|
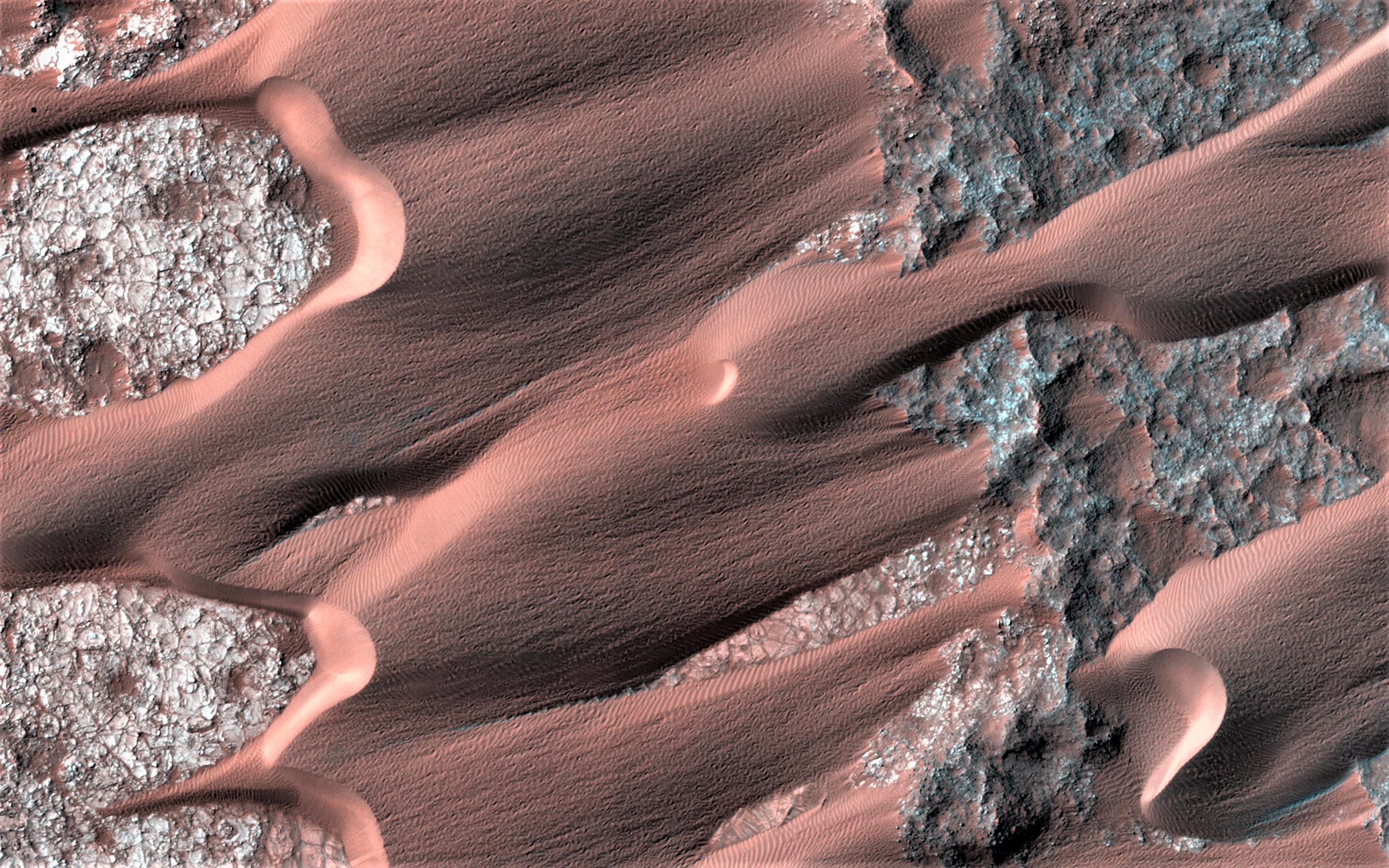
Siton Undae
Siton Undae is one of the largest and densest dune fields in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian northern polar ice-cap. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU on 20 March 2007. It extends from latitude 73.79°N to 77.5°N and from longitude 291.38°E to 301.4°E (43.98°W – 57.08°W). Its centre is located at latitude 75.55°N, longitude 297.28E (62.72°W), and has a diameter of . Siton Undae is part of a cluster of sand-seas (undae), which along with Hyperboreae, and Abalos Undae, overlay the lowlands of Vastitas Borealis. Siton Undae superposes the deepest basin of the northern region of Mars and contains amorphous silica-coated glass-rich dunes. It is theorised that the formation of Siton Undae may have occurred during early erosion incidents of the Planum Boreum cavi unit, and that Rupes Tenuis may also have been a sand source, although it is now depleted. Other dune fields sharing the same formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Of Dune Fields In The Planum Boreum Region
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogygis Undae
Ogygis Undae is the only named southern hemisphere dune field on Mars. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars, ''Ogygis Regio''. Its name, which refers to Ogyges, a primeval mythological ruler in ancient Greece, was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on September 17, 2015. It is situated just outside Argyre Planitia, a plain located in the southern highlands of Mars. The dunes of Ogygis Undae extend from latitude −49.94°N to −49.37°N and from longitude 292.64°E to 294.93°E (65.07°W – 67.36°W). They are centered at latitude −49.66°N, longitude 293.79°E (66.21°W), and extend approximately 87 km to the east and west from there. Ogygis Undae has an area of 1904 km2, and due to its large size is a primary subject for research on Martian dune morphology and sand composition. Morphology Ogygis Undae is the final sink of an extended sand transport system that was imaged with the HRSC camera onboard ESA M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
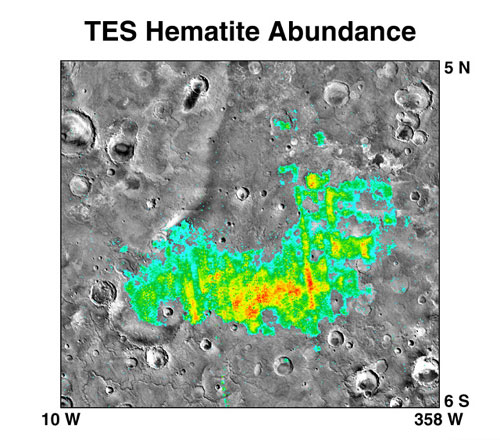
Nili Patera Dune Field
Nili Patera is a dune field on Mars. It is located on top of a lava bed, at the site of an ancient volcano, the Nili Patera caldera of Syrtis Major, near the Martian equator, and it is one of the most active dune fields of Mars. Its location coordinates on Mars are 8.7° N latitude, 67.3° E longitude. It is being actively studied by the HiRISE camera, on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, at the rate of one image every six weeks. The study of the movement of the dunes provides information regarding wind variation as a function of time and furthers the study of surface erosion characteristics of the Martian landscape. This information can then be used for the development and design of future Mars expeditions. The dunes of the Patera field are of the barchan type and their study by HiRISE was the first one to establish dune and ripple movement of a minimum of on Mars. The Patera dune field, was also the first to be investigated using the COSI-Corr software, which was origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagal Dune Field
Hagal is the informal name of a dune field on Mars located below the north pole of Mars. Its name derives from the sand dunes in Frank Herbert's novel ''Dune'' and the fictional planet Hagal. It is located at coordinates 78.0° N latitude, 84.0° E longitude, and consists of linear and round dunes with a southeast slipface orientation. It was one of the dune formations targeted for imaging by the HiRISE camera, on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, at the rate of one image every six weeks. in the third year (MY31–Mars Year 31) of its seasonal expedition. It is also known as the "Martian Morse Code" due to the linear and rounded formations of its dunes, which have the appearance of dots and dashes. Formation Although normally it is possible to obtain information about the wind direction from the orientation and form of sand dunes, the complexity of shapes of the Hagal dunes makes it difficult to determine the direction of the forming winds. In the case of the Hagal dune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Emission Imaging System
The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) is a camera on board the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. It images Mars in the visible and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order to determine the thermal properties of the surface and to refine the distribution of minerals on the surface of Mars as determined by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES). Additionally, it helps scientists to understand how the mineralogy of Mars relates to its landforms, and it can be used to search for thermal hotspots in the Martian subsurface. THEMIS is managed from the Mars Space Flight Facility at Arizona State University and was built by the Santa Barbara Remote Sensing division of Raytheon Technologies Corporation, an American multinational conglomerate headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts. The instrument is named after Themis, the goddess of justice in ancient Greek mythology. Infrared camera THEMIS detects thermal infrared energy emitted by the Martian surface at nine di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidalia Planitia
Acidalia Planitia is a plain on Mars, between the Tharsis volcanic province and Arabia Terra to the north of Valles Marineris, centered at . Most of this region is found in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle, but a small part is in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. The plain contains the famous Cydonia region at the contact with the heavily cratered highland terrain. The plain is named after a corresponding albedo feature on a map by Giovanni Schiaparelli, which was in turn named after the mythological fountain of Acidalia. Some places in Acidalia Planitia show cones, which some researchers have suggested are mud volcanoes. The scientific community is divided over whether an ancient ocean existed on the plain and other parts of the northern lowlands. Geological history There are several hypotheses regarding the geological history of Acidalia Planitia based on evidence from satellite data. Springs and steam vents Acidalia Planitia was once covered by ancient crust. Its surface e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juventae Chasma
Juventae Chasma is an enormous box canyon (250 km × 100 km) on Mars which opens to the north and forms the outflow channel Maja Valles. Juventae Chasma is located north of Valles Marineris in the Coprates quadrangle and cuts more than 5 km into the plains of Lunae Planum. Name Juventae was named by Giovanni Schiaparelli after the mythical ''Juventae Fons'', the fountain of youth. Observations The floor of Juventae Chasma is partly covered by sand dunes. There is also a 2.5 km high mountain inside Juventae, 59 km long and 23 km wide, that was confirmed by Mars Express to be composed of sulfate deposits. MRO discovered sulfates, hydrated sulfates, and iron oxides in Juventae Chasma. Juventae Chasma has four bright mounds or light-toned interior layered deposits (IlD's), as they are often called. Researchers have found that monohydrated sulfates were first deposited on the floor. And then polyhydrated sulfates were laid down. Kieserite, a magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valles Marineris
Valles Marineris (; Latin for ''Mariner program, Mariner Valleys'', named after the ''Mariner 9'' Mars orbiter of 1971–72 which discovered it) is a system of canyons that runs along the Mars, Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than long, wide and up to deep, Valles Marineris is one of the largest List of largest rifts and valleys in the Solar System, canyons of the Solar System, surpassed in length only by the rift valleys of the mid-ocean ridge system of Earth. Valles Marineris is located along the equator of Mars, on the east side of the Tharsis Bulge, and stretches for nearly a quarter of the planet's circumference. The canyon system starts in the west with Noctis Labyrinthus; proceeding to the east are Tithonium Chasma, Tithonium and Ius Chasma, Ius chasmata, then Melas Chasma, Melas, Candor Chasma, Candor and Ophir Chasma, Ophir chasmata, then Coprates Chasma, then Ganges Chasma, Ganges, Capri Chasma, Capri and Eos Chasma, Eos chasmata; finally it emptie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chryse Planitia
Chryse Planitia (Greek, "''Golden Plain''") is a smooth circular plain in the northern equatorial region of Mars close to the Tharsis region to the west, centered at . Chryse Planitia lies partially in the Lunae Palus quadrangle, partially in the Oxia Palus quadrangle, partially in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle. It is 1600 km or 994 mi in diameter and with a floor 2.5 km below the average planetary surface altitude, and has been suggested to be an ancient buried impact basin, though this is contested. It has several features in common with lunar maria, such as Wrinkle-ridge, wrinkle ridges. The density of impact craters in the range is close to half the average for lunar maria. Chryse Planitia shows evidence of water erosion in the past, and is the bottom end for many outflow channels from the southern highlands as well as from Valles Marineris and the flanks of the Tharsis bulge. It is one of the lowest regions on Mars ( below the mean surface elevation of Mars) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Glass
Volcanic glass is the amorphous (uncrystallized) product of rapidly cooling magma. Like all types of glass, it is a state of matter intermediate between the closely packed, highly ordered array of a crystal and the highly disordered array of liquid. Volcanic glass may refer to the interstitial material, or matrix, in an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock, or to any of several types of vitreous igneous rocks. Origin Volcanic glass is formed when magma is rapidly cooled. Magma rapidly cooled to below its normal crystallization temperature becomes a supercooled liquid, and, with further rapid cooling, this becomes an amorphous solid. The change from supercooled liquid to glass occurs at a temperature called the glass transition temperature, which depends on both cooling rate and the amount of water dissolved in the magma. Magma rich in silica and poor in dissolved water is most easily cooled rapidly enough to form volcanic glass. As a result, rhyolite magmas, which are high in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |