|
Sergei Fomchenkov
Sergei Alexandrovich Fomchenkov (russian: Сергей Александрович Фомченков, born on 8 December 1973 in Smolensk) is a Russian politician, a former member of the banned National Bolshevik Party The National Bolshevik Party (NBP; russian: Национал-большевистская партия), also known as the Nazbols (russian: нацболы), operated from 1993 to 2007 as a Russian political party with a political program of Nat ... (NBP) and then member of The Other Russia of E. V. Limonov, The Other Russia. During the Russo-Ukrainian war, he has been serving as commander of various military units; his call sign is "Fomich" (russian: ФОМИЧ). Biography Political career Fomchenkov was head of the Smolensk branch of the NBP since 1998 and later member of its Central Committee. He was one of the organizers of the Dissenters' March. After the dissolution of the NBP in 2007, he was one of its former members who in 2010 established The Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. Population: The city has been destroyed several times throughout its long history because it was on the invasion routes of various empires. Smolensk is known for its electronics, textiles, food processing, and diamond faceting industries. Etymology The name of the city is derived from the name of the Smolnya River. Smolnya river flows through Karelian and Murmansk areas of north-western Russia. The origin of the river's name is less clear. One possibility is the old Slavic word () for black soil, which might have colored the waters of the Smolnya. An alternative origin could be the Russian word (), which means resin, tar, or pitch. Pine trees grow in the area, and the city was once a center of resin processing and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissenters' March
The Dissenters' March (russian: Марш несогласных) was a series of Russian opposition protests that took place on December 16, 2006 in Moscow, on March 3, 2007 in Saint Petersburg, on March 24 in Nizhny Novgorod, on April 14 for the second time in Moscow, on April 15 again in Saint Petersburg, on May 18 in Samara, and on May 19 in Chelyabinsk. Some of them were featured in various media outlets. It was preceded by opposition rallies in Russian cities in December 2005 which involved fewer people. Most of the protests were unsanctioned. Usually, the authorities of the cities where the march was expected to take place have proposed protesters to meet at some more peripheral place and forbade processions. However, according to Russian legislation, organizers of a march should merely inform the authorities of the upcoming event and do not need a sanction, while the authorities have no right to prohibit a march in the specific places where it has been planned by the op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Bolshevik Party Politicians
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
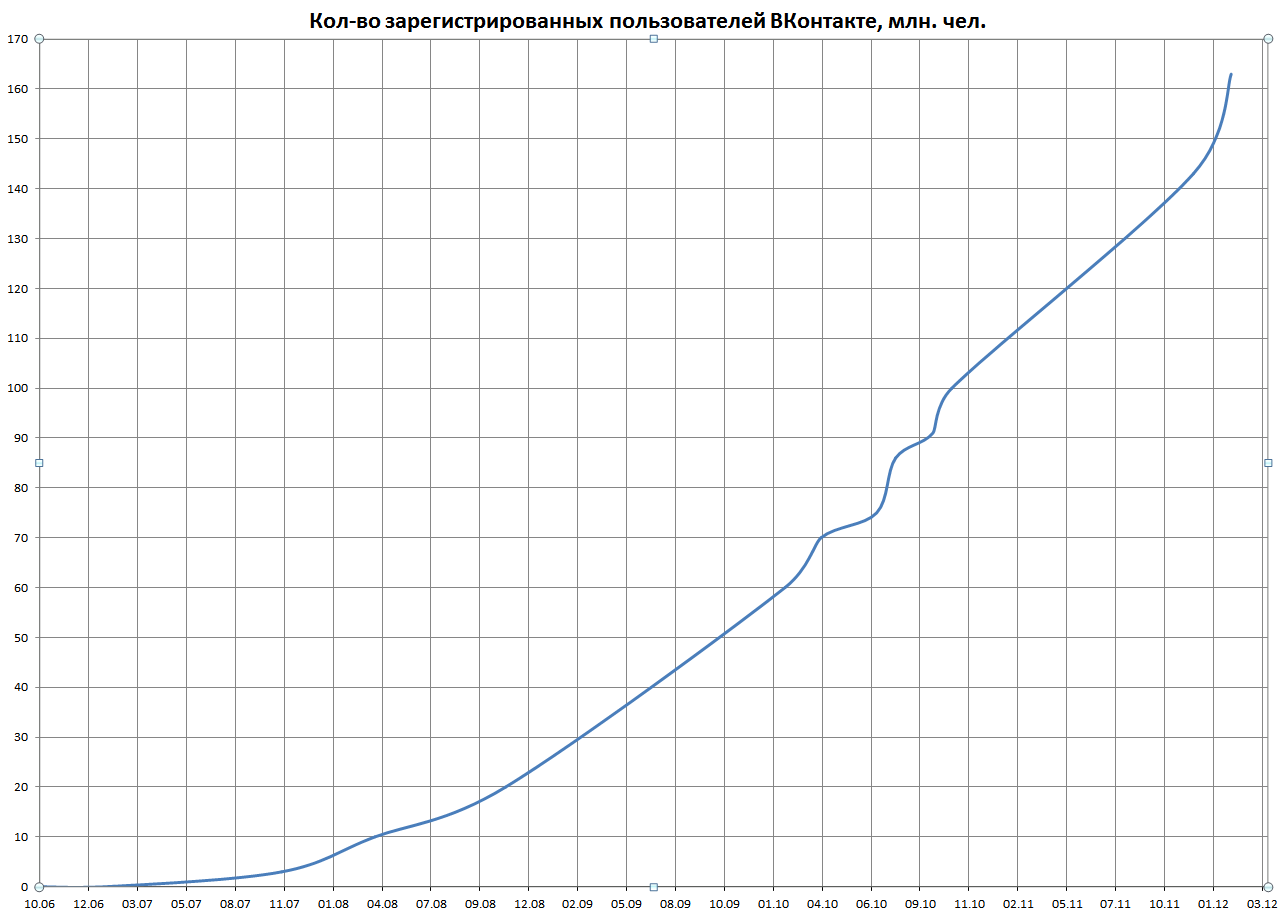
VK (social Networking Website)
VK (short for its original name ''VKontakte''; russian: ВКонтакте, meaning ''InContact'') is a Russian online social media and social networking service based in Saint Petersburg. VK is available in multiple languages but it is predominantly used by Russian speakers. VK users can message each other publicly or privately, create groups, public pages, and events; share and tag images, audio, and video; and play browser-based games. , VK had at least 500 million accounts. As of Novemer 2022, it is the sixth popular website in Russia. The network was also popular in Ukraine until it was banned by the Verkhovna Rada in 2017. According to SimilarWeb, VK is the 16th most visited website in the world. History VKontakte was incorporated on 19 January 2007 as a Russian private limited company. Founder Pavel Durov launched VKontakte for beta testing in September 2006, shortly after his graduation from St Petersburg State University. The following month, the domain name ''vkon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Kreminna
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units ( SI) is more precise:The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. Uses Analog clocks and watches often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreminna
Kreminna (; ) is a city in the Sievierodonetsk Raion of the Luhansk Oblast of Ukraine. Prior to 2020, it served as the administrative center of the former Kreminna Raion. It has a population of The city was occupied by Russian Armed Forces on 18 April 2022 during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. History Kreminna was founded in 1680. Kreminna acquired the status of a city in 1938. A local newspaper has been published in the city since December 1943. Russo-Ukrainian War In July 2014, fighting took place in the city during the 2014 pro-Russian conflict in Ukraine. Kreminna remained under Ukrainian control. In March 2022, during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the pro-Russian mayor Volodymyr Struk who welcomed the Russian move, was found shot dead in the street after having been kidnapped from his home. Official advisor and a former deputy minister at the Ukrainian Ministry of Internal Affairs Anton Herashchenko said that Struk was judged under the Lynch Law. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Lyman
The Second Battle of Lyman was a military engagement during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, as part of the 2022 Ukrainian eastern counteroffensive. The battle started on 10 September 2022 during the counteroffensive and ended three weeks later on 2 October. By 30 September, Ukrainian forces had closed in on the city after crossing the Siverskyi Donets River, advancing along Lyman's southern and eastern flanks while capturing land northwest of the settlement, allowing Ukrainian forces to cut off the only road left supplying the occupying forces from the north. On 1 October, Ukrainian forces entered Lyman after a Russian withdrawal. Background A month into the Russian invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022, Russia claimed to control 93% of Luhansk Oblast, leaving Sievierodonetsk and Lysychansk as strategically important Ukrainian holdouts in the area. Russian plans to capture Sievierodonetsk hinged upon its successes in the nearby cities of Rubizhne to the north and Pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armed Forces Of Ukraine
, imports = , exports = , history = , ranks = Military ranks of Ukraine , country=Ukraine The Armed Forces of Ukraine ( uk, Збро́йні си́ли Украї́ни), most commonly known in Ukraine as ZSU ( uk, ЗСУ) or anglicized as AFU, are the military forces of Ukraine. All military and security forces, including the Armed Forces, are under the command of the president of Ukraine and subject to oversight by a permanent Verkhovna Rada parliamentary commission. The modern armed forces were formed in 1991 and consisted of three former Soviet Armed Forces military districts stationed in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. Ukraine's armed forces are composed of the Ukrainian Ground Forces, the Ukrainian Air Force, the Ukrainian Navy, the Ukrainian Air Assault Forces and the Special Operations Forces. Ukraine's navy includes its own Ukrainian Naval Infantry, as well as Ukrainian Naval Aviation. The Territorial Defen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakhar Prilepin
Yevgeny Nikolayevich Prilepin (russian: link=no, Евге́ний Никола́евич Приле́пин; born 7 July 1975), writing as Zakhar Prilepin (russian: link=no, Захар Прилепин), and sometimes using another pseudonym, Yevgeny Lavlinsky (russian: link=no, Евгений Лавлинский), is a Russian writer and leader of the political party " For Truth" from 1 February 2020. Previously he was a member of Russia's unregistered National Bolshevik Party from 1996 to 2019. Biography Yevgeny Prilepin was born 7 July 1975 in the village of Ilyinka, Ryazan Oblast, in the family of a teacher and a nurse. His family lived there until 1984, when they moved to Dzerzhinsk. He started working at age 16 as a loader in a bread shop. He graduated from the Faculty of Philology of the Nizhny Novgorod State University and the School of Public Policy. He worked as a laborer, a security guard, and served as a squad leader in the Russian police group OMON, and subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhansk People's Republic
The Luhansk or Lugansk People's Republic (russian: Луга́нская Наро́дная Респу́блика, Luganskaya Narodnaya Respublika, ; abbreviated as LPR or LNR, rus, ЛНР) is a disputed entity created by Russian-backed separatists in eastern Ukraine, which claims Luhansk Oblast. It began as a breakaway state (2014–2022) and was then annexed by Russia in 2022. The city of Luhansk is the claimed capital city. Pro-Russian unrest erupted in the Donbas region in response to the Ukrainian Revolution of Dignity. In April 2014, armed pro-Russian separatists seized government buildings and declared the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) and Donetsk People's Republic (DPR) as independent states, which received no international recognition prior to 2022. Ukraine and others viewed them as Russian puppet states and as terrorist organisations. This sparked the War in Donbas, part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War which also saw the Russian occupation and annexatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014 Pro-Russian Unrest In Ukraine
From the end of February 2014, demonstrations by pro-Russian and anti-government groups took place in major cities across the Eastern Ukraine, eastern and Southern Ukraine, southern regions of Ukraine in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity, which resulted in the success of Euromaidan in ousting then-President of Ukraine, President Viktor Yanukovych. The unrest, supported by Russia in the midst of the Russo-Ukrainian War, has been referred to in Russia as the "Russian Spring" (russian: Русская весна, translit=Russkaya vesna, uk, Російська весна, translit=Rosiiska vesna). During its first phase in February–March 2014, the Ukrainian territory of Crimea was Russo-Ukrainian War#Russian annexation of Crimea (2014), invaded and subsequently Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed by Russia following an internationally unrecognized 2014 Crimean status referendum, referendum, with the United Nations General Assembly United Nations Gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |