Zaporizhian Sich on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Zaporozhian Sich ( ua, Запорозька Січ, ; also uk, Вольностi Вiйська Запорозького Низового, ; Free lands of the Zaporozhian Host the Lower) was a semi-autonomous polity and
 The Zaporozhian Sich emerged as a method of defence by Slavic colonists against the frequent and devastating raids of
The Zaporozhian Sich emerged as a method of defence by Slavic colonists against the frequent and devastating raids of

 The
The
 In May 1775, Russian General
In May 1775, Russian General
 The Zaporozhian Host was led by the
The Zaporozhian Host was led by the
Zaporozhian Sich
– Encyclopedia of Ukraine {{authority control Early Modern history of Ukraine History of the Cossacks in Ukraine States and territories established in 1552 States and territories disestablished in 1775 Zaporozhian Cossacks Zaporozhian Host
proto-state
A quasi-state (some times referred to as state-like entity or proto-state) is a political entity that does not represent a fully institutionalised or autonomous sovereign state.
The precise definition of ''quasi-state'' in political literature f ...
of Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
that existed between the 16th to 18th centuries, including as an independent stratocratic state within the Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis) ...
for over a hundred years, centred around the region now home to the Kakhovka Reservoir
The Kakhovka Reservoir (, ''Kakhovs′ke vodoskhovyshche'') is a water reservoir on the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It was created in 1956, when the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Power Plant was built. It is one of several reservoirs in the Dnieper reservo ...
and spanning the lower Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
river in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. In different periods the area came under the sovereignty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I i ...
, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
In 1775, shortly after Russia annexed the territories ceded to it by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
under the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayna ...
(1774), Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
disbanded the Sich. She incorporated its territory into the Russian province of Novorossiya
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
.
The term ''Zaporozhian Sich'' can also refer metonymically
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name ...
and informally to the whole military-administrative organisation of the Zaporozhian Cossack host
A Cossack host ( uk, козацьке військо, translit=kozatske viisko; russian: каза́чье во́йско, ''kazachye voysko''), sometimes translated as Cossack army, was an administrative subdivision of Cossack
The Cossac ...
.
Name
The name "Zaporizhia" refers to the military and political organization of the Cossacks and to the location of their autonomous territory 'beyond the Rapids' (') of theDnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
. The Dnieper Rapids
The Dnieper Rapids ( uk, Дніпрові пороги, ) are the historical rapids on the Dnieper river in Ukraine, composed of outcrops of granites, gneisses and other types of bedrock of the Ukrainian Shield. The rapids began below the present ...
were a major portage on the north-south Dnieper trade route. The term ''sich
A sich ( uk, січ), or sech, was an administrative and military centre of the Zaporozhian Cossacks. The word ''sich'' derives from the Ukrainian verb сікти ''siktý'', "to chop" – with the implication of clearing a forest for an encampme ...
'' is a noun related to the Eastern Slavic verb ''sich ( сѣчь), meaning "to chop" or "cut"; it may have been associated with the usual wood sharp-spiked stockades around Cossack settlements.
Zaporizhia was located in the region around Kakhovka Reservoir
The Kakhovka Reservoir (, ''Kakhovs′ke vodoskhovyshche'') is a water reservoir on the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It was created in 1956, when the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Power Plant was built. It is one of several reservoirs in the Dnieper reservo ...
in today's south-eastern Ukraine (much of its territory is now flooded by the reservoir). The area was also known under the historical term, Wild Fields
The Wild Fields ( uk, Дике Поле, translit=Dyke Pole, russian: Дикое Поле, translit=Dikoye Polye, pl, Dzikie pola, lt, Dykra, la, Loca deserta or , also translated as "the wilderness") is a historical term used in the Polish ...
.
History
A possible precursor of the Zaporozhian Sich was a fortification (''sich
A sich ( uk, січ), or sech, was an administrative and military centre of the Zaporozhian Cossacks. The word ''sich'' derives from the Ukrainian verb сікти ''siktý'', "to chop" – with the implication of clearing a forest for an encampme ...
'') built on the Tomakivka
Tomakivka ( uk, Томаківка, russian: Томаковка) is an urban-type settlement in Nikopol Raion, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast (province) of southeastern Ukraine. It is located on confluence of Tomakivka and Kyslichuvata rivers. Tomakivka h ...
island () in the middle of the Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
in the present-day Zaporizhzhia region of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. However there is no direct evidence about the exact time of the existence of Tomakivska Sich, whereas indirect data suggest that at the time of Tomakivska Sich there was no Zaporozhian Sich yet.
The history of Zaporozhian Sich spans six time-periods:
* the emergence of the Sich (construction of ) (1471–1583)
* as part of the Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown
, subdivision = Province
, nation = Poland
, year_start =
, event_end = Third Partition of Poland
, year_end =
, image_map = ProwincjaMalopolska.png
, image_map ...
by inclusion in the Kiev Voivodeship
The Kiev Voivodeship ( pl, województwo kijowskie, la, Palatinatus Kioviensis, uk, Київське воєводство, ''Kyjivśke vojevodstvo'') was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
(1583–1657)
* the struggle against the Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''rés pública'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in Engli ...
(the Polish-Lithuanian state), the Ottoman Empire, and the Crimea Khanate for the independence of the Ukrainian part of the Rzeczpospolita (Commonwealth) (1657–1686)
* the struggle with Crimea, the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian Empire for the unique identity of Cossacks (1686–1709)
* the standoff with the Russian government during its attempts to cancel the self-governing of the Sich, and its fall (1734–1775)
* the formation of the Danubian Sich
The Danubian Sich ( uk, Задунайська Сiч, translit=Zadunaiska Sich) was an organization of the part of former Zaporozhian Cossacks who settled in the territory of the Ottoman Empire (the Danube Delta, hence the name) after their pre ...
outside the Russian Empire and finding ways to return home (1775–1828)
Formation
 The Zaporozhian Sich emerged as a method of defence by Slavic colonists against the frequent and devastating raids of
The Zaporozhian Sich emerged as a method of defence by Slavic colonists against the frequent and devastating raids of Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace
...
, who captured and enslaved hundreds of thousands of Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
, Belorusians and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
in operations called "the harvesting of the steppe". The Ukrainians created a self-defence force, the Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s, fierce enough to stop the Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
hordes, and built fortified camps (''sichi'') that were later united to form a central fortress, the Zaporozhian Sich.
Prince in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Dmytro Vyshnevetsky
Dmytro Ivanovych Vyshnevetsky ( uk, Дмитро Іванович Вишневе́цький; russian: Дмитрий Иванович Вишневе́цкий; pl, Dymitr Wiśniowiecki) was a magnate of Ruthenian (Ukrainian) origin and an organi ...
established the first Zaporozhian Sich on the island of Small (Mala) Khortytsia
Khortytsia ( uk, Хортиця, Hortycja, translit-std=ISO, ) is the largest island in the Dnieper river, and is long and up to wide. The island forms part of the Khortytsia National Park. This historic site is located within the city limit ...
in 1552, building a fortress at ''Niz Dnieprovsky'' (Lower Dnieper) and placing a Cossack garrison there; Tatar forces destroyed the fortress in 1558. The Tomakivka Sich was built on a now-inundated island to the south, near the modern city of Marhanets
Marhanets ( uk, Марганець, ; russian: Марганец, ; ) is a city in Nikopol Raion of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast that was established in 1938 in southern Ukraine. It was established in place of the village of Horodyshche, which contained ...
; Tatars also razed that sich, in 1593. A third sich soon followed, on Bazavluk island, which survived until 1638, when it was destroyed by a Polish expeditionary force suppressing a Cossack uprising. These settlements, founded during the 16th century, were already complex enough to constitute an early proto-state
A quasi-state (some times referred to as state-like entity or proto-state) is a political entity that does not represent a fully institutionalised or autonomous sovereign state.
The precise definition of ''quasi-state'' in political literature f ...
.
Struggle for independence

 The
The Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
became included in the Kiev Voivodeship
The Kiev Voivodeship ( pl, województwo kijowskie, la, Palatinatus Kioviensis, uk, Київське воєводство, ''Kyjivśke vojevodstvo'') was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
from 1583 to 1657, part of the Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown
, subdivision = Province
, nation = Poland
, year_start =
, event_end = Third Partition of Poland
, year_end =
, image_map = ProwincjaMalopolska.png
, image_map ...
. They resented Polish rule, however, one of the reasons being religious differences, as the cossacks were Orthodox Christians whereas the Poles were mostly Catholics. They thus engaged in a long struggle for independence from surrounding powers, the Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''rés pública'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in Engli ...
(Polish state), the Ottoman Empire, the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to ...
, and the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I i ...
and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. The Sich became the centre of Cossack life, governed by the ''Sich Rada
The Sich Rada (, ''Sichova Rada'') was the highest branch of government of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, and based at their center, the Zaporizhian Sich. It was also called Viyskova Rada (Military Council). The Rada, a type of governing committee but ...
'' alongside its Kosh Ataman (sometimes called Hetman, from German "Hauptmann").
In 1648, Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Zynovii Mykhailovych Khmelnytskyi ( Ruthenian: Ѕѣнові Богданъ Хмелнiцкiи; modern ua, Богдан Зиновій Михайлович Хмельницький; 6 August 1657) was a Ukrainian military commander and ...
captured a sich at Mykytyn Rih, near the present-day city of Nikopol. From there he began an uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that led to the establishment of the Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis) ...
(1649–1764). After the Treaty of Pereyaslav
The Pereiaslav AgreementPereyaslav Agreement
in 1654, the Zaporozhian Host was split into the Hetmanate, with its capital at Chyhyryn
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
, and the more autonomous region of Zaporozhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populatio ...
, which continued to be centred on the Sich. During this period the Sich changed location several times. The Chortomlyk Sich The Chortomlyk Sich (also Old Sich) is a Zaporozhian Sich state founded by the Cossacks led by kish otaman Fedir Lutay in the summer of 1652 on the right bank of the Chortomlyk distributary of the Dnieper near modern village of Kapulivka.
The ...
was built at the mouth of the Chortomlyk River in 1652. In 1667 the Truce of Andrusovo
The Truce of Andrusovo ( pl, Rozejm w Andruszowie, russian: Андрусовское перемирие, ''Andrusovskoye Pieriemiriye'', also sometimes known as Treaty of Andrusovo) established a thirteen-and-a-half year truce, signed in 1667 bet ...
made the Sich a condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
ruled jointly by Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
During the reign of Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
, Cossacks were used for the construction of canals and fortification lines in northern Russia. An estimated 20–30 thousands were sent each year. Hard labour led to a high mortality rate among builders, and only an estimated 40% of Cossacks returned home.
After the Battle of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava; russian: Полта́вская би́тва; uk, Полта́вська би́тва (8 July 1709) was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. A Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeate ...
in 1709, the Chortomlyk Sich (sometimes referred to as the "Old Sich" (''Stara Sich'')) was destroyed and Baturyn
Baturyn ( uk, Бату́рин, ), is a historic city in Chernihiv Oblast (province) of northern Ukraine. It is located in Nizhyn Raion (district) on the banks of the Seym River. Baturyn lost its city status in 1923 and received it back only in 2 ...
, the capital of Hetman Ivan Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (also spelled Mazeppa; uk, Іван Степанович Мазепа, pl, Jan Mazepa Kołodyński; ) was a Ukrainian military, political, and civic leader who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host in 1687–1708. ...
, was razed. Another sich was built at the mouth of the Kamianets river but was destroyed in 1711 by the Russian government. The Cossacks then fled to the Crimean Khanate to avoid persecution and founded the Oleshky Sich in 1711 (today the city of Oleshky
Oleshky ( uk, Оле́шки, Oleshky, ; russian: Алёшки) is a town in Kherson Raion, Kherson Oblast, southern Ukraine, located on the left bank of the Dnieper River with the town of Solontsi to the south. It is the oldest city of the obl ...
). In 1734, they were allowed to return to the Russian Empire. Suffering from discrimination in the Khanate, Cossacks accepted the offer to return and built another Sich in close proximity to the former Chortomlyk Sich (referred to as the "New Sich").The population in steppe region numbered around 52,000 in the year 1768.
Fear of the independence of the Sich resulted in the Russian administration abolishing the Hetmanate in 1764. The Cossack officer class was incorporated into the Imperial Russian nobility (Dvoryanstvo
The Russian nobility (russian: дворянство ''dvoryanstvo'') originated in the 14th century. In 1914 it consisted of approximately 1,900,000 members (about 1.1% of the population) in the Russian Empire.
Up until the February Revolutio ...
). The rank and file Cossacks, however, including a substantial portion of the old Zaporozhians, were reduced to peasant status. Tension rose after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayna ...
, when the need for a southern frontier ended after the annexation of the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. The colonisation of Novorossiya
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
(New Russia) with Serbian and Romanians sponsored by Russia created further conflict. After the end of the war between Russia and the Ottoman Empire for possession of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and Crimean steppes, Russia no longer needed the Zaporozhian Cossacks for protection of the border region. Russia finally destroyed the Zaporozhian Sich through military force in 1775.
Destruction and aftermath
 In May 1775, Russian General
In May 1775, Russian General Peter Tekeli
Peter Tekeli (russian: Петр Авраамович Текели, Serbian: Петар Поповић Текелија or ''Petar Popović Tekelija'',''Popović'' is often omitted. hu, Tököly-Popovics Péter) (1720–1792) was a Russian genera ...
received orders to occupy and destroy the Zaporozhian Sich from Grigory Potemkin
Prince Grigory Aleksandrovich Potemkin-Tauricheski (, also , ;, rus, Князь Григо́рий Алекса́ндрович Потёмкин-Таври́ческий, Knjaz' Grigórij Aleksándrovich Potjómkin-Tavrícheskij, ɡrʲɪˈɡ ...
, who had been formally admitted into Cossackdom a few years earlier. Potemkin was given direct orders from Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
. On 5 June 1775, Tekeli surrounded the Sich with artillery and infantry. He postponed the assault and even allowed visits while the head of the Host, Petro Kalnyshevsky
Petro Kalnyshevsky (20 June 1690? – 31 October 1803) was the last Koshovyi Otaman of the Zaporozhian Host, serving in 1762 and from 1765 to 1775. Kalnyshevsky was a hero in the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 for which he was awarded the Gold ...
, was deciding how to react to the Russian ultimatum. The Zaporozhians decided to surrender. The Sich was officially disbanded by the 3 August 1775 manifesto of Catherine, "On the Liquidation of Zaporozhian Sich and Annexation thereof to Novorossiya Governorate
Novorossiya Governorate (russian: Новороссийская губерния, Novorossiyskaya guberniya, New Russia Governorate; uk, Новоросійська губернія), was a governorate of the Russian Empire in the previously O ...
", and the Sich was razed to the ground.
Some of the Cossack officer class, the ''starshyna
( rus, старшина, p=stərʂɨˈna, a=Ru-старшина.ogg or in Ukrainian transliteration) is a senior non-commissioned rank or designation in the military forces of some Slavic states, and a historical military designation.
In arm ...
'', became hereditary Russian nobility and obtained huge lands in spite of their previous attempts to relocate the Sich to either North America or Australia. Under the guidance of a ''starshyna'' named Lyakh, a conspiracy was formed among a group of 50 Cossacks to pretend to go fishing on the river Inhul next to the Southern Buh
, ''Pivdennyi Buh''
, name_etymology =
, image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg
, image_size = 270
, image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine
, map = PietinisBu ...
in the Ottoman provinces, and to obtain 50 passports for the expedition. The pretext was enough to allow about 5,000 Zaporozhians to flee, some travelling to the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta ( ro, Delta Dunării, ; uk, Дельта Дунаю, Deľta Dunaju, ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies in Ro ...
where they formed a new Danube Sich
The Danubian Sich ( uk, Задунайська Сiч, translit=Zadunaiska Sich) was an organization of the part of former Zaporozhian Cossacks who settled in the territory of the Ottoman Empire (the Danube Delta, hence the name) after their pr ...
, as a protectorate of the Ottoman Empire. Others moved to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
to form a Sich there as a protectorate of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
. According to folklore, some moved to Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, because Kosh otaman
Kish otaman ( uk, Кошовий отаман, ; russian: Кошевой атаман, ; pl, Ataman koszowy; also known as of the Zaporizhian Host) was a chief officer of the ''Kish'' (central body of government) of the Zaporozhian Host in the 1 ...
s and other senior members of the starshyna considered themselves a kind of Maltese chivalry.
The leader of the Zaporozhian Host, Petro Kalnyshevsky, was arrested and exiled to the Solovetsky Islands
The Solovetsky Islands (russian: Солове́цкие острова́), or Solovki (), are an archipelago located in the Onega Bay of the White Sea, Russia. As an administrative division, the islands are incorporated as Solovetsky District of ...
(where he lived to the age of 112 in the Solovetsky Monastery
The Solovetsky Monastery ( rus, Солове́цкий монасты́рь, p=səlɐˈvʲɛtskʲɪj mənɐˈstɨrʲ) is a fortified monastery located on the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea in northern Russia. It was one of the largest Chris ...
). Four high level ''starshynas'' were repressed and exiled, later dying in Siberian monasteries. Lower level ''starshynas'' who remained and went over to the Russian side were given army ranks and all the privileges that accompanied them, and allowed to join Hussar
A hussar ( , ; hu, huszár, pl, husarz, sh, husar / ) was a member of a class of light cavalry, originating in Central Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. The title and distinctive dress of these horsemen were subsequently widely ...
and Dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat w ...
regiments. Most of the ordinary Cossacks were made peasants and even serfs.
In 1780, after disbanding the Zaporozhian Cossack Host, General Grigorii Potemkin attempted to gather and reorganize the Cossacks on a voluntary basis, and they helped to defend Ukraine from the Turks during the Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1787–1792 involved an unsuccessful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to regain lands lost to the Russian Empire in the course of the previous Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774). It took place concomitantly with the Austro ...
. He was able to gather almost 12,000 Cossacks and called them the Black Sea Cossacks. After the conflict was over, rather than allowing the Cossacks to settle across Southern Ukraine, the Russian government began to resettle them on the Kuban River
The Kuban; Circassian: Псыжъ, ''Psyẑ'' or Псыжь, ''Psyź'' ; abq, Къвбина, ''Q̇vbina'' ; Karachay–Balkar: Къобан, ''Qoban''; Nogai: Кобан, ''Qoban'') is a river in Russia that flows through the Western Caucas ...
. In 1860, they changed their name to the Kuban Cossacks
Kuban Cossacks (russian: кубанские казаки, ''kubanskiye kаzaki''; uk, кубанські козаки, ''kubanski kozaky''), or Kubanians (russian: кубанцы, ; uk, кубанці, ), are Cossacks who live in the Kuban re ...
.
Ukrainian writer Adrian Kaschenko (1858–1921) and historian Olena Apanovich
Olena Apanovych ( uk, Олена Михайлівна Апанович) (9 November 1919 – 21 February 2000) was a Ukrainian historian, a researcher of Zaporozhian Cossackdom. She was an Antonovych prize recipient.
Biography
Olena Apanovych w ...
Olena Apanovich, "Ne propala ihnya slava", "Vitchizna" Magazine, N 9, 1990 note that the abolition of the Zaporozhian Sich had a strong symbolic effect, and memories of the event remained for a long time in local folklore.
Organization and government

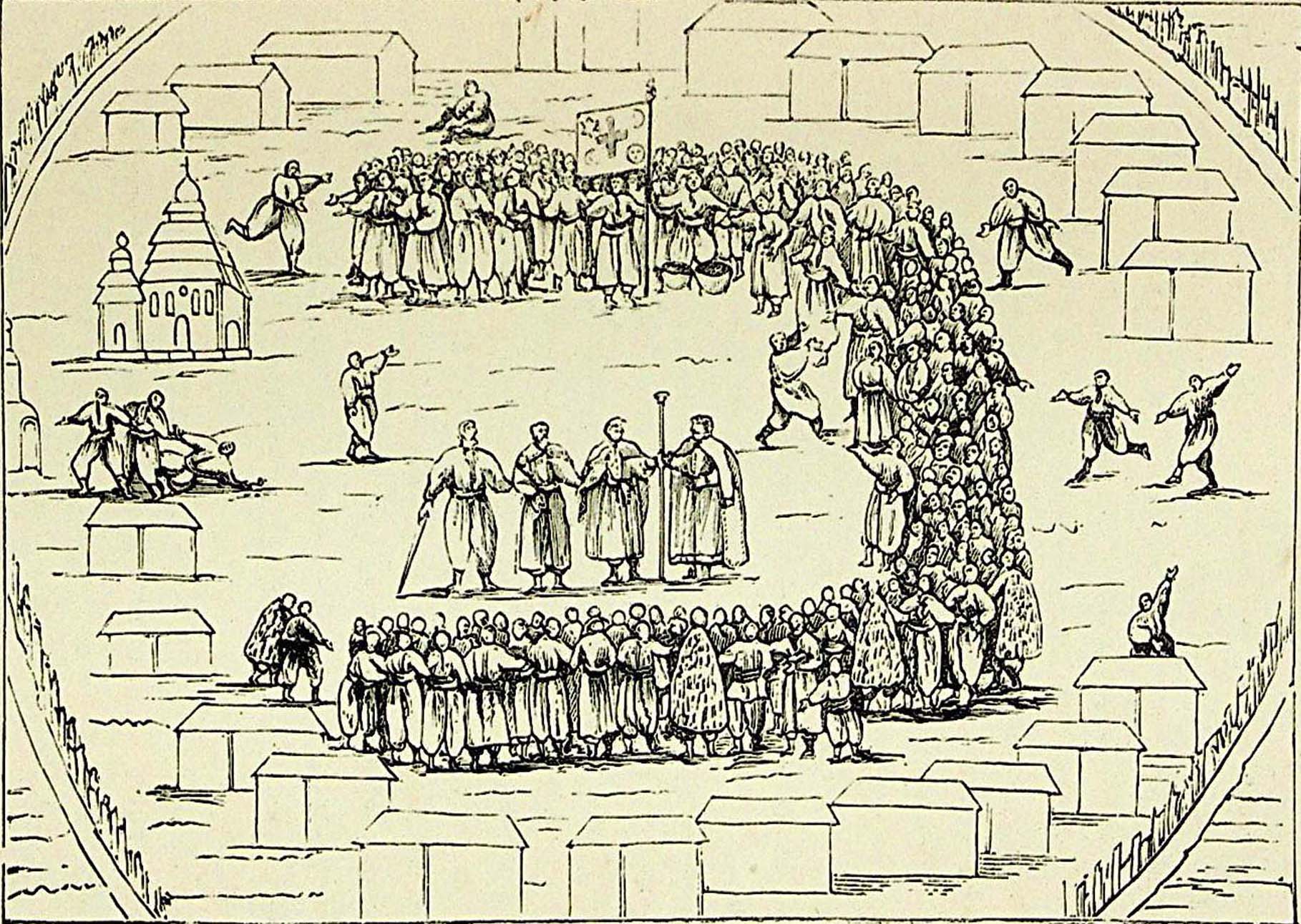
 The Zaporozhian Host was led by the
The Zaporozhian Host was led by the Sich Rada
The Sich Rada (, ''Sichova Rada'') was the highest branch of government of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, and based at their center, the Zaporizhian Sich. It was also called Viyskova Rada (Military Council). The Rada, a type of governing committee but ...
that elected a Kosh Otaman
Kish otaman ( uk, Кошовий отаман, ; russian: Кошевой атаман, ; pl, Ataman koszowy; also known as of the Zaporizhian Host) was a chief officer of the ''Kish'' (central body of government) of the Zaporozhian Host in the 1 ...
as the host's leader. He was aided by a head secretary (''pysar''), head judge, and head archivist. During military operations the Otaman
Ataman (variants: ''otaman'', ''wataman'', ''vataman''; Russian: атаман, uk, отаман) was a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds. In the Russian Empire, the term was the official title of the supreme military commande ...
carried unlimited power supported by his staff as the military collegiate. He decided with an agreement from the Rada whether to support a certain Hetman (such as Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Zynovii Mykhailovych Khmelnytskyi ( Ruthenian: Ѕѣнові Богданъ Хмелнiцкiи; modern ua, Богдан Зиновій Михайлович Хмельницький; 6 August 1657) was a Ukrainian military commander and ...
) or other leaders of state.
Some sources refer to the Zaporozhian Sich as a "Cossack republic", because the highest power in it belonged to the assembly of all its members, and its leaders (''starshyna'') were elected. The Cossacks formed a society (hromada
A hromada ( uk, територіальна громада, lit=territorial community, translit=terytorialna hromada) is a basic unit of administrative division in Ukraine, similar to a municipality. It was established by the Government of Ukra ...
) that consisted of "kurin
Kurin ( uk, курінь, translit=Kurin') has two definitions: a military and administrative unit of the Zaporozhian Cossacks, Black Sea Cossack Host, and others; and of a type of housing (see below).
In the administrative definition, a kurin us ...
s" (each with several hundred Cossacks). A Cossack military court severely punished violence and stealing among compatriots, the bringing of women to the Sich, the consumption of alcohol in periods of conflict, and other offenses. The administration of the Sich provided Orthodox churches and schools for the religious and secular education of children.
The population of the Sich had a cosmopolitan component, including Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
, Moldavians, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Uni ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
and many other ethnicities. The social structure was complex, consisting of destitute gentry and boyars
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, Russia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Boyars were sec ...
, ''szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
'' (Polish nobility), merchants, peasants, outlaws of every sort, runaway slaves from Turkish galley
A galley is a type of ship that is propelled mainly by oars. The galley is characterized by its long, slender hull, shallow draft, and low freeboard (clearance between sea and gunwale). Virtually all types of galleys had sails that could be used ...
s, and runaway serfs (as the Zaporozhian polkovnyk
''Polkovnik'' (russian: полковник, lit=regimentary; pl, pułkownik) is a military rank used mostly in Slavic-speaking countries which corresponds to a colonel in English-speaking states and oberst in several German-speaking and Scandin ...
Pivtorakozhukha). Some of those who were not accepted to the host formed gangs of their own, and also claimed to be Cossacks. However, after the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian language, Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніц ...
these formations largely disappeared and were integrated mainly into Hetmanate society.
Army and warfare
The Cossacks developed a large fleet of fast, light vessels. Their campaigns were targeted at rich settlements on theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
shores of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, and several times took them as far as Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
and Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the Bl ...
(formerly Trebizond).
Zaporozhian Sich centers and locations
* Khortytsia Sich (1556–1557) ** Khortytsia Island (today, part ofZaporizhzhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. It is the Capital city, administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zapor ...
)
* Tomakivka Sich (1564–1593)
** submerged (located near today's Marhanets
Marhanets ( uk, Марганець, ; russian: Марганец, ; ) is a city in Nikopol Raion of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast that was established in 1938 in southern Ukraine. It was established in place of the village of Horodyshche, which contained ...
)
* Bazavluk Sich, (1593–1638)
** submerged (located near today's village of Kapulivka, Nikopol Raion
Nikopol Raion ( uk, Нікопольський район, Nikopolskyi raion) is an administrative subdivision (''raion'') of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine, with the administrative center in the city of Nikopol. Population: .
On 18 July 2020, a ...
)
* Mykyta Sich (1639–1652)
** Nikopol
* Chortomlyk Sich (1652–1709)
** submerged (located near today's village of Kapulivka, Nikopol Raion
Nikopol Raion ( uk, Нікопольський район, Nikopolskyi raion) is an administrative subdivision (''raion'') of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine, with the administrative center in the city of Nikopol. Population: .
On 18 July 2020, a ...
)
* Kamyanka Sich (1709–1711)
** near village of Respublikanets, Beryslav Raion
Beryslav Raion ( uk, Бериславський район, ) is one of the five administrative raions (a ''district'') of Kherson Oblast in southern Ukraine. Its administrative center is located in the city of Beryslav. Its population was 55,976 ...
* Oleshky Sich (1711–1734)
** eastern outskirts of the city of Oleshky
Oleshky ( uk, Оле́шки, Oleshky, ; russian: Алёшки) is a town in Kherson Raion, Kherson Oblast, southern Ukraine, located on the left bank of the Dnieper River with the town of Solontsi to the south. It is the oldest city of the obl ...
* Nova idpilnenskaSich (1734–1775)
** near village of Pokrovske, Nikopol Raion
Nikopol Raion ( uk, Нікопольський район, Nikopolskyi raion) is an administrative subdivision (''raion'') of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine, with the administrative center in the city of Nikopol. Population: .
On 18 July 2020, a ...
(about same location of Chortomlyk and Bazavluk)
Zaporozhian Siches and their leaders
* Khortytsia Sich (1556–1557) ** Wężyk Chmielnicki (1534–1569) * Tomakivka Sich (1564–1593) ** Wężyk Chmielnicki (1534–1569) ** Michał Wiśniowiecki (1529–1584) (1569–1570) ** Iwan Swiergowski (1574) ** Samiylo Kishka (1574–1575) ** Bohdan Ruzhynski (1575–1576) ** Jacub Szach (1576–1578) ** Ioan Potcoavă (1577–1578) **Lukyan Chornynsky
Lukyan is a variant of the Latin masculine given name Lucian. It means 'light', or 'bringer of light'. It is also used as a given name in Russian, and sometimes a surname.
People named Lukyan
* Lukyan Popov, Russian painter
* Lukyan Stepano ...
(1578)
** Jan Oryszowski (1581)
** Samuel Zborowski
Samuel Zborowski (died 1584) was a Polish military commander and a notable member of the ''szlachta'' (Polish nobility). He is best remembered for having been executed by supporters of the Polish king Stefan Batory and chancellor Jan Zamoyski; an ...
(1581–1584)
** Bohdan Mokoshynsky (1584)
** Mykhailo Ruzhynski (1585)
** Zakhar Kulaha (1585)
** Bohdan Mokoshynsky (1586)
** Lukyan Chornynsky
Lukyan is a variant of the Latin masculine given name Lucian. It means 'light', or 'bringer of light'. It is also used as a given name in Russian, and sometimes a surname.
People named Lukyan
* Lukyan Popov, Russian painter
* Lukyan Stepano ...
(1586)
** Demyan Skalozub (1585–1589)
** Krzysztof Kosiński
Krzysztof Kosiński, also Kryshtof Kosynsky
''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'', vol. 2 (1989)< ...
(−1593)
* Bazavluk Sich, (1593–1638)
** ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'', vol. 2 (1989)< ...
Hryhoriy Loboda
Hryhory Loboda ( ro, Grigore Lobodă; uk, Григорій Лобода, ; pl, Grzegorz Łoboda; born in the Kyiv (Kiev) region — May 1596), was a Kosh Otaman of the Zaporizhian Host (1593–6, with interruptions) of Moldavian descent. In 159 ...
(1593–1596)
** Bohdan Mokoshynsky (1594)
** Jan Oryszowski (1596)
** Severyn Nalyvaiko
Severyn (Semeriy) Nalyvaiko (, , in older historiography also ''Semen Nalewajko'', died 21 April 1597) was a leader of the Ukrainian Cossacks who became a hero of Ukrainian folklore. He led the failed Nalyvaiko Uprising for which he was tortured ...
(1596)
** Khrystofor Netkovsky (1596–1597)
** Hnat Vasylevych (1596–1597)
** Tykhin Baybuza (1597–1598)
** Fedir Polous (1598)
** Semen Skalozub (1599)
** Samiylo Kishka (1600–1602)
** Havrylo Krutnevych (1602–1603)
** Ivan Kutskovych (1602–1603)
** Ivan Kosyi (1603)
** Kaletnyk Andriyevych (1609–1610)
** Olifer Holub (1622–1623)
** Mykhailo Doroshenko
Mykhailo Doroshenko ( uk, Михайло Дорошенко; died 1628) was the Hetman of the registered Ukrainian Cossacks from 1623 to 1628.
Brief biography
He was elevated to the rank of Cossack colonel in 1616, and he was active in Petro ...
(1623–1625)
** Kaletnyk Andriyevych (1624–1625)
** Marek Zhmaylo Marko Zhmaylo-Kulchytsky (; Polish language, Polish: Marek Żmajło – Date of birth and death unknown), hetman Registered Cossacks, Cossack and leader of the Zhmaylo Uprising against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1625. According to o ...
(1625)
** Mykhailo Doroshenko
Mykhailo Doroshenko ( uk, Михайло Дорошенко; died 1628) was the Hetman of the registered Ukrainian Cossacks from 1623 to 1628.
Brief biography
He was elevated to the rank of Cossack colonel in 1616, and he was active in Petro ...
(1625–1628)
** Hryhoriy Chorny Hryhoriy Savych Chorny ( uk, Григорій (Грицько) Савич Чорний, pl, Hryćko Czarny), died 1630, was a Hetman of the Dnieper Cossacks from 1628 to 1630 who represented the registered Cossacks while the larger bulk of unregist ...
(1628–1630)
** Ivan Sulyma
Ivan Sulyma ( pl, Iwan Sulima, uk, Іван Михайлович Сулима – ''Ivan Mykhailovych Sulyma'') was a Senior of Registered Cossacks in 1628–29 and a Kosh Otaman in 1630–35.
Life and death
Son of Mykhailo Sulyma, Ivan came fr ...
(1628–1629)
** Lev Ivanovych (1629–1630)
** Taras Tryasylo (1630)
** Timothy Orendarenko (1630–1631)
** Semen Perevyazka (1632)
** Timothy Orendarenko (1632–1633)
** Ivan Petrizhitsky-Kulaga (1632)
** Andriy Didenko (1633)
** Dorothy Doroshenko (1633)
** Ivan Sulyma
Ivan Sulyma ( pl, Iwan Sulima, uk, Іван Михайлович Сулима – ''Ivan Mykhailovych Sulyma'') was a Senior of Registered Cossacks in 1628–29 and a Kosh Otaman in 1630–35.
Life and death
Son of Mykhailo Sulyma, Ivan came fr ...
(1633–1635)
** Sava Kononovych
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
(1637)
** Pavlo Pavlyuk (1637)
** Illyash Karayimovych (1638)
** Yakiv Ostryanyn (1638)
** Dmytro Hunia
Dmytro Hunia (; ) was elected hetman of the Zaporozhian Host in 1638. He was one of the leaders of the Ostryanyn Uprising, a 1638 Cossack uprising against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The rebellion was sparked by the Sejm act of the same ...
(1638)
* Mykytyn Sich (1639–1652)
** Karpo Pivtora-Kozhukha (1639–1642)
** Maksym Hulak (1642–1646)
** establishment of the Hetman of Zaporizhian Host
The Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host ( uk, Гетьман Війська Запорозького, la, Cosaccorum Zaporoviesium Supremus Belli Dux) was the head of state of the Cossack Hetmanate in what is now Ukraine. The office was disestablishe ...
* Chortomlyk Sich (1652–1709)
* Kamyanka Sich (1709–1711)
* Oleshky Sich (1711–1734)
* Nova Podpolnenska Sich (1734–1775)
* Danubian Sich
The Danubian Sich ( uk, Задунайська Сiч, translit=Zadunaiska Sich) was an organization of the part of former Zaporozhian Cossacks who settled in the territory of the Ottoman Empire (the Danube Delta, hence the name) after their pre ...
(1775–1828)
See also
*History of the Cossacks
The history of the Cossacks spans several centuries.
Early history
Several theories speculate about the origins of the Cossacks. According to one theory, Cossacks have Slavic origins, while another theory states that the Constitution of Pyly ...
* Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
* Tatar invasions
This article lists conflicts in Europe during the invasions of and subsequent occupations by the Mongol Empire and its successor states. The Mongol invasion of Europe took place in the 13th century. This resulted in the occupation of much of Easter ...
References
Works cited
*External links
Zaporozhian Sich
– Encyclopedia of Ukraine {{authority control Early Modern history of Ukraine History of the Cossacks in Ukraine States and territories established in 1552 States and territories disestablished in 1775 Zaporozhian Cossacks Zaporozhian Host