
Arvind Joshi (1936 29 January 2021) was an Indian film and theatre actor, playwright and director known for his work in Gujarati theatre and Gujarati cinema. He was the father of actors Manasi Joshi Roy and Sharman Joshi. Biography He was born and raised in Mumbai. He worked as a theatre artist for around a decade before starting his career in Hindi film industry. He played major roles in Gujarati films including ''Garvo Garasiyo'', ''Gher Gher Matina Chula'' and ''Dhola Maru'', ''Tadka Chhaya'', '' Mehndi Rang Lagyo'' and ''Govaliyo''. He acted in Hindi films like Sholay (1975), '' Ittefaq'' (1969), ''Apmaan Ki Aag'' (1990), '' Ab To Aaja Saajan Mere'', and ''Love Marriage''. He died on 29 January 2021 in Vile Parle, Mumbai, aged 84. He was married and had two children, Manasi Joshi Roy and Sharman Joshi. He acted in the play like ''Rahuketu'', ''Lady Lalkunwar'', ''Khelando'', ''Banshayya'', ''Baraf Na Chehra'', ''Jaldi Kar Koi Joee Jashe''. Filmography Hindi films *'' It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Language
Gujarati (; gu, ગુજરાતી, Gujarātī, translit-std=ISO, label=Gujarati script, ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati (). In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in ''Nationalencyklopedin''. Asterisks mark th2010 estimatesfor the top dozen languages. Outside of Gujarat, Gujarati is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in England that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research or Dovepress. It is a division of Informa, Informa plc, a United Kingdom–based publisher and conference company. Overview The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis (chemist), William Francis joined Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the company was renamed Taylor & Francis Group to reflect the growing number of Imprint (trade name), imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_and_his_legendary_illicit_love.jpg)



.jpg)