|
Scottish Gaelic Education
Gaelic-medium education (G.M.E. or GME; gd, Foghlam tro Mheadhan na Gàidhlig) is a form of education in Scotland that allows pupils to be taught primarily through the medium of Scottish Gaelic, with English being taught as the secondary language. Gaelic-medium education is increasingly popular throughout Scotland, and the number of pupils who are in Gaelic-medium education has risen from 24 in 1985 (its first year) to 5,066 in 2021. The current figure is the highest number of Gaelic-medium education pupils in Scotland since the 2005 passage of the Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act by the Scottish Parliament. Not included in this figure are university students at , Lews Castle College, or who are taking their degrees through the medium of Gaelic. Current provision In 2021, 11,874 pupils in Scotland were receiving some kind of education in Gaelic representing 1.7% of the country's student population. This figure is higher than Scotland's overall proportion of Gaelic speakers whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sgoil Ghàidhlig Ghlaschu
Glasgow Gaelic School (Scottish Gaelic: ''Sgoil Ghàidhlig Ghlaschu'') is a primary and secondary school in Glasgow, Scotland which teaches through the medium of Scottish Gaelic. This teaching method is commonly known as Gaelic medium education. The secondary school catchment area serves the whole of Glasgow and the primary school catchment is in the west of the city. GME primary provision is offered at Bun-Sgoil Sgoil Ghàidhlig Ghlaschu, Glendale Gaelic Primary and Bun-sgoil Ghàidhlig Bhaile a’ Ghobhainn (Govan Gaelic Primary School). History The first Gaelic School opened in 1999 as a primary school only: Bun-Sgoil Ghàidhlig Ghlaschu (Glasgow Gaelic Primary School) situated in Ashley Street, Woodlands. As the school roll grew it became necessary to relocate to larger premises. Unused buildings at Berkeley Street, Sandyford (also a site used by Woodside Secondary School until 1999), were identified, and reopened in August 2006 as Glasgow Gaelic School, providing Gaelic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bun-sgoil Taobh Na Pàirce
Bun-sgoil Taobh na Pàirce (English: Parkside Primary School, referring to the adjoining Pilrig Park) is a Gaelic medium primary school in Edinburgh, Scotland. Administered by the City of Edinburgh Council, the school is open to any parents in the city or surrounding areas who wish to have their children learn and be educated through Scottish Gaelic. The opening of Edinburgh's first dedicated Gaelic school on 16 August 2013, after many years of campaigning by parents and supporters, was hailed as a "landmark day" for the Scottish capital. Situated in the south of the district (and former municipal burgh) of Leith, Bun-sgoil Taobh na Pàirce is housed in the refurbished former Bonnington Primary School building. The original 2-storey T-shaped school was built between 1875 and 1877 to the plans of James Simpson (1832-1894), then architect of the Leith School Board, and subsequently extended in 1907 by Simpson's old apprentice and eventual successor, George Craig (1852-1928). Bun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland Scotland
The Lowlands ( sco, Lallans or ; gd, a' Ghalldachd, , place of the foreigners, ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Lowlands and the Highlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. Geography The Lowlands is not an official geographical or administrative area of the country. There are two main topographic regions: the Lowlands and the Southern Uplands. The term "Lowlands" mainly refers to the Central Lowlands. However, in normal usage it refers to those parts of Scotland not in the Highlands (or Gàidhealtachd). The boundary is usually considered to be a line between Stonehaven and Helensburgh (on the Firth of Clyde). The Lowlands lie south and east of the line. Note that some parts of the Lowlands (such as the Southern Uplands) are not physically "low," Merrick for example reaching , while some areas indisputably in the Highlands (such as Islay) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statutes Of Iona
The Statutes of Iona, passed in Scotland in 1609, required that Highland Scottish clan chiefs send their heirs to Lowland Scotland to be educated in English-speaking Protestant schools. As a result, some clans, such as the MacDonalds of Sleat and the MacLeods of Harris, adopted the new religion. Other Clans, notably the MacLeans of Morvern & Mull, MacDonalds of Clanranald, Keppoch, Glengarry The Glengarry bonnet is a traditional Scots cap made of thick-milled woollen material, decorated with a toorie on top, frequently a rosette cockade on the left side, and ribbons hanging behind. It is normally worn as part of Scottish military ..., and Glencoe, remained resolutely Roman Catholic. Provisions Among the provisions of the statutes were: *The provision and support of Protestant ministers to Highland Parishes *The establishment of inns "to be set up in convenient places in all the Islands for accommodation of travellers" and to end the custom of "sorning", the practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Kilbride
East Kilbride (; gd, Cille Bhrìghde an Ear ) is the largest town in South Lanarkshire in Scotland and the country's sixth-largest locality by population. It was also designated Scotland's first new town on 6 May 1947. The area lies on a raised plateau to the south of the Cathkin Braes, about southeast of Glasgow and close to the boundary with East Renfrewshire. The town ends close to the White Cart Water to the west and is bounded by the Rotten Calder Water to the east. Immediately to the north of the modern town centre is The Village, the part of East Kilbride that existed before its post-war development into a New Town. East Kilbride is twinned with the town of Ballerup, in Denmark. History and prehistory The earliest-known evidence of occupation in the area dates as far back as the late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, as archaeological investigation has demonstrated that burial cairns in the district began as ceremonial or ritual sites of burial during the Neolithic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cameron Primary School
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England * Mounts, Indiana, a community in Gibson County, Indiana, United States People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
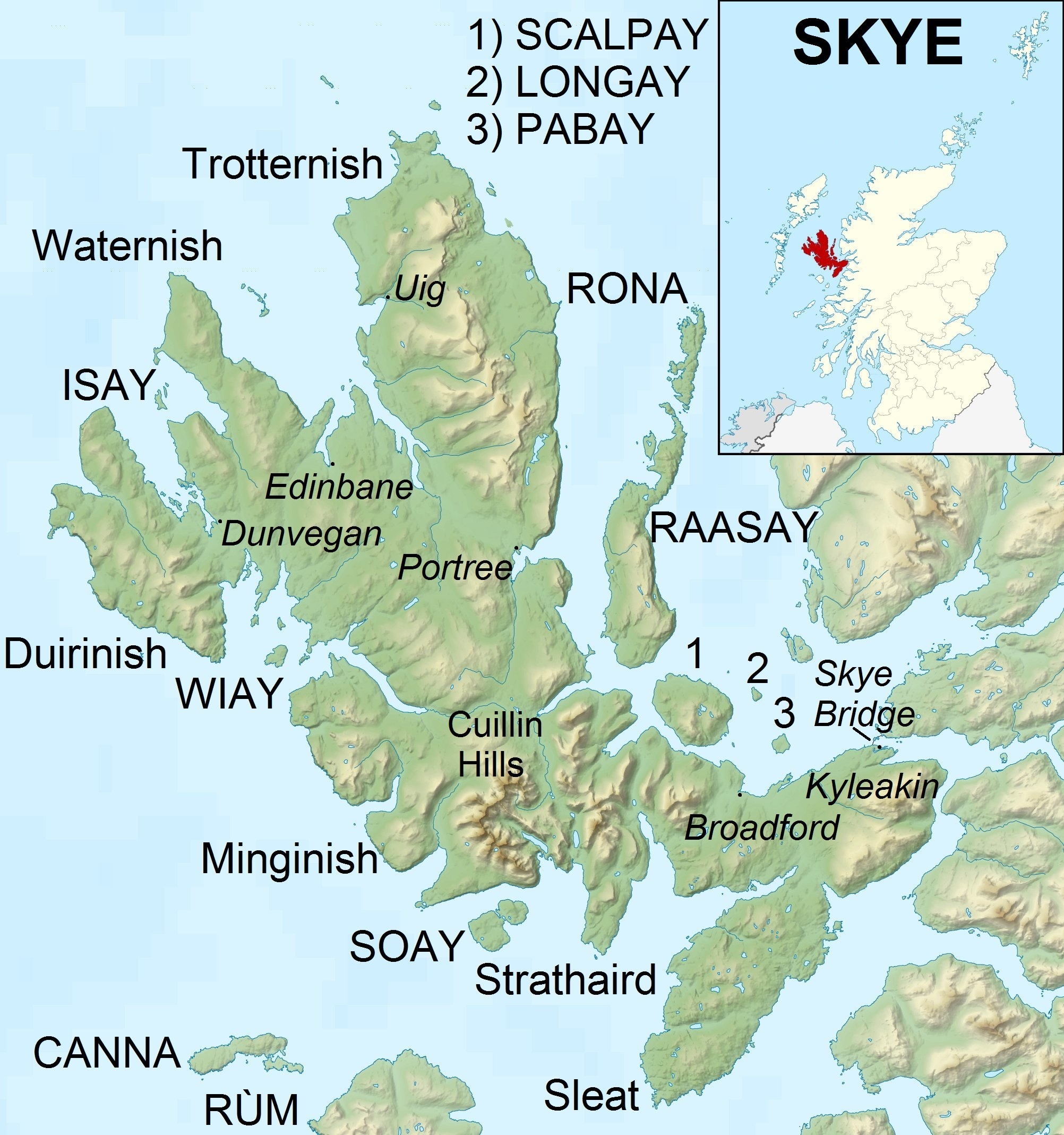
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bun-sgoil Shlèite
Bun-sgoil Shlèite is a primary school on the Sleat peninsula of the island of Skye in Scotland. It is Scotland's only Gaelic Medium School with an English department. It was established in August 2007 though the building originally opened in November 1983. Gaelic medium education In January 2006, Highland Council decided to conduct a formal consultation on a proposal to change Sleat Primary School to a dedicated Gaelic school. The responses indicated that community and parents' views were polarised between those preferring exclusively English and Gaelic educations. The Education, Culture and Sport Committee of the Council met on 21 September 2006 to make a final decision, opting for the compromise of a Gaelic medium school with an English department. Visual arts project In 2009, pupils from the school, along with pupils from Tollcross Primary School in Edinburgh started an 18-month visual art and nature project, designed to link the children who experience Gaelic Medium Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Schools Providing Gaelic-medium Education In Scotland
This is a list of schools and institutions providing Scottish Gaelic–medium education (GME) by area. For convenience the areas listed are not necessarily council or education authority areas unless otherwise noted. There are at least 46 nurseries, 62 primary schools and 29 secondary schools providing GME education in Scotland. Aberdeen City Primary schools * Gilcomstoun Primary School – Provides nursery and primary school GME.Gaelic Education on Aberdeen Council Website Secondary schools * – only provides education in the subject of Gaelic, not Gaelic-medium educat ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmarnock
Kilmarnock (, sco, Kilmaurnock; gd, Cill Mheàrnaig (IPA:[kʰʲɪʎˈveaːɾnəkʲ]), "Marnock's church") is a large town and former burgh in East Ayrshire, Scotland and is the administrative centre of East Ayrshire, East Ayrshire Council. With a population of 46,770, Kilmarnock is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, 14th most populated settlement in Scotland and the largest town in Ayrshire. The town is continuous to nearby neighbouring villages Crookedholm and Hurlford to the east, and Kilmaurs to the west of the town. It includes former villages subsumed by the expansion of the town such as Bonnyton, East Ayrshire, Bonnyton and new purpose built suburbs such as New Farm Loch. The town and the surrounding Greater Kilmarnock area is home to 32 Listed building, listed buildings and structures designated by Historic Environment Scotland. The River Irvine runs through the eastern section of Kilmarnock, and the River Irvine, Kilmarnock Water passes through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portree
Portree (; gd, Port Rìgh, ) is the largest town on, and capital of, the Isle of Skye in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Murray, W.H. (1966) ''The Hebrides''. London. Heinemann. Pages 154-155. It is the location for the only secondary school on the island, Portree High School. Public transport services are limited to buses. Portree has a harbour, fringed by cliffs, with a pier designed by Thomas Telford. Attractions in the town include the Aros centre which celebrates the island's Gaelic heritage. Further arts provision is made through arts organisation ATLAS Arts, a Creative Scotland regularly-funded organisation. The town also serves as a centre for tourists exploring the island.Haswell-Smith, Hamish. (2004) ''The Scottish Islands''. Edinburgh. Canongate. Pages 173-4 Around 939 people (37.72% of the population) can speak Scottish Gaelic. The A855 road leads north out of the town, passing through villages such as Achachork, Staffin and passes the rocky landscape of the Sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)