|
Se-methylselenocysteine
Methylselenocysteine, also known as ''Se''-methylselenocysteine, is an analog of ''S''-methylcysteine in which the sulfur atom is replaced with a selenium atom. It is an inhibitor of DMBA-induced mammary tumors and a " chemopreventive agent that blocks cell cycle progression and proliferation of premalignant mammary lesions and induces apoptosis of cancer cell lines in culture." Apoptosis has been proposed as the most plausible mechanism for the chemopreventive activities of selenocompounds. ''Se''-Methylselenocysteine was more efficient at inducing apoptosis than selenite, but was less toxic. The "selenite-induced cell death could be derived from necrosis rather than apoptosis, since selenite did not significantly induce several apoptotic phenomena, including the activation of caspase-3." In the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Trial, selenized yeast resulted in "a reduction in the incidence of prostate cancer and in total cancer incidence"; subsequent anticancer studies u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoselenium Compounds
Organoselenium compounds (or seleno-organic) are chemical compounds containing carbon-to-selenium chemical bonds. Organoselenium chemistry is the corresponding science exploring their properties and reactivity. Selenium belongs with oxygen and sulfur to the group 16 elements or chalcogens, and similarities in chemistry are to be expected. Organoselenium compounds are found at trace levels in ambient waters, soils and sediments. Selenium can exist with oxidation state −2, +2, +4, +6. Se(II) is the dominant form in organoselenium chemistry. Down the group 16 column, the bond strength becomes increasingly weaker (234 kilojoule, kJ/mole (unit), mol for the C−Se bond and 272 kJ/mol for the C−S bond) and the bond lengths longer (C−Se 198 pm, C−S 181 pm and C−O 141 pm). Selenium compounds are more nucleophilic than the corresponding sulfur compounds and also more acidic. The pKa, p''K''a values of XH2 are 16 for oxygen, 7 for sulfur and 3.8 for selenium. In contrast to sulfoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broccoli
Broccoli (''Brassica oleracea'' var. ''italica'') is an edible green plant in the cabbage family (family Brassicaceae, genus ''Brassica'') whose large flowering head, stalk and small associated leaves are eaten as a vegetable. Broccoli is classified in the Italica cultivar group of the species ''Brassica oleracea''. Broccoli has large flower heads, usually dark green, arranged in a tree-like structure branching out from a thick stalk which is usually light green. The mass of flower heads is surrounded by leaves. Broccoli resembles cauliflower, which is a different but closely related cultivar group of the same ''Brassica'' species. It is eaten either raw or cooked. Broccoli is a particularly rich source of vitamin C and vitamin K. Contents of its characteristic sulfur-containing glucosinolate compounds, isothiocyanates and sulforaphane, are diminished by boiling but are better preserved by steaming, microwaving or stir-frying. Rapini, sometimes called "broccoli rabe," i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Derivatives
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Food
The Scientific Committee on Food (SCF), established in 1974, was the main committee providing the European Commission with scientific advice on food safety. "Scientific Committee on Food - FOOD STANDARDS AGENCY" (overview), Gov.uk, February 2010, webpage: -->facnews/issue2/page4.htm Gov.uk-maff "Glossary: European Commission Scientific Committee on Food", Greenfacts.org, February 2010, webpage: Its responsibilities have been transferred to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Purpose and scope The SCF provided the European Commission with independent scientific advice on issues of public health related to food consumption. The Commission was required to consult the SCF in the cases laid down by EU legislation, but could also decide to consult it on any other matter relating to food safety or consumer health, in conjunction with other committees. The SCF could also alert the Commission to any specific or emerging concern. Most of the SCF's early activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is generally lower than that of intravenous due to intestinal endothelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Selenide
Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compoundhttp://www.epa.gov/ttnatw01/hlthef/selenium.html, US Environmental Protection Agency, Air Toxins website with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period.https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7783075.html, Documentation of Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations: Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Healthhttps://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/81-123/pdfs/0336.pdf Occupational Health Guideline for Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 1978 Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations. Structure and propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
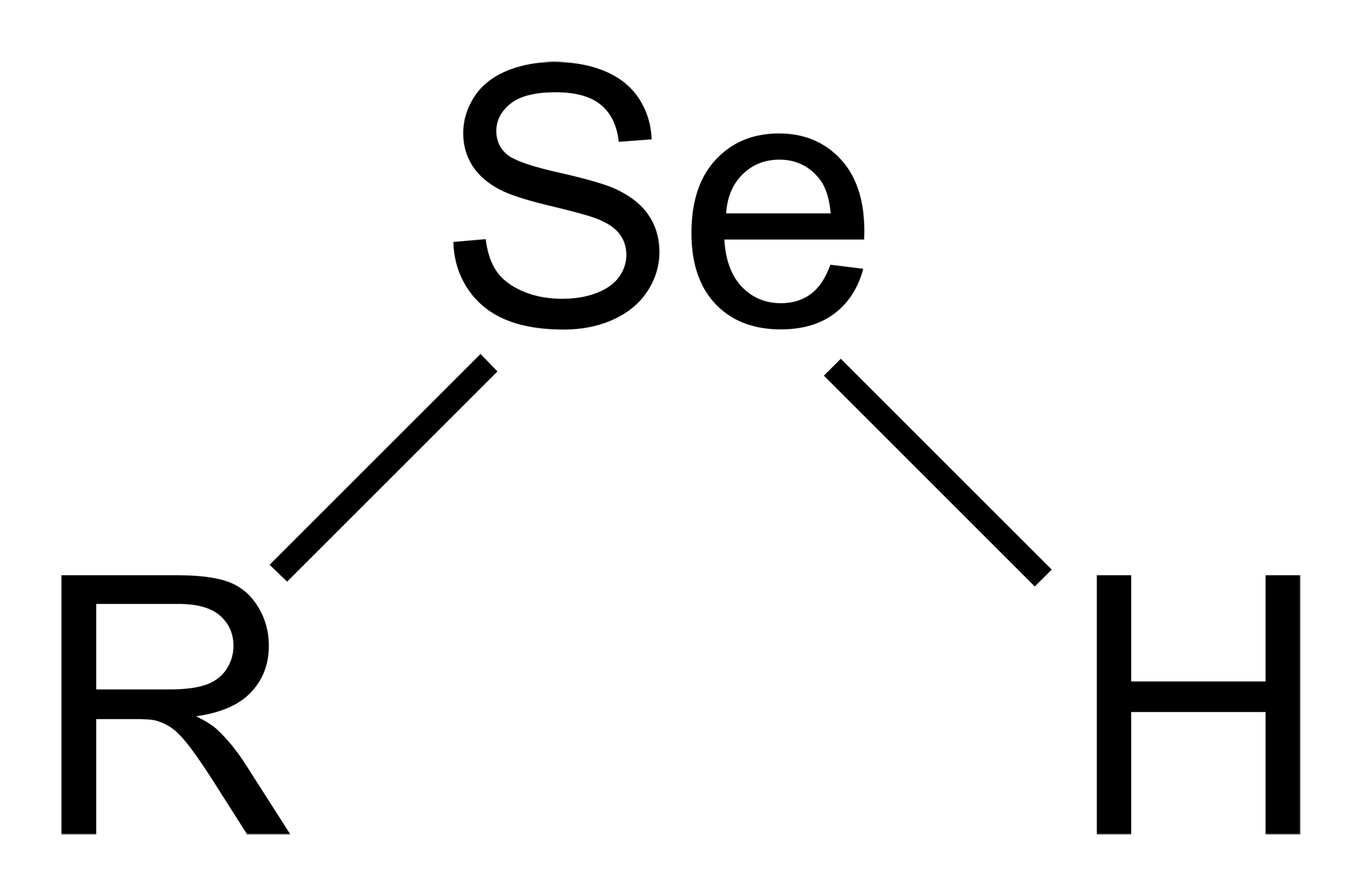
Methylselenol
Selenols are organic compounds that contain the functional group with the connectivity C– Se–H. Selenols are sometimes also called selenomercaptans and selenothiols. Selenols are one of the principal classes of organoselenium compounds. The best known member of the group is the amino acid selenocysteine. Structure, bonding, properties Selenols are structurally similar to thiols, but the C-Se bond is about 8% longer at 196 pm. The C–Se–H angle approaches 90°. The bonding involves almost pure p-orbitals on Se, hence the near 90 angles. The Se–H bond energy is weaker than the S–H bond, consequently selenols are easily oxidized and serve as H-atom donors. The Se-H bond is much weaker than the S-H bond as reflected in their respective bond dissociation energy (BDE). For C6H5Se-H, the BDE is 326 kJ/mol, while for C6H5S-H, the BDE is 368 kJ/mol. Selenol acids are about 1000 times stronger than thiols: the p''K''a of CH3SeH is 5.2 vs 8.3 for CH3SH. Deprotonation affords the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, are a large and agriculturally important of |
Astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch (most species), locoweed (in North America, some species) and goat's-thorn ( ''A. gummifer'', ''A. tragacantha''). Some pale-flowered vetches (''Vicia'' spp.) are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than ''Astragalus''. Description Most species in the genus have pinnately compound leaves. There are annual and perennial species. The flowers are formed in clusters in a raceme, each flower typical of the legume family, with three types of petals: banner, wings, and keel. The calyx is tubular or bell-shaped. Ecology ''Astragalus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including many case-bearing moths of the genus ''Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk Vetch
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch (most species), locoweed (in North America, some species) and goat's-thorn ( ''A. gummifer'', ''A. tragacantha''). Some pale-flowered vetches (''Vicia'' spp.) are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than ''Astragalus''. Description Most species in the genus have pinnately compound leaves. There are annual and perennial species. The flowers are formed in clusters in a raceme, each flower typical of the legume family, with three types of petals: banner, wings, and keel. The calyx is tubular or bell-shaped. Ecology ''Astragalus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including many case-bearing moths of the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |