|
Soomaa - Garden
Soomaa National Park ( et, Soomaa rahvuspark) is a national park in south-western Estonia. Soomaa ("land of bogs") protects 390 km², the park was created in 1993. Soomaa is Important Bird Area since 1989 and a Ramsar site of protected wetlands since 1997 and a Natura 2000 area since 2004. Geography The national park, situated in Vahe-Eesti (aka Meso-Estonia), was created in 1993 to protect large raised bogs, flood plain grasslands, paludified forests, and meandering rivers. The territory of the national park is mostly covered with large mires, separated from each other by the rivers of the Pärnu River basin — the Navesti, Halliste, Raudna and Lemmjõgi rivers. Of the raised bogs, the most noteworthy is the Kuresoo Bog, whose steep southern slope, falling into Lemmejõgi, rises by 8 metres over a distance of 100 m. On the eastern margin of the national park, lie the highest dunes on the Estonian mainland, situated some 50 kilometres off the contemporary coastline. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viljandi County
Viljandi County ( et, Viljandi maakond or ''Viljandimaa''; german: Kreis Fellin) is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is located in southern Estonia bordering Pärnu, Järva, Jõgeva, Tartu and Valga counties. History Viljandimaa, under the German name of ''Kreis Fellin'', was an important centre of commerce and power in the Middle Ages. Today, there are numerous castle ruins there dating from that time. Soomaa National Park is a national park located partially within Viljandi County, Estonia. Soomaa ("land of bogs") protects 390 km2, and is a Ramsar site of protected wetlands. The park was created in 1993. Retrieved 25 January 2016. County government The |
Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism is a concept that covers the complete tourism experience, including concern for economic, social and environmental issues as well as attention to improving tourists' experiences and addressing the needs of host communities. Sustainable tourism should embrace concerns for environmental protection, social equity, and the quality of life, cultural diversity, and a dynamic, viable economy delivering jobs and prosperity for all. It has its roots in sustainable development and there can be some confusion as to what "sustainable tourism" means. There is now broad consensus that tourism should be sustainable. In fact, all forms of tourism have the potential to be sustainable if planned, developed and managed properly. Tourist development organizations are promoting sustainable tourism practices in order to mitigate negative effects caused by the growing impact of tourism, for example its environmental impacts. The United Nations World Tourism Organization emphasized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunlin
The dunlin (''Calidris alpina'') is a small wader, formerly sometimes separated with the other "stints" in the genus ''Erolia''. The English name is a dialect form of "dunling", first recorded in 1531–1532. It derives from ''dun'', "dull brown", with the suffix ''-ling'', meaning a person or thing with the given quality. It is a circumpolar breeder in Arctic or subarctic regions. Birds that breed in northern Europe and Asia are long-distance migrants, wintering south to Africa, southeast Asia and the Middle East. Birds that breed in Alaska and the Canadian Arctic migrate short distances to the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of North America, although those nesting in northern Alaska overwinter in Asia. Many dunlins winter along the Iberian south coast. Taxonomy The dunlin was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Tringa alpina''. Linnaeus specified the location as Lapland. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Golden Plover
The European golden plover (''Pluvialis apricaria''), also known as the European golden-plover, Eurasian golden plover, or just the golden plover within Europe, is a largish plover. This species is similar to two other golden plovers: the American golden plover, ''Pluvialis dominica'', and Pacific golden plover, ''Pluvialis fulva'', which are both smaller, slimmer and relatively longer-legged than European golden plover, and both have grey rather than white axillary feathers (only properly visible in flight). Taxonomy The European golden plover was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it with the other plovers in the genus ''Charadrius'' and coined the binomial name ''Charadrius apricarius''. The species is now placed in the genus ''Pluvialis'' that was introduced in 1760 by the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson. The genus name is Latin and means "relating to rain", from ''pluvia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Whimbrel
The Eurasian whimbrel or common whimbrel (''Numenius phaeopus'') is a wader in the large family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across much of subarctic Asia and Europe as far south as Scotland. This species and the Hudsonian whimbrel have recently been split, although some taxonomic authorities still consider them to be conspecific. Taxonomy The Eurasian whimbrel was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Scolopax phaeopus''. It is now placed with the curlews in the genus '' Numenius'' that was introduced by the French ornithologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson in 1760. The genus name ''Numenius'' is from Ancient Greek ''noumenios'', a bird mentioned by Hesychius. It is associated with the curlews because it appears to be derived from ''neos'', "new" and ''mene'' "moon", referring to the crescent-shaped bill. The specific epithet ''phaeopus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of prey, birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. These birds are dark brown, with lighter golden-brown plumage on their napes. Immature eagles of this species typically have white on the tail and often have white markings on the wings. Golden eagles use their agility and speed combined with powerful feet and large, sharp talons to hunt a variety of prey, mainly hares, rabbits, and marmots and other ground squirrels. Golden eagles maintain home ranges or territories that may be as large as . They build large bird nest, nests in cliffs and other high places to which they may return for several breeding years. Most breeding activities take place in the spring; they are monogamous and may remain together for several years or possibly for life. Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
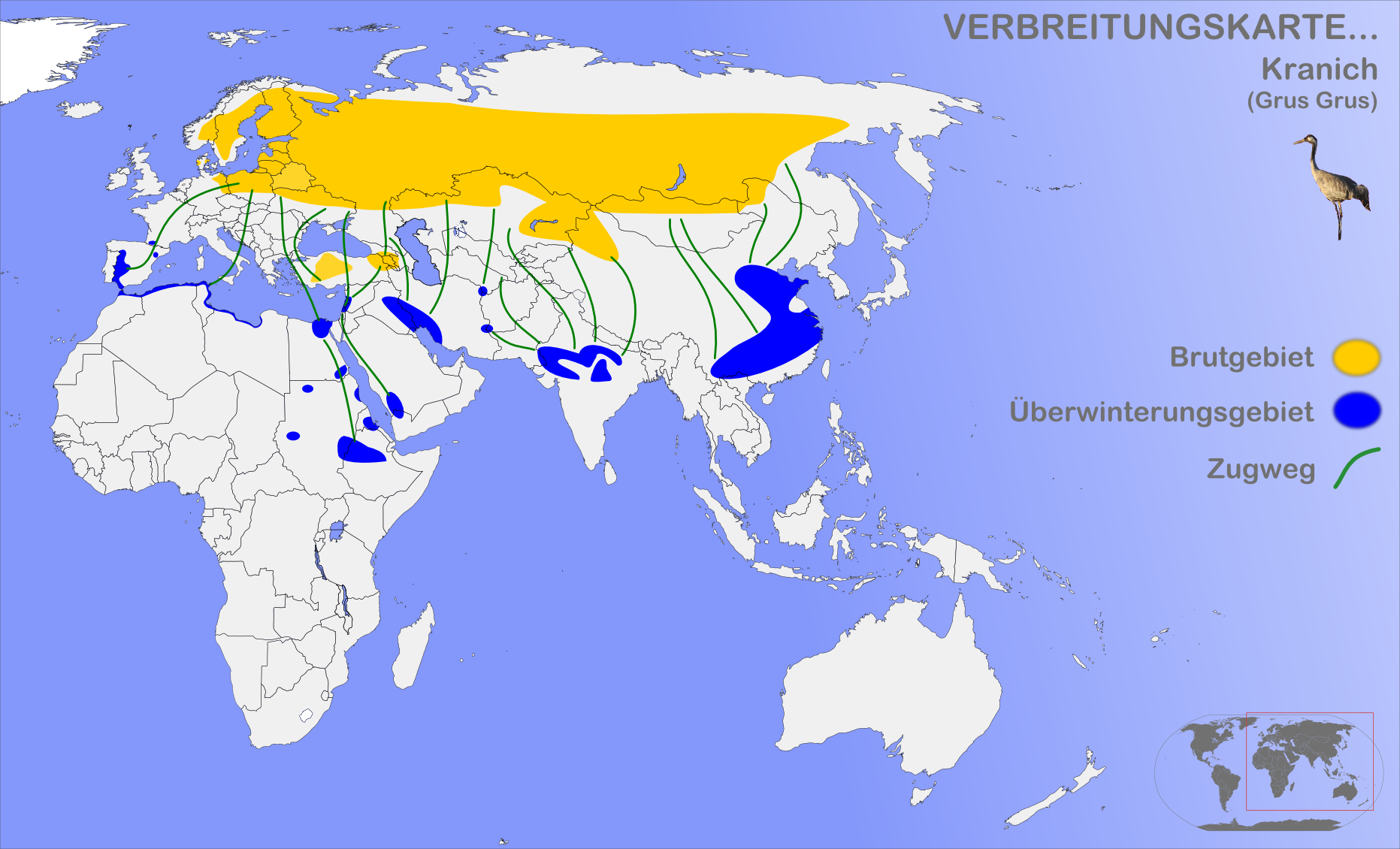
Common Crane
The common crane (''Grus grus''), also known as the Eurasian crane, is a bird of the family Gruidae, the cranes. A medium-sized species, it is the only crane commonly found in Europe besides the demoiselle crane (''Grus virgo'') and the Siberian crane (''Leucogeranus leucogeranus''). Along with the sandhill (''Antigone canadensis'') and demoiselle cranes and the brolga (''Antigone rubicunda''), it is one of only four crane species not currently classified as threatened with extinction or conservation dependent on the species level. Despite the species' large numbers, local extinctions and extirpations have taken place in part of its range, and an ongoing reintroduction project is underway in the United Kingdom. Taxonomy The first formal description of the common crane was by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Ardea grus''. The current genus ''Grus'' was erected by the French zoologist Mathuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bewick's Swan
The tundra swan (''Cygnus columbianus'') is a small swan of the Holarctic. The two taxa within it are usually regarded as conspecific, but are also sometimes split into two species: Bewick's swan (''Cygnus bewickii'') of the Palaearctic and the whistling swan (''C. columbianus'') proper of the Nearctic. Birds from eastern Russia (roughly east of the Taymyr Peninsula) are sometimes separated as the subspecies ''C. c. jankowskii'', but this is not widely accepted as distinct, with most authors including them in ''C. c. bewickii''. Tundra swans are sometimes separated in the subgenus ''Olor'' together with the other Arctic swan species. Bewick's swan was named in 1830 by William Yarrell after the engraver Thomas Bewick, who specialised in illustrations of birds and animals. ''Cygnus'' is the Latin for "swan", and '' columbianus'' comes from the Columbia River, the type locality. Description ''C. columbianus'' is the smallest of the Holarctic swans, at in length, in wingspan and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carr (landform)
A carr is a type of waterlogged wooded terrain that, typically, represents a succession stage between the original reedy marsh and the likely eventual formation of forest in a sub-maritime climate.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984. . Carrs are wetlands that are dominated by shrubs rather than trees. The carr is one stage in a hydrosere: the progression of vegetation beginning from a terrain submerged by fresh water along a river or lake margin. In sub-maritime regions, it begins with reed-marsh. As the reeds decay, the soil surface eventually rises above the water, creating fens that allow vegetation such as sedge to grow. As this progression continues, riparian trees and bushes appear and a carr landscape is created – in effect a wooded fen in a waterlogged terrain. At this stage, overall, unlike the overwhelming acidity of decaying reeds, the pH is not too acidic and the soil is not too deficient in minerals, making a habitat fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedum Telephium
''Hylotelephium telephium'' ( synonym ''Sedum telephium''), known as orpine, livelong, frog's-stomach, harping Johnny, life-everlasting, live-forever, midsummer-men, Orphan John and witch's moneybags, is a succulent perennial groundcover of the family Crassulaceae native to Eurasia. The flowers are held in dense heads and can be reddish or yellowish-white. A number of cultivars, often with purplish leaves, are grown in gardens as well as hybrids between this species and the related '' Hylotelephium spectabile'' (iceplant), especially the popular 'Herbstfreude' ('Autumn Joy'). Occasionally garden plants may escape and naturalise as has happened in parts of North America. Taxonomy The plant was known to botanists, including Dioscorides (, 40 AD – 90 AD) in his De Materia Medica ( grc-gre, Περὶ ὕλης ἰατρικῆς) as Telephion ( grc-gre, Τηλεφιον). Pliny, Gerard and Parkinson were among many later authors to describe ''Telephium''. It was first formall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris Sibirica
''Iris sibirica'' ( commonly known as Siberian iris or Siberian flag), is a species in the genus ''Iris''. It is a rhizomatous herbaceous perennial, from Europe (including France, Italy, Switzerland, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Bulgaria, Former Yugoslavia, Belarus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Ukraine and northern Turkey) and Central Asia (including Armenia, Azerbaijan and Siberia). It has long green grass-like leaves, tall stem, 2–5 violet-blue, to blue, and occasionally white flowers. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions. Description ''Iris sibirica'' was often confused with ''Iris sanguinea'', another blue flowering Asian iris, but ''Iris sanguinea'' has unbranched stems, while ''Iris sibirica'' has branched stems. It has creeping rhizome (approximately diameter), forming a dense clumping plant.Richard Lynch The rhizomes are covered with the brown remnants of old leaves, from previous seasons. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_Ystad-2020.jpg)