|
Signal Theory
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing System
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various separate instants in the case of discrete time. An oscilloscope is a tool commonly used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes with time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. Though most precisely referring to time in physics, the term ''time domain'' may occasionally informally refer to position in space when dealing with spatial frequencies, as a substitute for the more precise term ''spatial domain''. Origin of term The use of the contrasting terms ''time domain'' and '' frequency domain'' developed in U.S. communication engineering in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Signal
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "points in time", or equivalently as being unchanged throughout each non-zero region of time ("time period")—that is, time is viewed as a discrete variable. Thus a non-time variable jumps from one value to another as time moves from one time period to the next. This view of time corresponds to a digital clock that gives a fixed reading of 10:37 for a while, and then jumps to a new fixed reading of 10:38, etc. In this framework, each variable of interest is measured once at each time period. The number of measurements between any two time periods is finite. Measurements are typically made at sequential integer values of the variable "time". A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of quantities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Oscillator
A microwave (12–18GHz) voltage-controlled oscillator A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop. VCOs are used in synthesizers to generate a waveform whose pitch can be adjusted by a voltage determined by a musical keyboard or other input. A voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC) is a special type of VCO designed to be very linear in frequency control over a wide range of input control voltages. Types VCOs can be generally categorized into two groups based on the type of waveform produced. * ''Linear'' or ''harmonic oscillators'' generate a sinusoidal waveform. Harmonic oscillators in electronics usually consist of a reson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Filter
A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is an electronic filter whose operating characteristics (primarily cutoff frequency) can be set by an input control voltage. Voltage controlled filters are widely used in synthesizers. A music synthesizer VCF allows its cutoff frequency, and sometimes its Q factor (resonance at the cutoff frequency), to be continuously varied. The filter outputs often include a lowpass response, and sometimes highpass, bandpass or notch responses. Some musical VCFs offer a variable ''slope'' which determines the rate of attenuation outside the bandpass, often at 6 dB/octave, 12 dB/octave, 18 dB/octave or 24 dB/octave (one-, two-, three- and four-pole filters, respectively). In modular analog synthesizers, VCFs receive signal input from signal sources, including oscillators and noise, or the output of other processors. By varying the cutoff frequency, the filter passes or attenuates partials of the input signal. In some popular electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Amplifier
A variable-gain (VGA) or voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) is an electronic amplifier that varies its gain depending on a control voltage (often abbreviated CV). VCAs have many applications, including audio level compression, synthesizers and amplitude modulation. A crude example is a typical inverting op-amp configuration with a light-dependent resistor (LDR) in the feedback loop. The gain of the amplifier then depends on the light falling on the LDR, which can be provided by an LED (an optocoupler). The gain of the amplifier is then controllable by the current through the LED. This is similar to the circuits used in optical audio compressors. A voltage-controlled amplifier can be realised by first creating a voltage-controlled resistor (VCR), which is used to set the amplifier gain. The VCR is one of the numerous interesting circuit elements that can be produced by using a JFET (junction field-effect transistor) with simple biasing. VCRs manufactured in this way can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
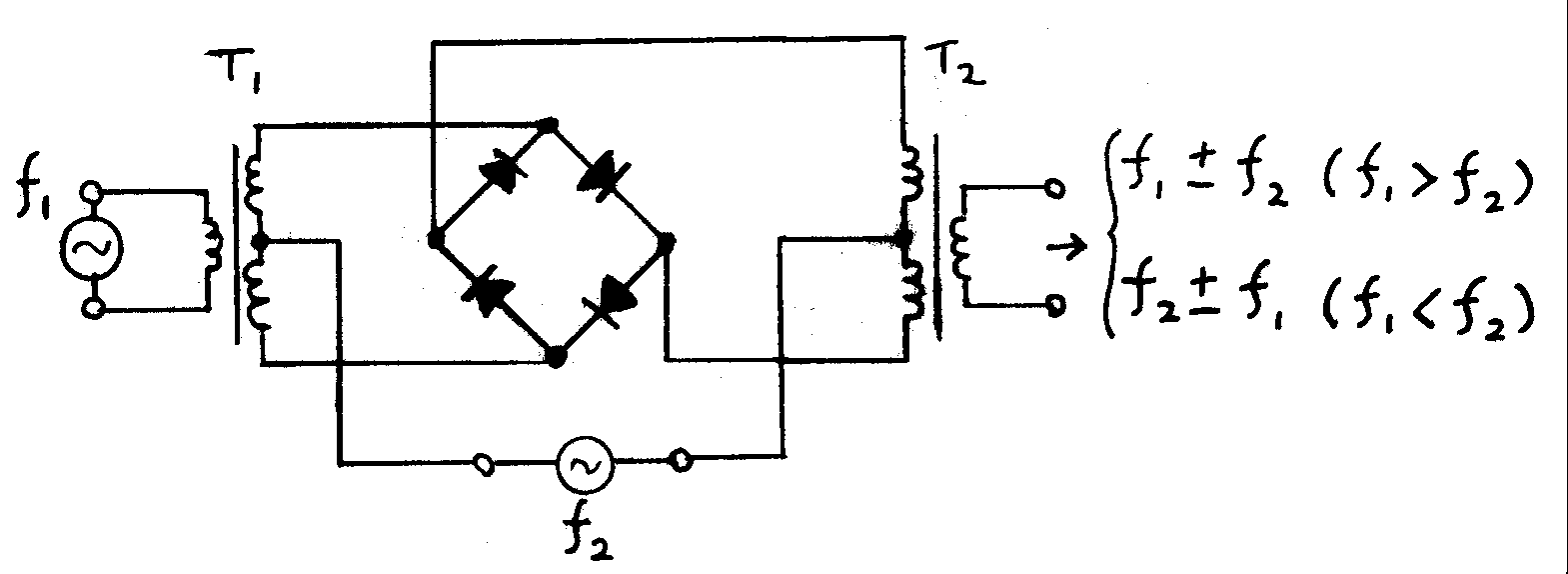
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulate a carrier signal in radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use one or more diodes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compandor
In telecommunication and signal processing, companding (occasionally called compansion) is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range. The name is a portmanteau of the words compressing and expanding, which are the functions of a compander at the transmitting and receiving end respectively. The use of companding allows signals with a large dynamic range to be transmitted over facilities that have a smaller dynamic range capability. Companding is employed in telephony and other audio applications such as professional wireless microphones and analog recording. How it works The dynamic range of a signal is compressed before transmission and is expanded to the original value at the receiver. The electronic circuit that does this is called a compander and works by compressing or expanding the dynamic range of an analog electronic signal such as sound recorded by a microphone. One variety is a triplet of amplifiers: a logarithmic amplifier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Delay Line
An analog delay line is a network of electrical components connected in cascade, where each individual element creates a time difference between its input and output. It operates on analog signals whose amplitude varies continuously. In the case of a periodic signal, the time difference can be described in terms of a change in the phase of the signal. One example of an analog delay line is a bucket-brigade device. Other types of delay line include acoustic (usually ultrasonic), magnetostrictive, and surface acoustic wave devices. A series of resistor–capacitor circuits (RC circuits) can be cascaded to form a delay. A long transmission line can also provide a delay element. The delay time of an analog delay line may be only a few nanoseconds or several milliseconds, limited by the practical size of the physical medium used to delay the signal and the propagation speed of impulses in the medium. Analog delay lines are applied in many types of signal processing circuits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output. Integration is an important part of many engineering and scientific applications. Mechanical integrators are the oldest application, and are still used in such as metering of water flow or electric power. Electronic analogue integrators are the basis of analog computer An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. ...s and charge amplifiers. Integration is also performed by digital computing algorithms. In signal processing circuits :''See also Operational amplifier applications#Integration and differentiation, Integrator at op amp applications'' An electronics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)