|
Sharovipterygidae
Sharovipterygidae is a family of strange gliding archosauromorphs from the mid-Triassic of Eurasia, notable for their short forelimbs and long, wing-like hindlimbs, which supported membranes for gliding. They are represented by ''Sharovipteryx ''Sharovipteryx'' ("Sharov's wing", known until 1981 as ''Podopteryx'', "foot wing"), is a genus of early gliding reptiles containing the single species ''Sharovipteryx mirabilis''. It is known from a single fossil and is the only glider with a m ...'' and '' Ozimek volans''. A 2019 phylogenetic analysis suggested that ''Ozimek'', and by extension ''Sharovipteryx'', may belong to the Tanystropheidae. References Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Prehistoric archosauromorphs Gliding animals Late Triassic reptiles of Asia Late Triassic reptiles of Europe Prehistoric reptile families {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
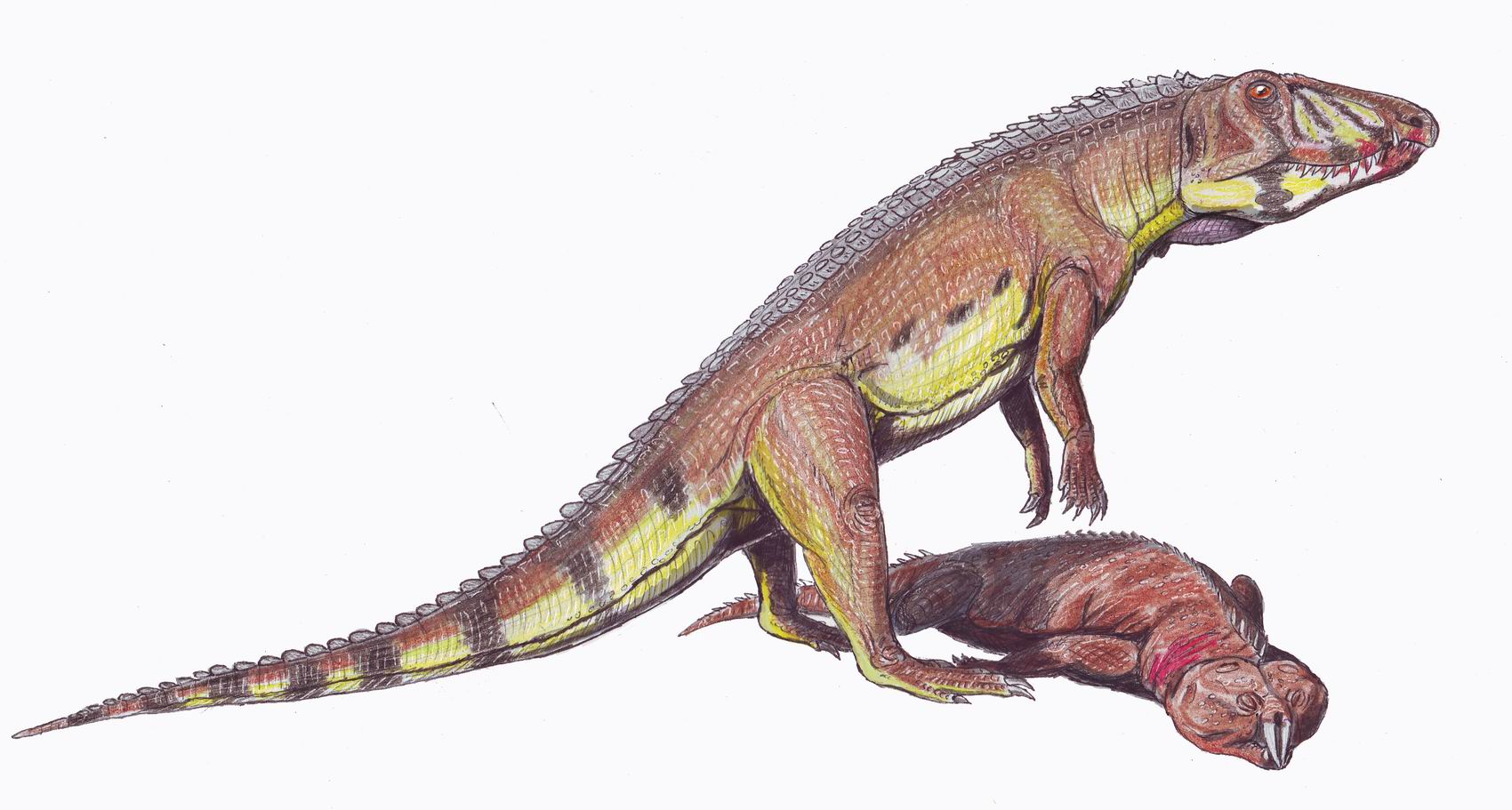
Ozimek Volans
''Ozimek'' (named after the Ozimek, town of the same name) is a genus of sharovipterygidae, sharovipterygid archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile, known from Late Triassic deposits in Poland and closely related to the Kyrgyzstani ''Sharovipteryx''. It contains one species, ''O. volans'', named in 2016 by Jerzy Dzik and Tomasz Sulej. Like ''Sharovipteryx'', ''Ozimek'' had long, slender limbs with the hindlimbs longer than the forelimbs; the hindlimbs likely supported gliding membranes as fossilized in ''Sharovipteryx''. Another unusual characteristic was the shoulder girdle, where the massive coracoids formed a shield-like structure covering the bottom of the shoulder region that would have limited mobility. In other respects, such as its long neck, it was a typical member of the non-natural grouping Protorosauria. Phylogenetic analysis has indicated that it, possibly along with ''Sharovipteryx'', may have been an unusual member of the protorosaur group Tanystropheidae, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheidae
Tanystropheidae is an extinct family of mostly marine archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic Period. They are characterized by their long, stiff necks formed from elongated cervical vertebrae with very long cervical ribs. Some tanystropheids such as ''Tanystropheus'' had necks that were several meters long, longer than the rest of their bodies. Tanystropheids are known from Europe, Asia (Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia), North America and probably South America (Brazil). The presence of tanystropheids in Europe and China indicate that they lived along much of the coastline of the Tethys Ocean. However, species in western North America are found in terrestrial deposits, suggesting that as a group, tanystropheids were ecologically diverse. Relationships among tanystropheid species have been difficult to resolve because most specimens were flattened during fossilization and are preserved two-dimensionally. Three-dimensional fossils are known from Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliding Animals
A number of animals are capable of aerial locomotion, either by powered flight or by gliding. This trait has appeared by evolution many times, without any single common ancestor. Flight has evolved at least four times in separate animals: insects, pterosaurs, birds, and bats. Gliding has evolved on many more occasions. Usually the development is to aid canopy animals in getting from tree to tree, although there are other possibilities. Gliding, in particular, has evolved among rainforest animals, especially in the rainforests in Asia (most especially Borneo) where the trees are tall and widely spaced. Several species of aquatic animals, and a few amphibians and reptiles have also evolved this gliding flight ability, typically as a means of evading predators. Types Animal aerial locomotion can be divided into two categories: powered and unpowered. In unpowered modes of locomotion, the animal uses aerodynamic forces exerted on the body due to wind or falling through the air. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series (or earliest age of the Late Triassic Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event (known as the Carnian pluvial episode characterized by substantial rainfall) occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Stratigraphic definitions The Carnian was named in 1869 by Mojsisovics. It is unclear if it was named after the Carnic Alps or after the Austrian region of Carinthia (''Kärnten'' in German) or after the Carnia historical region in northwestern Italy. The name, however, was first used referring to a part of the Hallstatt Limestone cropping out in Austria. The base of the Carnian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of '' Klamathites macrolobatus'' and '' Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of '' Metapolygnathus communisti'' and '' Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Cochloceras amoenum''. The base of the Rheatian is also close to the first appearance of conodont species '' Misikella spp.'' and '' Epigondolella mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
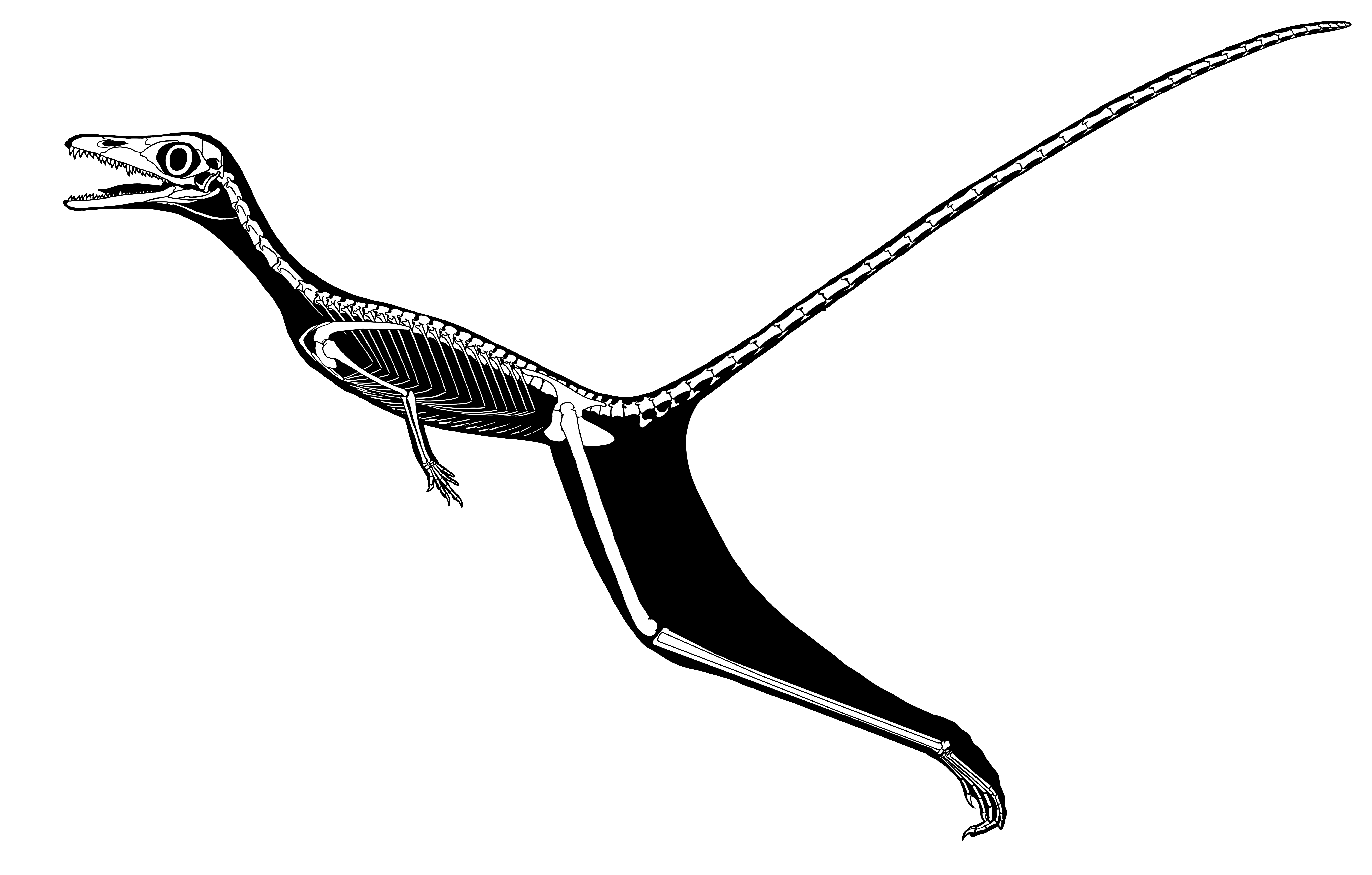
Sharovipteryx
''Sharovipteryx'' ("Sharov's wing", known until 1981 as ''Podopteryx'', "foot wing"), is a genus of early gliding reptiles containing the single species ''Sharovipteryx mirabilis''. It is known from a single fossil and is the only glider with a membrane surrounding the pelvis instead of the pectoral girdle. This lizard-like reptile was found in 1965 in the Madygen Formation, Dzailauchou, on the southwest edge of the Fergana Valley in Kyrgyzstan, in what was then the Asian part of the U.S.S.R. dating to the middle-late Triassic period (about 225 million years ago). The Madygen horizon displays flora that put it in the Upper Triassic. An unusual reptile, ''Longisquama,'' was also found there. ''S. mirabilis'' is known from a unique holotype specimen, which was first described by Aleksandr Grigorevich Sharov in 1971.Sharov, A. G. 1971. New flying reptiles from the Mesozoic of Kazakhstan and Kirghizia. – Transactions of the Paleontological Institute, Akademia Nauk, USSR, Moscow, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Grigorevich Sharov
Aleksandr Grigorevich Sharov (А.Г. Шаров, 1922–1973) was a Soviet palaeoentomologist, paleontologist and expert on Pterosauria. He graduated from Moscow State University. In 1951 he defended Candidate of Science dissertation on the embryology of Apterygota. Since 1951 he worked at the Paleontological Institute in Moscow, where in 1966 he defended dissertation of Doctor of Science. His major contribution to the phylogeny of Arthropods was published in 1966. He worked during the 1960s and 1970s on the Karatau rocks and discovered many of the fossils, of which some have been named after him, as in the case of the '' Karatausuchus sharovi'' (a crocodile), and ''Sharovipteryx ''Sharovipteryx'' ("Sharov's wing", known until 1981 as ''Podopteryx'', "foot wing"), is a genus of early gliding reptiles containing the single species ''Sharovipteryx mirabilis''. It is known from a single fossil and is the only glider with a m ...'' (an early gliding reptile). He also discovered and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorph
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift. Lifting structures used in water include various foils, such as hydrofoils. Hydrodynamics is the governing science, rather than aerodynamics. Applications of underwater foils occur in hydroplanes, sailboats and submarines. Etymology and usage For many centuries, the word "wing", from the Old Norse ''vængr'', referred mainly to the foremost limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_in_flight%2C_Cley%2C_Norfolk_1700.jpg)