|
Slowly Changing Dimension
A slowly changing dimension (SCD) in data management and data warehousing is a dimension which contains relatively static data which can change slowly but unpredictably, rather than according to a regular schedule. Some examples of typical slowly changing dimensions are entities as names of geographical locations, customers, or products. Some scenarios can cause referential integrity problems. For example, a database may contain a fact table that stores sales records. This fact table would be linked to dimensions by means of foreign keys. One of these dimensions may contain data about the company's salespeople: e.g., the regional offices in which they work. However, the salespeople are sometimes transferred from one regional office to another. For historical sales reporting purposes it may be necessary to keep a record of the fact that a particular sales person had been assigned to a particular regional office at an earlier date, whereas that sales person is now assigned to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource. Concept The concept of data management arose in the 1980s as technology moved from sequential processing (first punched cards, then magnetic tape) to random access storage. Since it was now possible to store a discrete fact and quickly access it using random access disk technology, those suggesting that data management was more important than business process management used arguments such as "a customer's home address is stored in 75 (or some other large number) places in our computer systems." However, during this period, random access processing was not competitively fast, so those suggesting "process management" was more important than "data management" used batch processing time as their primary argument. As application software evolved into real-time, interactive usage, it became obvious that both management processes were important. If the data was not well defined, the data wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Data
Master data represents "data about the business entities that provide context for business transactions". The most commonly found categories of master data are parties (individuals and organisations, and their roles, such as customers, suppliers, employees), products, financial structures (such as ledgers and cost centers) and locational concepts. Master data should be distinguished from reference data. While both provide context for business transactions, reference data is concerned with classification and categorisation, while master data is concerned with business entities. Master data is, by its nature, almost always non-transactional in nature. There exist edge cases where an organization may need to treat certain transactional processes and operations as "master data". This arises, for example, where information about master data entities, such as customers or products, is only contained within transactional data such as orders and receipts and is not housed separately. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multitenancy
Software multitenancy is a software architecture in which a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple tenants. Systems designed in such manner are "shared" (rather than "dedicated" or "isolated"). A tenant is a group of users who share a common access with specific privileges to the software instance. With a multitenant architecture, a software application is designed to provide every tenant a dedicated share of the instance - including its data, configuration, user management, tenant individual functionality and non-functional properties. Multitenancy contrasts with multi-instance architectures, where separate software instances operate on behalf of different tenants. Some commentators regard multitenancy as an important feature of cloud computing. Adoption History of multitenant applications Multitenant applications have evolved from—and combine some characteristics of—three types of services: # Timesharing: From the 1960s companies rented spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entity–attribute–value Model
Entity–attribute–value model (EAV) is a data model to encode, in a space-efficient manner, entities where the number of attributes (properties, parameters) that can be used to describe them is potentially vast, but the number that will actually apply to a given entity is relatively modest. Such entities correspond to the mathematical notion of a sparse matrix. EAV is also known as object–attribute–value model, vertical database model, and open schema. Data structure This data representation is analogous to space-efficient methods of storing a sparse matrix, where only non-empty values are stored. In an EAV data model, each attribute–value pair is a fact describing an entity, and a row in an EAV table stores a single fact. EAV tables are often described as "long and skinny": "long" refers to the number of rows, "skinny" to the few columns. Data is recorded as three columns: * The ''entity'': the item being described. * The ''attribute'' or ''parameter'': typically implem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log Trigger
In relational databases, the log trigger or history trigger is a mechanism for automatic recording of information about changes inserting or/and updating or/and deleting rows in a database table. It is a particular technique for change data capturing, and in data warehousing for dealing with slowly changing dimensions. Definition Suppose there is a table which we want to audit. This table contains the following columns: Column1, Column2, ..., Columnn The column Column1 is assumed to be the primary key. These columns are defined to have the following types: Type1, Type2, ..., Typen The Log Trigger works writing the changes (INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE operations) on the table in another, history table, defined as following: CREATE TABLE HistoryTable ( Column1 Type1, Column2 Type2, : : Columnn Typen, StartDate DATETIME, EndDate DATETIME ) As shown above, this new table contains the same columns as the original table, and additionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Change Data Capture
In databases, change data capture (CDC) is a set of software design patterns used to determine and track the data that has changed so that action can be taken using the changed data. CDC is an approach to data integration that is based on the identification, capture and delivery of the changes made to enterprise data sources. CDC occurs often in data-warehouse environments since capturing and preserving the state of data across time is one of the core functions of a data warehouse, but CDC can be utilized in any database or data repository system. Methodology System developers can set up CDC mechanisms in a number of ways and in any one or a combination of system layers from application logic down to physical storage. In a simplified CDC context, one computer system has data believed to have changed from a previous point in time, and a second computer system needs to take action based on that changed data. The former is the source, the latter is the target. It is possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
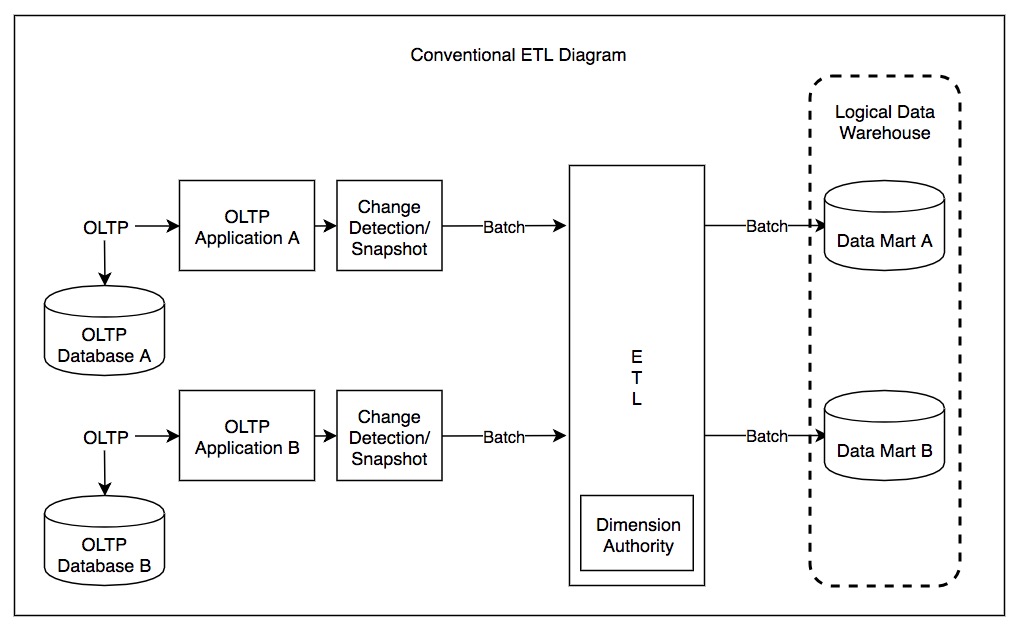
Extract, Transform, Load
In computing, extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase process where data is extracted, transformed (cleaned, sanitized, scrubbed) and loaded into an output data container. The data can be collated from one or more sources and it can also be outputted to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on reoccurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process became a popular concept in the 1970s and is often used in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of business intelligence technologies include reporting, online analytical processing, analytics, dashboard development, data mining, process mining, complex event processing, business performance management, benchmarking, text mining, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics. BI tools can handle large amounts of structured and sometimes unstructured data to help identify, develop, and otherwise create new strategic business opportunities. They aim to allow for the easy interpretation of these big data. Identifying new opportunities and implementing an effective strategy based on insights can provide businesses with a competitive market advantage and long-term stability, and help them take strategic decisions. Business intelligence can be used by enterprises to support a wide range of business decisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Database
A temporal database stores data relating to time instances. It offers temporal data types and stores information relating to past, present and future time. Temporal databases could be uni-temporal, bi-temporal or tri-temporal. More specifically the temporal aspects usually include valid time, transaction time or decision time. * Valid time is the time period during which a fact is true in the real world. * Transaction time is the time at which a fact was recorded in the database. * Decision time is the time at which the decision was made about the fact. Uni-temporal A uni-temporal database has one axis of time, either the validity range or the system time range. Bi-temporal A bi-temporal database has two axes of time: * valid time * transaction time or decision time Tri-temporal A tri-temporal database has three axes of time: * valid time * transaction time * decision time This approach introduces additional complexities. Temporal databases are in contrast to current databa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referential Integrity
Referential integrity is a property of data stating that all its references are valid. In the context of relational databases, it requires that if a value of one attribute (column) of a relation (table) references a value of another attribute (either in the same or a different relation), then the referenced value must exist. For referential integrity to hold in a relational database, any column in a base table that is declared a foreign key can only contain either null values or values from a parent table's primary key or a candidate key. In other words, when a foreign key value is used it must reference a valid, existing primary key in the parent table. For instance, deleting a record that contains a value referred to by a foreign key in another table would break referential integrity. Some relational database management systems (RDBMS) can enforce referential integrity, normally either by deleting the foreign key rows as well to maintain integrity, or by returning an error and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Kimball
Ralph Kimball (born July 18, 1944) is an author on the subject of data warehousing and business intelligence. He is one of the original architects of data warehousing and is known for long-term convictions that data warehouses must be designed to be understandable and fast. His bottom-up methodology, also known as dimensional modeling or the Kimball methodology, is one of the two main data warehousing methodologies alongside Bill Inmon. He is the principal author of the best-selling books ''The Data Warehouse Toolkit'', ''The Data Warehouse Lifecycle Toolkit'', ''The Data Warehouse ETL Toolkit'' and ''The Kimball Group Reader'', published by Wiley and Sons. Career After receiving a Ph.D. in 1973 from Stanford University in electrical engineering (specializing in man-machine systems), Ralph joined the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). At PARC Ralph was a principal designer of the Xerox Star Workstation, the first commercial product to use mice, icons and windows. Kimball the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |