|
Sich Rada
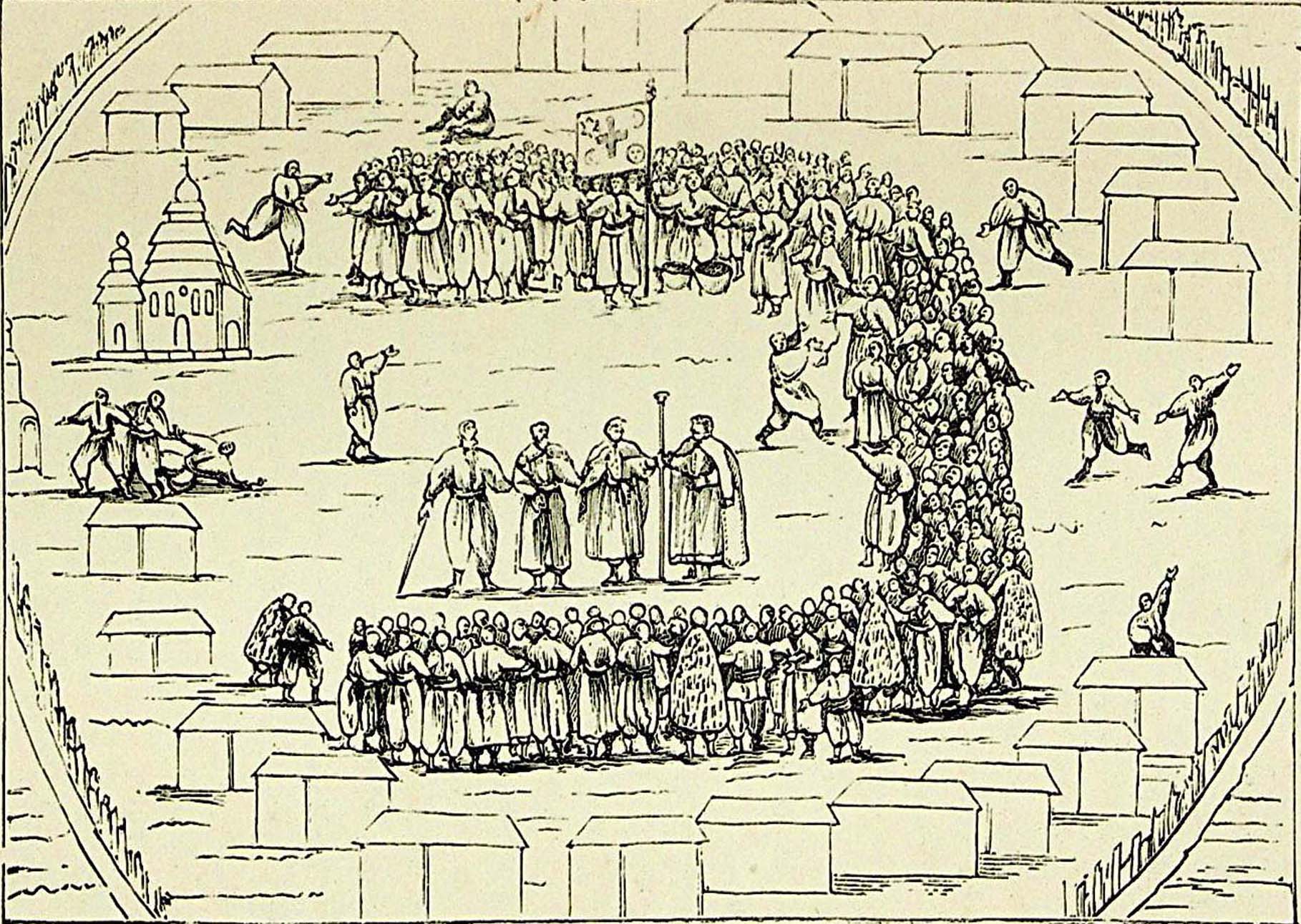
The Sich Rada (, ''Sichova Rada'') was the highest branch of government of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, and based at their center, the Zaporizhian Sich. It was also called Viyskova Rada (Military Council). The Rada, a type of governing committee but with participation from the cossack members, was involved in legislative, executive and judicial matters.Magocsi, P. (1996) ''A history of Ukraine'', University of Toronto Press , Functions As an institution, the Sich Rada was a form of direct democracy where rights of individual[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Sich Rada
Zaporizhzhia or Zaporizhia is a city in Ukraine. Zaporizhzhia, Zaporozhzhia, or Zaporozhye may also refer to: Places in Ukraine * Zaporizhzhia (region), a historical region in central east Ukraine below the Dnieper river rapids * Zaporizhzhia Governorate, (1920–22) Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union * Zaporizhzhia Oblast (1939–), a first-level administrative unit in Ukraine ** Zaporizhzhia Raion, an administrative unit of Zaporizhzhia Oblast ** Nove Zaporizhzhia, Zaporizhzhia Raion, a village in Zaporizhzhia Raion ** Zaporizhzhia, city and administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast and Zaporizhzhia Raion Facilities and structures * Zaporizhzhia International Airport, Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine * Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, Enerhodar, Ukraine * Zaporizhzhia thermal power station Zaporizhzhia thermal power station is a large non-nuclear thermal power plant ( DRES) in the purpose-built city of Enerhodar in Ukraine that was built by the Soviet Union between 1971 and 1977. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporozhtsi, translit-std=ungegn) were Cossacks who lived beyond (that is, downstream from) the Dnieper Rapids, the land also known historically as the Wild Fields in what is today central and eastern Ukraine. Much of this territory is now flooded by the waters of the Kakhovka Reservoir. The Zaporozhian Sich grew rapidly in the 15th century from serfs fleeing the more controlled parts of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It became established as a well-respected political entity with a parliamentary system of government. During the course of the 16th, 17th and well into the 18th century, the Zaporozhian Cossacks were a strong political and military force that challenged the authority of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Tsardom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaporizhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich ( ua, Запорозька Січ, ; also uk, Вольностi Вiйська Запорозького Низового, ; Free lands of the Zaporozhian Host the Lower) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of Cossacks that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, including as an independent stratocratic state within the Cossack Hetmanate for over a hundred years, centred around the region now home to the Kakhovka Reservoir and spanning the lower Dnieper river in Ukraine. In different periods the area came under the sovereignty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, the Tsardom of Russia, and the Russian Empire. In 1775, shortly after Russia annexed the territories ceded to it by the Ottoman Empire under the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (1774), Catherine the Great disbanded the Sich. She incorporated its territory into the Russian province of Novorossiya. The term ''Zaporozhian Sich'' can also refer metonymically and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rada
The Royal Academy of Dramatic Art (RADA; ) is a drama school in London, England, that provides vocational conservatoire training for theatre, film, television, and radio. It is based in the Bloomsbury area of Central London, close to the Senate House complex of the University of London and is a founding member of the Federation of Drama Schools. It is one of the oldest drama schools in the United Kingdom, founded in 1904 by Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree. It moved to buildings on Gower Street in 1905. It was granted a Royal Charter in 1920 and a new theatre was built on Malet Street, behind the Gower Street buildings that was opened by Edward, Prince of Wales, in 1921. It received its first government subsidy in 1924. RADA currently has five theatres and a cinema. The school’s Principal Industry Partner is Warner Bros. Entertainment. RADA offers a number of foundation, undergraduate and postgraduate courses. Its higher education awards are validated by King's College Londo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more fully than would be possible if the assembly itself were considering them. Committees may have different functions and their types of work differ depending on the type of the organization and its needs. A member of a legislature may be delegated a committee assignment, which gives them the right to serve on a certain committee. Purpose A deliberative assembly may form a committee (or "commission") consisting of one or more persons to assist with the work of the assembly. For larger organizations, much work is done in committees. Committees can be a way to formally draw together people of relevant expertise from different parts of an organization who otherwise would not have a good way to share information and coordinate actions. They may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy, participant democracy or participative democracy is a form of government in which citizens participate individually and directly in political decisions and policies that affect their lives, rather than through elected representatives. Elements of direct and representative democracy are combined in this model. Overview Participatory democracy is a type of democracy, which is itself a form of government. The term "democracy" is derived from the Greek expression (dēmokratia) ''(δῆμος/ dēmos'': people, ''Κράτος/ kratos'': rule). It has two main subtypes, direct and representative democracy. In the former, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation; in the latter, they choose governing officials to do so. While direct democracy was the original concept, its representative version is the most widespread today. Public participation, in this context, is the inclusion of the public in the activities of a polity. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate decides on policy initiatives without elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently established democracies, which are representative democracies. The theory and practice of direct democracy and participation as its common characteristic was the core of work of many theorists, philosophers, politicians, and social critics, among whom the most important are Jean Jacques Rousseau, John Stuart Mill, and G.D.H. Cole. Overview In direct democracy, the people decide on policies without any intermediary or representative, whereas in a representative democracy people vote for representatives who then enact policy initiatives. Depending on the particular system in use, direct democracy might entail passing executive decisions, the use of sortition, making laws, directly electing or dismissing officials, and conducting trials. Two leading forms of direct democracy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starshina
( rus, старшина, p=stərʂɨˈna, a=Ru-старшина.ogg or in Ukrainian transliteration) is a senior non-commissioned rank or designation in the military forces of some Slavic states, and a historical military designation. In army terminology, a starshina is equivalent to "Sergeant Major" (Most senior member at the company level) or a rank equal to a NATO OR-8. In naval terminology, ''starshina'' is a general term for junior and middle-ranking non-commissioned officers, similar in usage to "Chief Petty Officer". The word originates from the russian: старший, starshij, older, more senior, from russian: старый, staryj, old. Cossack Hetmanate Among Cossacks in Ukraine, ''starshyna'' was a collective noun for categories of military officers and state officials. It derived from the offices in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Sharshyna was subdivided into: *General Starshyna (), headed by Hetman (or Quartermaster General as acting Hetman) **Quartermast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosh Otaman
Kish otaman ( uk, Кошовий отаман, ; russian: Кошевой атаман, ; pl, Ataman koszowy; also known as of the Zaporizhian Host) was a chief officer of the ''Kish'' (central body of government) of the Zaporozhian Host in the 16th through 18th centuries. Overview The otaman was elected by a council of elder officers (the ) of the Zaporozhian Host. The position contained the highest military, administrative and judicial powers. Until the establishment of the Cossack Hetmanate, the title was interchangeably used with Hetman. During military campaigns, powers of an otaman were virtually unrestricted, but in peacetime he addressed the most important military and political issues to the and other military councils. A Kish otaman was elected for a term of one year and in exceptional cases was reelected. Upon expiration of his term amounted to report on his activities to a military council. The Kish otaman that was not re-elected, returned to his assigned .'' The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or international organizations. The main functions of diplomats are: representation and protection of the interests and nationals of the sending state; initiation and facilitation of strategic agreements; treaties and conventions; promotion of information; trade and commerce; technology; and friendly relations. Seasoned diplomats of international repute are used in international organizations (for example, the United Nations, the world's largest diplomatic forum) as well as multinational companies for their experience in management and negotiating skills. Diplomats are members of foreign services and diplomatic corps of various nations of the world. The sending state is required to get the consent of the receiving state for a person proposed to serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomacy
Diplomacy comprises spoken or written communication by representatives of states (such as leaders and diplomats) intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 Diplomacy is the main instrument of foreign policy which represents the broader goals and strategies that guide a state's interactions with the rest of the world. International treaties, agreements, alliances, and other manifestations of international relations are usually the result of diplomatic negotiations and processes. Diplomats may also help to shape a state by advising government officials. Modern diplomatic methods, practices, and principles originated largely from 17th-century European custom. Beginning in the early 20th century, diplomacy became professionalized; the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, ratified by most of the world's sovereign states, provides a framework for diplomatic procedures, methods, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |