|
Socionics
Socionics, in psychology and sociology, is a pseudoscientific theory of information processing and personality types. It incorporates Carl Jung's work on '' Psychological Types'' with Antoni Kępiński's theory of information metabolism. Socionics is modification of Jung's personality type theory that uses eight psychic functions instead of four. These cognitive functions are supposed to process information at varying levels of competency and interact with the corresponding function in other individuals, giving rise to predictable reactions and impressions—a theory of intertype relations. In contrast to the generally accepted views in personality psychology on age-related variability of the human psyche, socionics distinguishes 16 рsychophysiological types or types of informational metabolism unchanged throughout life. The issue of the existence of personality types is considered by modern personality psychology to be extremely controversial. However, the immutability of socion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociotype
Socionics, in psychology and sociology, is a pseudoscientific theory of information processing and personality types. It incorporates Carl Jung's work on ''Psychological Types'' with Antoni Kępiński's theory of information metabolism. Socionics is modification of Jung's personality type theory that uses eight psychic functions instead of four. These cognitive functions are supposed to process information at varying levels of competency and interact with the corresponding function in other individuals, giving rise to predictable reactions and impressions—a theory of intertype relations. In contrast to the generally accepted views in personality psychology on age-related variability of the human psyche, socionics distinguishes 16 рsychophysiological types or types of informational metabolism unchanged throughout life. The issue of the existence of personality types is considered by modern personality psychology to be extremely controversial. However, the immutability of socioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aušra Augustinavičiūtė
Aušra Augustinavičiūtė (April 4, 1927 – August 19, 2005) was a Lithuanian economist, and dean of the Vilnius Pedagogical University's department of family science. Founder of socionics, the theory of information processing and personality types. Augustinavičiūtė was born not far from the city of Kaunas, in Lithuania. In 1956 she graduated from the economic faculty of Vilnius University as a financier. She worked at the Ministry of Finance of Lithuania and later as a teacher of political economics and sociology in different educational institutions in Vilnius. Her works on socionics, with the exception of few, were not published during the period of Soviet power, but became more and more popular during the 1990s. The current structure of her theory was standardized by Alexander Bukalov, Victor Gulenko, and Gregory Reinin after the founding of the International Institute of Socionics in Kyiv Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoni Kępiński
Antoni Ignacy Tadeusz Kępiński (16 November 1918 – 8 June 1972) was a Polish psychiatrist and philosopher. He is known as the originator of concepts of information metabolism (IM) and axiological psychiatry. Biography Kępiński was born in Dolina, which at that time was part of Poland (now southwestern Ukraine). During the childhood years, he resided in Nowy Sącz where his father held the position of starosta. He attended the high-ranking Bartłomiej Nowodworski High School in Kraków. In 1936, Kępiński entered the Medical Faculty of the Jagiellonian University. In 1939, he interrupted his studies before graduation and volunteered for the Polish Army to defend his country from the German invasion. After the successful invasion of Poland by Germany, Kępiński was captured and imprisoned in Hungary, to where he had fled. In 1940, he managed to escape imprisonment and headed to France, then Spain, where he was imprisoned in Miranda del Ebro. Later he was freed and moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personality Type
In psychology, personality type refers to the psychological classification of different types of individuals. Personality types are sometimes distinguished from personality traits, with the latter embodying a smaller grouping of behavioral tendencies. Types are sometimes said to involve ''qualitative'' differences between people, whereas traits might be construed as ''quantitative'' differences. According to type theories, for example, introverts and extraverts are two fundamentally different categories of people. According to trait theories, introversion and extraversion are part of a continuous dimension, with many people in the middle. In contrast to personality traits, the existence of personality types remains extremely controversial. Clinically effective personality typologies Effective personality typologies reveal and increase knowledge and understanding of individuals, as opposed to diminishing knowledge and understanding as occurs in the case of stereotyping. Effective ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
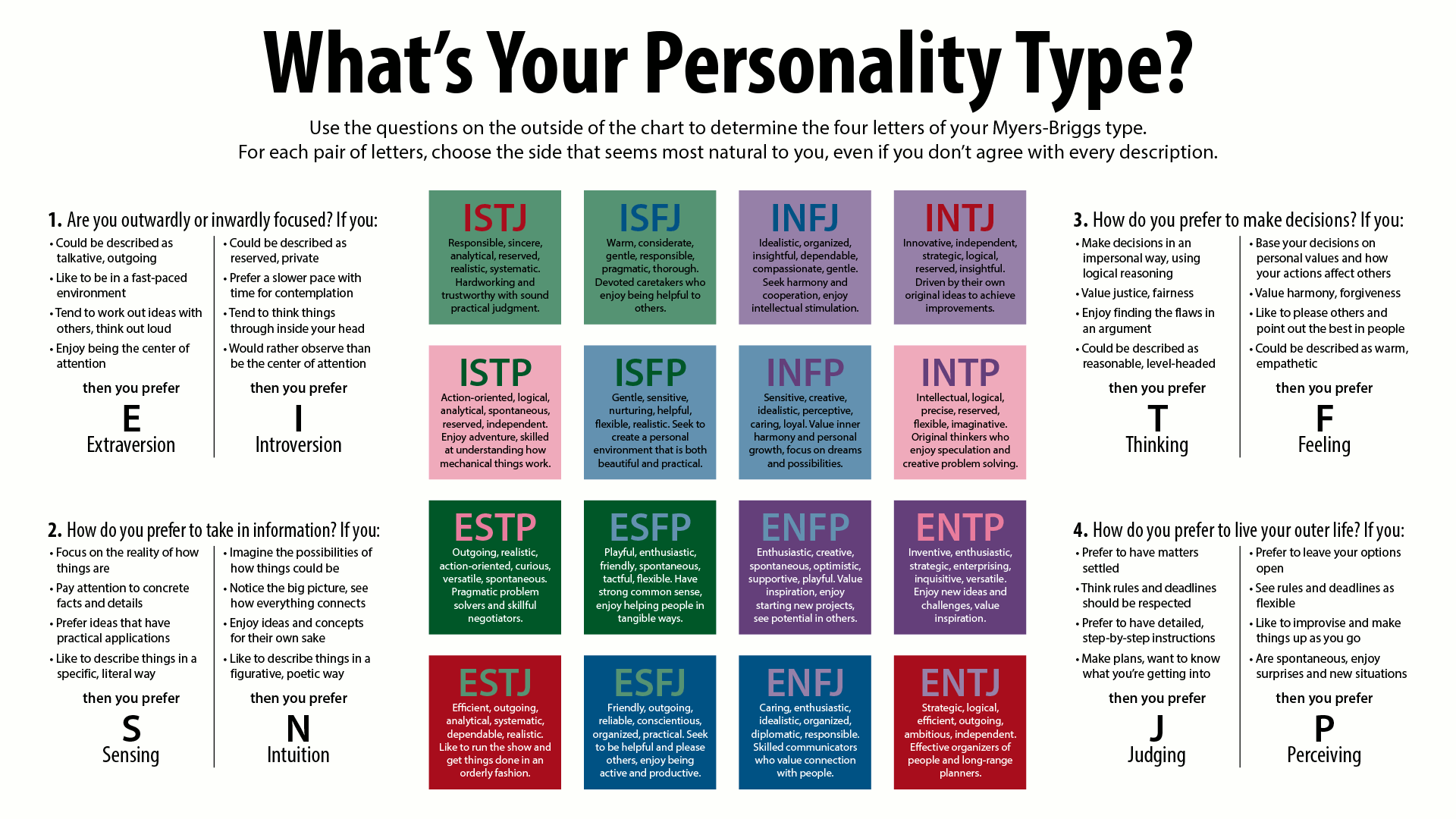
Myers–Briggs Type Indicator
In Personality type, personality typology, the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an introspection, introspective self-report study, self-report questionnaire indicating differing Psychology, psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. The test attempts to assign a value to each of four categories: introversion or extraversion, sensing or intuition, thinking or feeling, and judging or perceiving. One letter from each category is taken to produce a four-letter test result, such as "INTP" or "ESFJ". The MBTI was constructed by two Americans: Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, who were inspired by the book ''Psychological Types'' by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung. Isabel Myers was particularly fascinated by the concept of introversion and she typed herself as an INFP. However, she felt the book was too complex for the general public, and therefore she tried to organize the Jungian cognitive functions to make it more acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociometry
Sociometry is a quantitative method for measuring social relationships. It was developed by psychotherapist Jacob L. Moreno and Helen Hall Jennings in their studies of the relationship between social structures and psychological well-being, and used during Remedial Teaching. Definition The term sociometry relates to its Latin etymology, ''socius'' meaning companion, and ''metrum'' meaning measure. Jacob Moreno defined sociometry as "the inquiry into the evolution and organization of groups and the position of individuals within them." He goes on to write "As the ...science of group organization, it attacks the problem not from the outer structure of the group, the group surface, but from the inner structure". "Sociometric explorations reveal the hidden structures that give a group its form: the alliances, the subgroups, the hidden beliefs, the forbidden agendas, the ideological agreements, the "stars" of the show." Moreno developed sociometry as one of the newly developing soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Metabolism
Information metabolism, sometimes referred to as informational metabolism or energetic-informational metabolism, is a psychological theory of interaction between biological organisms and their environment, developed by Polish psychiatrist Antoni Kępiński. Overview Kępiński described his psychological theory in several books but the most detailed description is given in his 1974 book ''Melancholy'' (in Polish: "Melancholia"). In order to explain psychological phenomena encountered in humans, he borrowed many concepts from the field of cybernetics which gained popularity in Poland at that time, thanks to the works of Marian Mazur (the father of the Polish school of cybernetics). Kępiński starts with the consideration of most basic organisms and how they are different from inanimate matter. First of all, any organism may be treated as an autonomous but open system, separated from its environment by means of a boundary (skin or cell membrane). As an open system, it is en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. Jung worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital, in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. During this time, he came to the attention of Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis. The two men conducted a lengthy correspondence and collaborated, for a while, on a joint vision of human psychology. Freud saw the younger Jung as the heir he had been seeking to take forward his "new science" of psychoanalysis and to this end secured his appointment as president of his newly founded International Psychoanalytical Association. Jung's research and personal vision, however, made it difficult for him to follow his older colleague's doctrine and they parted ways. This division was person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |