Skye on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of
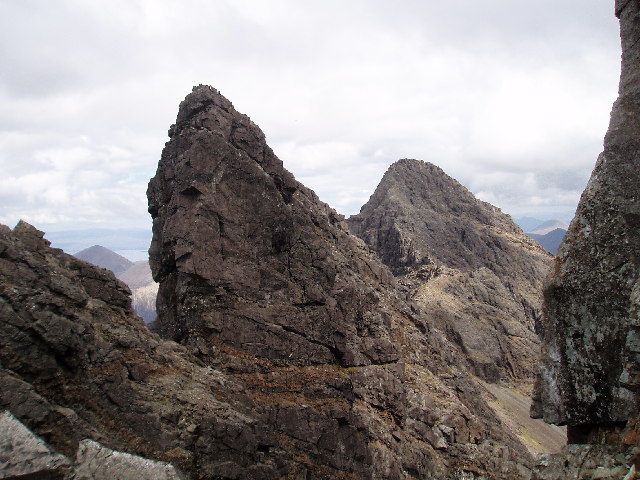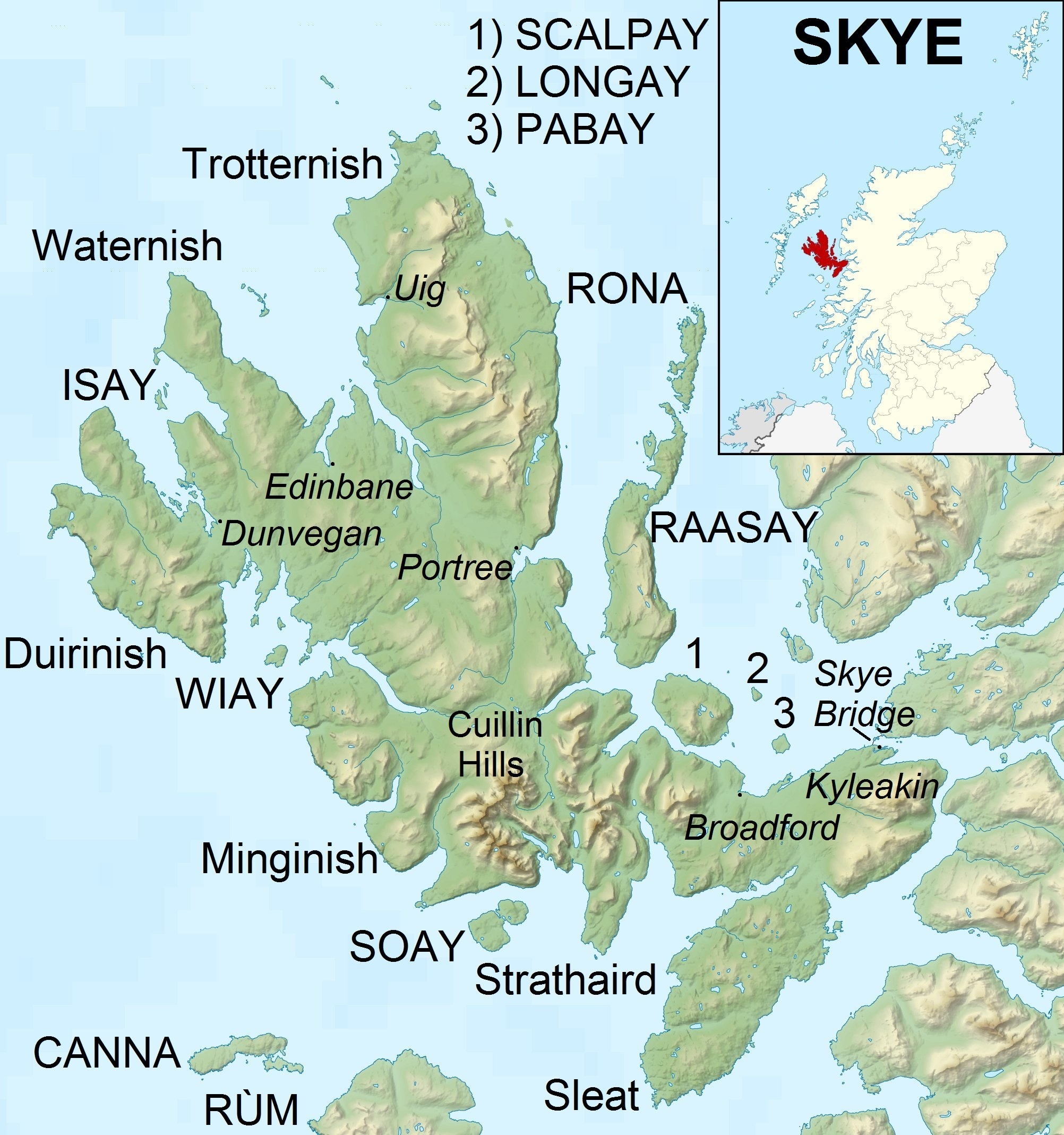


 At , Skye is the second-largest island in Scotland after Lewis and Harris. The coastline of Skye is a series of peninsulas and bays radiating out from a centre dominated by the Cuillin hills (Gaelic: ). Malcolm Slesser suggested that its shape "sticks out of the west coast of northern Scotland like a lobster's claw ready to snap at the fish bone of Harris and Lewis" and W. H. Murray, commenting on its irregular coastline, stated, "Skye is 60 miles 00 kmlong, but what might be its breadth is beyond the ingenuity of man to state".
Martin Martin, a native of the island, reported on it at length in a 1703 publication. His geological observations included a note that:
The Black Cuillin, which are mainly composed of
At , Skye is the second-largest island in Scotland after Lewis and Harris. The coastline of Skye is a series of peninsulas and bays radiating out from a centre dominated by the Cuillin hills (Gaelic: ). Malcolm Slesser suggested that its shape "sticks out of the west coast of northern Scotland like a lobster's claw ready to snap at the fish bone of Harris and Lewis" and W. H. Murray, commenting on its irregular coastline, stated, "Skye is 60 miles 00 kmlong, but what might be its breadth is beyond the ingenuity of man to state".
Martin Martin, a native of the island, reported on it at length in a 1703 publication. His geological observations included a note that:
The Black Cuillin, which are mainly composed of
 Portree in the north at the base of Trotternish is the largest settlement (estimated population 2,264 in 2011)"Highland Profile"
Portree in the north at the base of Trotternish is the largest settlement (estimated population 2,264 in 2011)"Highland Profile"
. The Highland Council (2011 estimate). Retrieved 26 December 2012 and is the main service centre on the island. A December 2018 report recommended the village as "Skye's best home base" for visitors", since it has "a few hotels, hostels and bed-and-breakfasts in town, while more B&Bs line the roads into and out of town". The village also has "banks, churches, cafes and restaurants, a cinema at the Aros Centre, a swimming pool and library ... fuel filling stations and supermarkets". Broadford, the location of the island's only airstrip, is on the east side of the island and Dunvegan in the north-west is well known for its
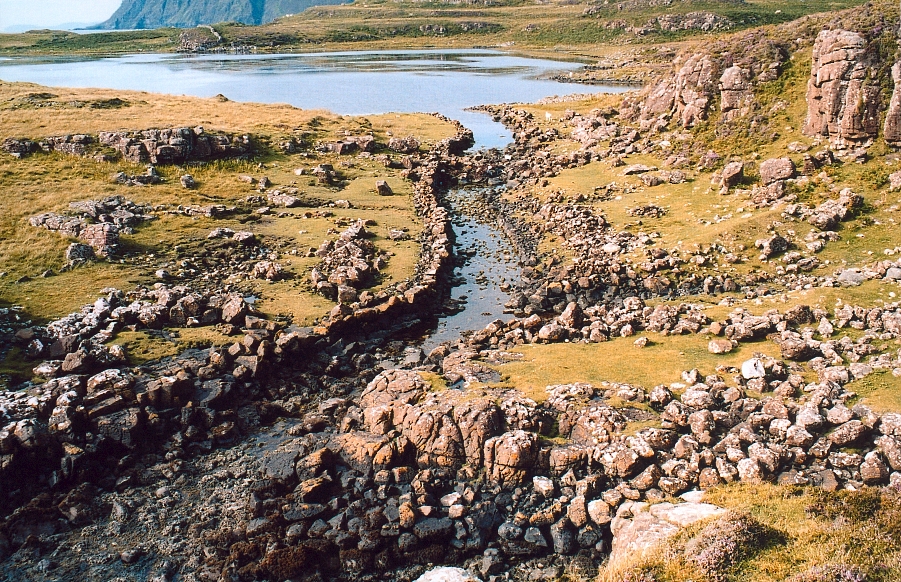 , an uninhabited peninsula to the south of the Cuillin, has a variety of archaeological sites dating from the
, an uninhabited peninsula to the south of the Cuillin, has a variety of archaeological sites dating from the
 After the failure of the
After the failure of the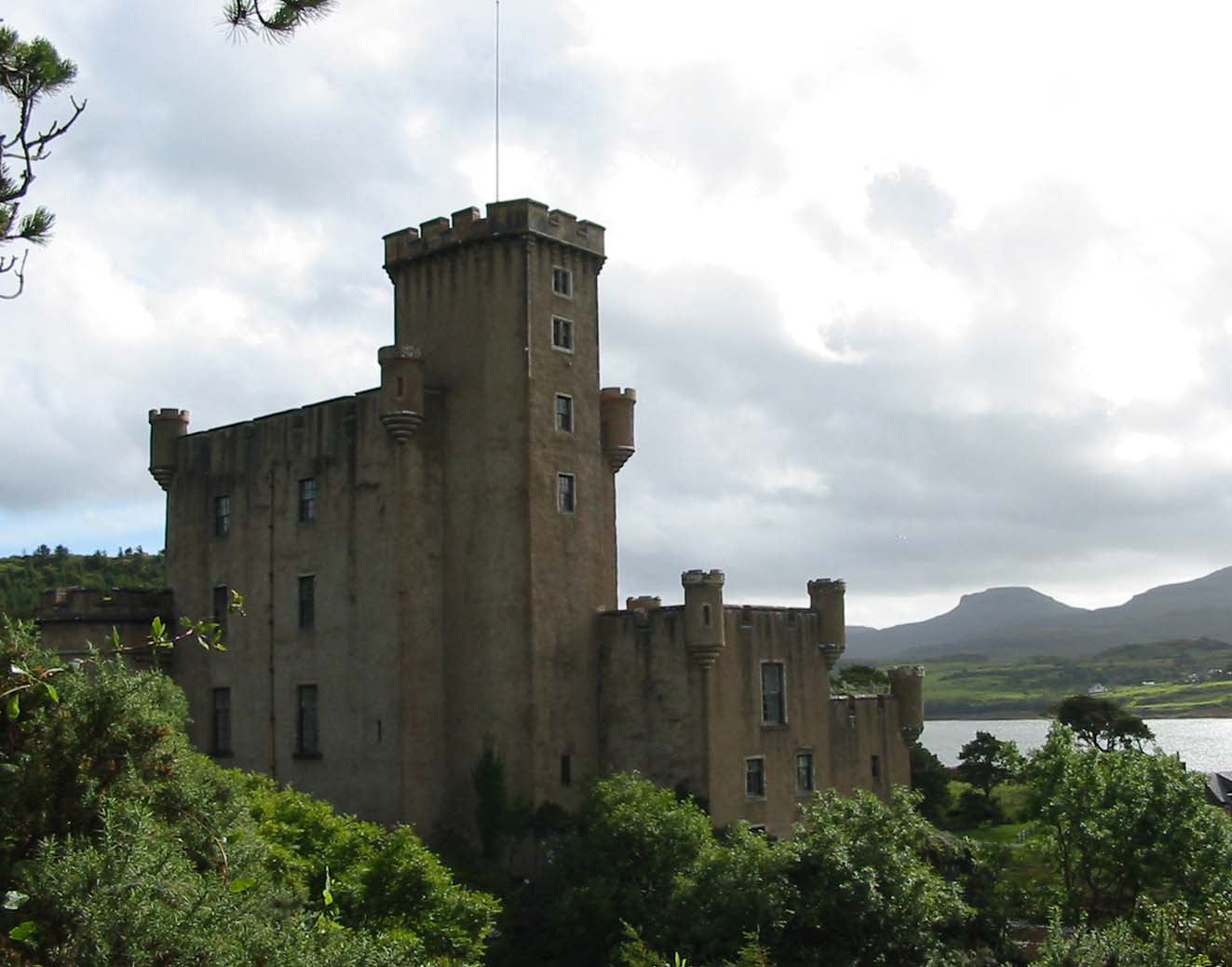  Skye has a rich heritage of ancient monuments from this period. Dunvegan Castle has been the seat of Clan MacLeod since the 13th century. It contains the Fairy Flag and is reputed to have been inhabited by a single family for longer than any other house in Scotland. The 18th-century Armadale Castle, once home of Clan Donald of Sleat, was abandoned as a residence in 1925, but now hosts the Clan Donald Centre. Nearby are the ruins of two more MacDonald strongholds, Knock Castle, and Dunscaith Castle (called "Fortress of Shadows"), the legendary home of warrior woman, martial arts instructor (and, according to some sources, Queen) . , a fortress built in the late 15th century near Kyleakin and once a seat of Clan MacKinnon, is another ruin. Coventry (2008) pp. 381–82.
Skye has a rich heritage of ancient monuments from this period. Dunvegan Castle has been the seat of Clan MacLeod since the 13th century. It contains the Fairy Flag and is reputed to have been inhabited by a single family for longer than any other house in Scotland. The 18th-century Armadale Castle, once home of Clan Donald of Sleat, was abandoned as a residence in 1925, but now hosts the Clan Donald Centre. Nearby are the ruins of two more MacDonald strongholds, Knock Castle, and Dunscaith Castle (called "Fortress of Shadows"), the legendary home of warrior woman, martial arts instructor (and, according to some sources, Queen) . , a fortress built in the late 15th century near Kyleakin and once a seat of Clan MacKinnon, is another ruin. Coventry (2008) pp. 381–82.
 In the late 18th century the harvesting of kelp became a significant activity, but from 1822 onward cheap imports led to a collapse of this industry throughout the Hebrides. During the 19th century, the inhabitants of Skye were also devastated by
In the late 18th century the harvesting of kelp became a significant activity, but from 1822 onward cheap imports led to a collapse of this industry throughout the Hebrides. During the 19th century, the inhabitants of Skye were also devastated by
Canmore. Retrieved 28 December 2012. and Tusdale on Minginish."Skye, Tusdale"
Canmore. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
''1901–2001 Gaelic in the Census''
(PowerPoint) Linguae Celticae. Retrieved 1 June 2008. In the 2001 census Kilmuir had just under half Gaelic speakers, and overall, Skye had 31 per cent, distributed unevenly. The strongest Gaelic areas were in the north and south-west of the island, including Staffin at 61 per cent. The weakest areas were in the west and east (e.g. Luib 23 per cent and Kylerhea 19 per cent). Other areas on Skye ranged between 48 per cent and 25 per cent.
 In terms of
In terms of
The Highland Council. Retrieved 8 March 2008. Following the
 The largest employer on the island and its environs is the public sector, which accounts for about a third of the total workforce, principally in administration, education and health. The second-largest employer in the area is the distribution, hotels and restaurants sector, highlighting the importance of tourism. Key attractions include Dunvegan Castle, the
The largest employer on the island and its environs is the public sector, which accounts for about a third of the total workforce, principally in administration, education and health. The second-largest employer in the area is the distribution, hotels and restaurants sector, highlighting the importance of tourism. Key attractions include Dunvegan Castle, the
 A report published in mid-2020 indicated that visitors to Skye added £211 million in 2019 to the island's economy, prior to travel restrictions imposed because of the
A report published in mid-2020 indicated that visitors to Skye added £211 million in 2019 to the island's economy, prior to travel restrictions imposed because of the
 The Skye Bridge opened in 1995 under a
The Skye Bridge opened in 1995 under a
 Students of Scottish Gaelic travel from all over the world to attend , the Scottish Gaelic college based near Kilmore in Sleat. In addition to members of the
Students of Scottish Gaelic travel from all over the world to attend , the Scottish Gaelic college based near Kilmore in Sleat. In addition to members of the  The poet Sorley MacLean, a native of the Isle of Raasay, which lies off the island's east coast, lived much of his life on Skye. The island has been immortalised in the traditional song " The Skye Boat Song" and is the notional setting for the novel '' To the Lighthouse'' by
The poet Sorley MacLean, a native of the Isle of Raasay, which lies off the island's east coast, lived much of his life on Skye. The island has been immortalised in the traditional song " The Skye Boat Song" and is the notional setting for the novel '' To the Lighthouse'' by
The Ice Twins
by S K Tremayne, published around the world in 2015–2016, is set in southern Skye, especially around the settlement and islands of Isleornsay.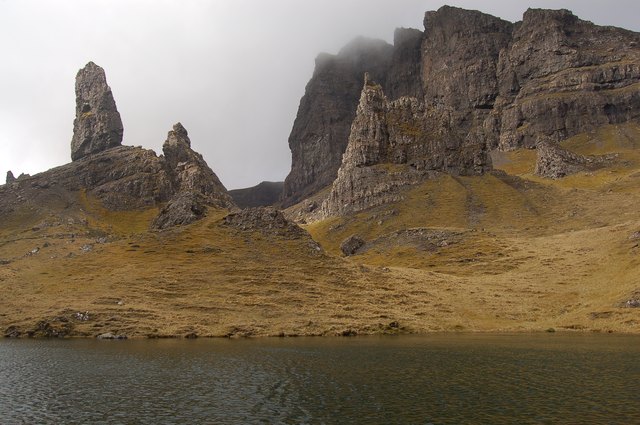 Skye has been used as a location for a number of feature films. The Ashaig aerodrome was used for the opening scenes of the 1980 film '' Flash Gordon''. ''
Skye has been used as a location for a number of feature films. The Ashaig aerodrome was used for the opening scenes of the 1980 film '' Flash Gordon''. ''
. Prometheus News. Retrieved 4 July 2012. In 1973 '' The Highlands and Islands - a Royal Tour'', a documentary about Prince Charles's visit to the Highlands and Islands, directed by Oscar Marzaroli, was shot partly on Skye. Scenes from the Scottish Gaelic-language BBC Alba television series '' Bannan'' were filmed on the island. The '' West Highland Free Press'' is published at Broadford. This weekly newspaper takes as its motto ("The Land, the Language and the People"), which reflects its radical, campaigning priorities. The ''Free Press'' was founded in 1972 and circulates in Skye, Wester Ross and the Outer Hebrides.
The '' West Highland Free Press'' is published at Broadford. This weekly newspaper takes as its motto ("The Land, the Language and the People"), which reflects its radical, campaigning priorities. The ''Free Press'' was founded in 1972 and circulates in Skye, Wester Ross and the Outer Hebrides.
reflects the Island's Gaelic heritage, the Viking heritage and the history of Flora MacDonald. The flag has a birlinn in the canton, and there are five oars representing the five areas of Skye, Trotternish, Waternish, Duirinish, Minginish and Sleat. Yellow represents the MacLeods, and Blue the MacDonalds or the MacKinnons.
 In the modern era avian life includes the corncrake, red-throated diver, kittiwake, tystie, Atlantic puffin, goldeneye and
In the modern era avian life includes the corncrake, red-throated diver, kittiwake, tystie, Atlantic puffin, goldeneye and
''Clan chief Hugh Macleod’s forest will rewild Skye landscape''
The Times, 2 December 2020
Skye - Wikivoyage
edited by
Skye photos
Skye Birding Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Skye, Isle of Islands of Highland (council area) Islands of the Inner Hebrides Islands of the United Kingdom Cleared places in the Inner Hebrides
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins.
The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of
MacLeod and MacDonald
Macdonald, MacDonald or McDonald may refer to:
Organisations
* McDonald's, a chain of fast food restaurants
* McDonald & Co., a former investment firm
* MacDonald Motorsports, a NASCAR team
* Macdonald Realty, a Canadian real estate brokerage f ...
. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearances that replaced entire communities with sheep farms, some of which involved forced emigrations to distant lands. Resident numbers declined from over 20,000 in the early 19th century to just under 9,000 by the closing decade of the 20th century. Skye's population increased by 4% between 1991 and 2001. About a third of the residents were Gaelic speakers in 2001, and although their numbers are in decline, this aspect of island culture remains important.
The main industries are tourism, agriculture, fishing, and forestry. Skye is part of the Highland Council
The Highland Council (' ), the political body covering the Highland (council area), Highland Local authorities of Scotland, local authority created in 1995, comprises 21 wards, each electing three or four councillors by the single transferable v ...
local government area. The island's largest settlement is Portree, which is also its capital, known for its picturesque harbour. Links to various nearby islands by ferry are available, and since 1995, to the mainland by a road bridge. The climate is mild, wet, and windy. The abundant wildlife includes the golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
, red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
, and Atlantic salmon. The local flora is dominated by heather moor, and nationally important invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
populations live on the surrounding sea bed. Skye has provided the locations for various novels and feature films, and is celebrated in poetry and song.
Etymology
The first written references to the island are Roman sources such as the ''Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Tex ...
'', which refers to ''Scitis'' and ''Scetis'', which can be found on a map by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
. One possible derivation comes from ''skitis'', an early Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
ic word for "winged", which may describe how the island's peninsulas radiate out from a mountainous centre. Haswell-Smith (2004) pp. 173–79. Subsequent Gaelic-, Norse- and English-speaking peoples have influenced the history of Skye; the relationships between their names for the island are not straightforward. Various etymologies have been proposed, such as the "winged isle" or "the notched isle", p. 105. but no definitive solution has been found to date; the place name may be from an earlier, non-Gaelic language.
In the Norse sagas, Skye is called , for example in the and a skaldic poem in the from around 1230 contains a line that translates as "the hunger battle-birds were filled in Skye with blood of foemen killed". The island was also referred to by the Norse as (misty isle), or (isle of cloud). The traditional Gaelic name is (the island of Skye), being a more recent and less common spelling. In 1549, Donald Munro, High Dean of the Isles, wrote of "Sky": "" but the meaning of this Gaelic name is unclear.
, which means "island of the mist" (a translation of the Norse name), is a poetic Gaelic name for the island.
Geography



 At , Skye is the second-largest island in Scotland after Lewis and Harris. The coastline of Skye is a series of peninsulas and bays radiating out from a centre dominated by the Cuillin hills (Gaelic: ). Malcolm Slesser suggested that its shape "sticks out of the west coast of northern Scotland like a lobster's claw ready to snap at the fish bone of Harris and Lewis" and W. H. Murray, commenting on its irregular coastline, stated, "Skye is 60 miles 00 kmlong, but what might be its breadth is beyond the ingenuity of man to state".
Martin Martin, a native of the island, reported on it at length in a 1703 publication. His geological observations included a note that:
The Black Cuillin, which are mainly composed of
At , Skye is the second-largest island in Scotland after Lewis and Harris. The coastline of Skye is a series of peninsulas and bays radiating out from a centre dominated by the Cuillin hills (Gaelic: ). Malcolm Slesser suggested that its shape "sticks out of the west coast of northern Scotland like a lobster's claw ready to snap at the fish bone of Harris and Lewis" and W. H. Murray, commenting on its irregular coastline, stated, "Skye is 60 miles 00 kmlong, but what might be its breadth is beyond the ingenuity of man to state".
Martin Martin, a native of the island, reported on it at length in a 1703 publication. His geological observations included a note that:
The Black Cuillin, which are mainly composed of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
and gabbro, include 12 Munros and provide some of the most dramatic and challenging mountain terrain in Scotland. The ascent of is one of the longest rock climbs in Britain and the Inaccessible Pinnacle
Inaccessible Island is a volcanic island located in the South Atlantic Ocean, south-west of Tristan da Cunha. Its highest point, Cairn Peak, reaches , and the island is in area. The volcano was last active six million years ago and is curren ...
is the only peak in Scotland that requires technical climbing skills to reach the summit. Nearby Sgùrr Alasdair, meanwhile, is the tallest mountain on any Scottish island. These hills make demands of the hill walker that exceed any others found in Scotland and a full traverse of the Cuillin ridge may take 15–20 hours. The Red Hills (Gaelic: ) to the east are also known as the Red Cuillin. They are mainly composed of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
that has weathered into more rounded hills with many long scree slopes on their flanks. The highest point of these hills is Glamaig, one of only two Corbetts on Skye.
The northern peninsula of Trotternish is underlain by basalt, which provides relatively rich soils and a variety of unusual rock features. The Kilt Rock is named after the columnar structure of the cliffs, said to resemble the pleats in a kilt. The Quiraing is a spectacular series of rock pinnacles on the eastern side of the main spine of the peninsula and further south is the rock pillar of the Old Man of Storr. The view of the Quiraing and the Old Man of Storr is one of the most iconic in all of Scotland, and is frequently used on calendars and tourism guides and brochures.
Beyond Loch Snizort to the west of Trotternish is the Waternish peninsula, which ends in Ardmore Point's double rock arch. Duirinish peninsula is separated from Waternish by Loch Dunvegan, which contains the island of Isay. It is ringed by sea cliffs that reach on the west at Waterstein Head and on the northwest at Biod an Athair where, a metre from the summit trig pillar, the cliffs drop to the ocean. Oolitic loam provides good arable land in the main valley. Lochs Bracadale and Harport and the island of Wiay lie between Duirinish and Minginish, which includes the narrower defiles of Talisker
Talisker ( gd, Talasgair) is a settlement on the Minginish peninsula in the Isle of Skye, Scotland.
History
Talisker was for centuries a possession of the Clan Macleod. For nearly two hundred years it was associated with a cadet branch of the ...
and Glen Brittle and whose beaches are formed from black basaltic sands. Strathaird is a relatively small peninsula close to the Cuillin hills with only a few crofting communities, the island of Soay lies offshore. The bedrock of Sleat in the south is Torridonian sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, which produces poor soils and boggy ground, although its lower elevations and relatively sheltered eastern shores enable a lush growth of hedgerows and crops. The islands of Raasay, Rona
Rona, RONA or Róna may refer to:
Places
* Rona (Kristiansand), a neighbourhood in Kristiansand, Norway
*Rona (river), a river in Maramureș County, Romania
*Rona, Bellevue Hill, a historic house in the Sydney suburb of Bellevue Hill
* Rona, Swit ...
, Scalpay and Pabay all lie to the north and east between Skye and the mainland.
Towns and villages
 Portree in the north at the base of Trotternish is the largest settlement (estimated population 2,264 in 2011)"Highland Profile"
Portree in the north at the base of Trotternish is the largest settlement (estimated population 2,264 in 2011)"Highland Profile". The Highland Council (2011 estimate). Retrieved 26 December 2012 and is the main service centre on the island. A December 2018 report recommended the village as "Skye's best home base" for visitors", since it has "a few hotels, hostels and bed-and-breakfasts in town, while more B&Bs line the roads into and out of town". The village also has "banks, churches, cafes and restaurants, a cinema at the Aros Centre, a swimming pool and library ... fuel filling stations and supermarkets". Broadford, the location of the island's only airstrip, is on the east side of the island and Dunvegan in the north-west is well known for its
castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
and the nearby Three Chimneys restaurant. The 18th-century Stein Inn on the Waternish coast is the oldest pub on Skye. Kyleakin is linked to Kyle of Lochalsh on the mainland by the Skye Bridge, which spans the narrows of Loch Alsh. Uig UIG, Uig or uig is a placename meaning "bay" (from Norse) and may refer to:
Places
* Uig, Coll, a hamlet on the island of Coll, Argyll and Bute, Scotland
* Uig, Duirinish, a hamlet near Totaig, on the Isle of Skye, Highland Scotland
* Uig, Lewi ...
, the port for ferries to the Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coas ...
, is on the west of the Trotternish peninsula and Edinbane is between Dunvegan and Portree. Much of the rest of the population lives in crofting townships scattered around the coastline.
Climate
The influence of theAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
and the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Uni ...
create a mild oceanic climate. Temperatures are generally cool, averaging in January and in July at Duntulm in Trotternish. Snow seldom lies at sea level and frosts are less frequent than on the mainland. Winds are a limiting factor for vegetation. South-westerlies are the most common and speeds of have been recorded. High winds are especially likely on the exposed coasts of Trotternish and Waternish. Murray (1966) p. 147. In common with most islands of the west coast of Scotland, rainfall is generally high at per annum and the elevated Cuillin are wetter still. Variations can be considerable, with the north tending to be drier than the south. Broadford, for example, averages more than of rain per annum. Trotternish typically has 200 hours of bright sunshine in May, the sunniest month. On 28 December 2015, the temperature reached 15 °C, beating the previous December record of 12.9 °C, set in 2013. On 9 May 2016, a temperature of 26.7 °C (80.1 °F) was recorded at Lusa in the south-east of the island.
History
Prehistory
AMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
hunter-gatherer site dating to the seventh millennium BC at in Staffin is one of the oldest archaeological sites in Scotland. Its occupation is probably linked to that of the rock shelter at Sand, Applecross, on the mainland coast of Wester Ross, where tools made of a mudstone from have been found. Surveys of the area between the two shores of the Inner Sound and Sound of Raasay have revealed 33 sites with potentially Mesolithic deposits. Finds of bloodstone
Bloodstone may refer to:
*Heliotrope (mineral) or bloodstone, a form of chalcedony
Film
* ''Bloodstone'' (1988 film), an Indian-American action/comedy film
*'' Bloodstone: Subspecies II'', a 1993 horror film
* Bloodstone: An Epic Dwarven Tale, ano ...
microliths on the foreshore at Orbost on the west coast of the island near Dunvegan also suggest Mesolithic occupation. These tools probably originated from the nearby island of . Similarly, bloodstone from Rum, and baked mudstone, from the Staffin area, were found at the Mesolithic site of Camas Daraich, also from the seventh millennium BC, on the Point of Sleat, which has led archaeologists to believe that Mesolithic people on Skye would travel fairly significant distances, at least 70 km, both by land and sea.
 , an uninhabited peninsula to the south of the Cuillin, has a variety of archaeological sites dating from the
, an uninhabited peninsula to the south of the Cuillin, has a variety of archaeological sites dating from the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
onwards. A second- or third-millennium BC chambered cairn, an Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
promontory fort, and the remains of another prehistoric settlement dating from the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
are nearby. on the peninsula is linked to the sea by an artificial "Viking" canal that may date from the later period of Norse settlement. Dun Ringill
Dun Ringill (Gaelic: ''Dùn'', 'fort', ''Ringill'', 'point of the ravine') is an Iron Age hill fort on the Strathaird peninsula on the island of Skye, Scotland. Further fortified in the Middle Ages, tradition holds that it was for several centu ...
is a ruined Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
hill fort on the Strathaird Peninsula, which was further fortified in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and may have become the seat of Clan MacKinnon.
Early history
The late Iron Age inhabitants of the northern and western Hebrides were probably Pictish, although the historical record is sparse. Three Pictish symbol stones have been found on Skye and a fourth on Raasay. More is known of the kingdom of to the south; Adomnán's life ofColumba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is tod ...
, written shortly before 697, portrays the saint visiting Skye (where he baptised a pagan leader using an interpreter) and Adomnán himself is thought to have been familiar with the island. The Irish annals record a number of events on Skye in the later seventh and early eighth centuries – mainly concerning the struggles between rival dynasties that formed the background to the Old Irish language romance .
Legendary hero Cú Chulainn
Cú Chulainn ( ), called the Hound of Ulster ( Irish: ''Cú Uladh''), is a warrior hero and demigod in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology, as well as in Scottish and Manx folklore. He is believed to be an incarnation of the Irish god Lug ...
is said to have trained on the Isle of Skye with warrior woman Scáthach.
The Norse held sway throughout the Hebrides from the 9th century until after the Treaty of Perth in 1266. However, apart from placenames, little remains of their presence on Skye in the written or archaeological record. Apart from the name "Skye" itself, all pre-Norse placenames seem to have been obliterated by the Scandinavian settlers. Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and s ...
heritage, with Celtic heritage is claimed by Clan MacLeod. Norse tradition is celebrated in the winter fire festival at Dunvegan, during which a replica Viking long boat is set alight.
Clans and Scottish rule
The most powerful clans on Skye in the post–Norse period were Clan MacLeod, originally based in Trotternish, andClan Macdonald of Sleat
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
. The isle was held by Donald Macdonald, Lord of the Isles’ half-brother, Godfrey, from 1389 until 1401, at which time Skye was declared part of Ross. When the Donald Macdonald, Lord of the Isles, re-gained Ross after the battle of Harlaw in 1411, they added "Earl of Ross" to their lords' titles. Skye came with Ross.
Following the disintegration of the Lordship of the Isles, Clan Mackinnon also emerged as an independent clan, whose substantial landholdings in Skye were centred on Strathaird. Clan MacNeacail
Clan MacNeacail, sometimes known as Clan MacNicol, is a Scottish clan long associated with the Isle of Skye. Tradition states that, early in its history, the clan held the Isle of Lewis, as well as extensive territory on the north-western mai ...
also have a long association with Trotternish, and in the 16th century many of the MacInnes clan
Clan MacInnes is a Scottish clan originally from the western highlands of Scotland. The origin of clan (MacInnes, McInnes, or in Gaelic: Mhic Aonghais or MacAonghais) is Morvern and Ardgour, Argylshire, with its clan name coming into exis ...
moved to Sleat. The MacDonalds of South Uist were bitter rivals of the MacLeods, and an attempt by the former to murder church-goers at Trumpan in retaliation for a previous massacre on Eigg, resulted in the Battle of the Spoiling Dyke of 1578.
 After the failure of the
After the failure of the Jacobite
Jacobite means follower of Jacob or James. Jacobite may refer to:
Religion
* Jacobites, followers of Saint Jacob Baradaeus (died 578). Churches in the Jacobite tradition and sometimes called Jacobite include:
** Syriac Orthodox Church, sometimes ...
rebellion of 1745, Flora MacDonald
Flora MacDonald (Gaelic: ''Fionnghal nic Dhòmhnaill'', 1722 - 5 March 1790) was a member of Clan Macdonald of Sleat, best known for helping Charles Edward Stuart evade government troops after the Battle of Culloden in April 1746. Her family ...
became famous for rescuing Prince Charles Edward Stuart from the Hanoverian
The adjective Hanoverian is used to describe:
* British monarchs or supporters of the House of Hanover, the dynasty which ruled the United Kingdom from 1714 to 1901
* things relating to;
** Electorate of Hanover
** Kingdom of Hanover
** Province o ...
troops. Although she was born on South Uist, her story is strongly associated with their escape via Skye, and she is buried at Kilmuir in Trotternish. Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. The ''Oxford D ...
and James Boswell's visit to Skye in 1773 and their meeting with Flora MacDonald in Kilmuir is recorded in Boswell's ''The Journal of a Tour to the Hebrides
''The Journal of a Tour to the Hebrides with Samuel Johnson, LL.D.'' is a travel journal by Scotland, Scotsman James Boswell first published in 1785. In 1773, Boswell enticed his English friend Samuel Johnson to accompany him on a tour through ...
''. Boswell wrote, "To see Dr Samuel Johnson, the great champion of the English Tories, salute Miss Flora MacDonald in the isle of Sky, was a striking sight; for though somewhat congenial in their notions, it was very improbable they should meet here". Johnson's words that Flora MacDonald was "A name that will be mentioned in history, and if courage and fidelity be virtues, mentioned with honour" are written on her gravestone. After this rebellion, the clan system was broken up and Skye became a series of landed estates.
Of the island in general, Johnson observed:
 Skye has a rich heritage of ancient monuments from this period. Dunvegan Castle has been the seat of Clan MacLeod since the 13th century. It contains the Fairy Flag and is reputed to have been inhabited by a single family for longer than any other house in Scotland. The 18th-century Armadale Castle, once home of Clan Donald of Sleat, was abandoned as a residence in 1925, but now hosts the Clan Donald Centre. Nearby are the ruins of two more MacDonald strongholds, Knock Castle, and Dunscaith Castle (called "Fortress of Shadows"), the legendary home of warrior woman, martial arts instructor (and, according to some sources, Queen) . , a fortress built in the late 15th century near Kyleakin and once a seat of Clan MacKinnon, is another ruin. Coventry (2008) pp. 381–82.
Skye has a rich heritage of ancient monuments from this period. Dunvegan Castle has been the seat of Clan MacLeod since the 13th century. It contains the Fairy Flag and is reputed to have been inhabited by a single family for longer than any other house in Scotland. The 18th-century Armadale Castle, once home of Clan Donald of Sleat, was abandoned as a residence in 1925, but now hosts the Clan Donald Centre. Nearby are the ruins of two more MacDonald strongholds, Knock Castle, and Dunscaith Castle (called "Fortress of Shadows"), the legendary home of warrior woman, martial arts instructor (and, according to some sources, Queen) . , a fortress built in the late 15th century near Kyleakin and once a seat of Clan MacKinnon, is another ruin. Coventry (2008) pp. 381–82.
Economic turmoil and mass emigration
 In the late 18th century the harvesting of kelp became a significant activity, but from 1822 onward cheap imports led to a collapse of this industry throughout the Hebrides. During the 19th century, the inhabitants of Skye were also devastated by
In the late 18th century the harvesting of kelp became a significant activity, but from 1822 onward cheap imports led to a collapse of this industry throughout the Hebrides. During the 19th century, the inhabitants of Skye were also devastated by famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accom ...
and Clearances. Thirty thousand people were evicted between 1840 and 1880 alone, many of them forced to emigrate to the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
. The " Battle of the Braes" involved a demonstration against a lack of access to land and the serving of eviction notices. The incident involved numerous crofters and about 50 police officers. This event was instrumental in the creation of the Napier Commission, which reported in 1884 on the situation in the Highlands. Disturbances continued until the passing of the 1886 Crofters' Act and on one occasion 400 marines were deployed on Skye to maintain order. The ruins of cleared villages can still be seen at Lorgill, Boreraig and Suisnish in Strath Swordale, Haswell-Smith (2004) p. 176."Suisnish, Skye"Canmore. Retrieved 28 December 2012. and Tusdale on Minginish."Skye, Tusdale"
Canmore. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
Overview of population trends
As with many Scottish islands, Skye's population peaked in the 19th century and then declined under the impact of the Clearances and the military losses in theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
. From the 19th century until 1975 Skye was part of the county of Inverness-shire, but the crofting economy languished and according to Slesser, "Generations of UK governments have treated the island people contemptuously" --a charge that has been levelled at both Labour and Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
administrations' policies in the Highlands and Islands. By 1971 the population was less than a third of its peak recorded figure in 1841. However, the number of residents then grew by over 28 per cent in the thirty years to 2001. The changing relationship between the residents and the land is evidenced by Robert Carruthers's remark circa 1852 that, "There is now a village in Portree containing three hundred inhabitants." Even if this estimate is inexact the population of the island's largest settlement has probably increased sixfold or more since then. During the period the total number of island residents has declined by 50 per cent or more.The island-wide population increase of 4 per cent between 1991 and 2001 occurred against the background of an overall reduction in Scottish island populations of 3 per cent for the same period. By 2011 the population had risen a further 8.4% to 10,008 with Scottish island populations as a whole growing by 4% to 103,702.
Language
Historically, Skye was overwhelmingly Gaelic-speaking, but this changed between 1921 and 2001. In both the 1901 and 1921 censuses, all Skye parishes were more than 75 per cent Gaelic-speaking. By 1971, only Kilmuir parish had more than three-quarters Gaelic speakers while the rest of Skye ranged between 50 and 74 per cent. At that time, Kilmuir was the only area outside the Western Isles that had such a high proportion of Gaelic speakers.Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2004''1901–2001 Gaelic in the Census''
(PowerPoint) Linguae Celticae. Retrieved 1 June 2008. In the 2001 census Kilmuir had just under half Gaelic speakers, and overall, Skye had 31 per cent, distributed unevenly. The strongest Gaelic areas were in the north and south-west of the island, including Staffin at 61 per cent. The weakest areas were in the west and east (e.g. Luib 23 per cent and Kylerhea 19 per cent). Other areas on Skye ranged between 48 per cent and 25 per cent.
Government and politics
 In terms of
In terms of local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-lo ...
, from 1975 to 1996, Skye, along with the neighbouring mainland area of Lochalsh
Lochalsh is a district of mainland Scotland that is currently part of the Highland council area. The Lochalsh district covers all of the mainland either side of Loch Alsh - and of Loch Duich - between Loch Carron and Loch Hourn, ie. from Stromef ...
, constituted a local government district within the Highland administrative area. In 1996 the district was included into the unitary Highland Council
The Highland Council (' ), the political body covering the Highland (council area), Highland Local authorities of Scotland, local authority created in 1995, comprises 21 wards, each electing three or four councillors by the single transferable v ...
, () based in Inverness and formed one of the new council's area committees
Many large local government councils in the United Kingdom have a system of area committees or area boards, which involve local people and organisations in decisions affecting council spending within their area. They cover a geographical area su ...
."The Highland Council ()"The Highland Council. Retrieved 8 March 2008. Following the
2007 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 2007.
* Electoral calendar 2007
* Elections in 2007
* 2007 United Nations Security Council election
Africa
* 52nd National Conference of the African National Congress
* 2007 Algerian legislative elec ...
, Skye now forms a four-member ward called ; it is currently represented by two independents, one Scottish National Party, and one Liberal Democrat councillor.
Skye is in the Highlands and Islands electoral region and comprises a part of the Skye, Lochaber and Badenoch constituency of the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holy ...
, which elects one member under the first past the post
In a first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP or FPP), formally called single-member plurality voting (SMP) when used in single-member districts or informally choose-one voting in contrast to ranked voting, or score voting, voters cast thei ...
basis to represent it. Kate Forbes is the current MSP for the SNP. In addition, Skye forms part of the wider Ross, Skye and Lochaber constituency, which elects one member to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
in Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buck ...
. The present MP Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house ...
is Ian Blackford of the Scottish National Party, who took office after the SNP's sweep in the General Election of 2015. Prior to this, Charles Kennedy, a Liberal Democrat, had represented the area since the 1983 general election
The following elections occurred in the year 1983.
Africa
* 1983 Cameroonian parliamentary election
* 1983 Equatorial Guinean legislative election
* 1983 Kenyan general election
* 1983 Malagasy parliamentary election
* 1983 Malawian general e ...
.
Economy
 The largest employer on the island and its environs is the public sector, which accounts for about a third of the total workforce, principally in administration, education and health. The second-largest employer in the area is the distribution, hotels and restaurants sector, highlighting the importance of tourism. Key attractions include Dunvegan Castle, the
The largest employer on the island and its environs is the public sector, which accounts for about a third of the total workforce, principally in administration, education and health. The second-largest employer in the area is the distribution, hotels and restaurants sector, highlighting the importance of tourism. Key attractions include Dunvegan Castle, the Clan Donald Visitor Centre
Armadale Castle is a ruined Scottish estate houses, country house in Armadale, Skye, former home of the MacDonalds. A mansion house was first built here around 1790, facing south-east over the Sound of Sleat. In 1815 a square Tudor-Gothic mock-ca ...
, and The Aros Experience arts and exhibition centre in Portree. There are about a dozen large landowners on Skye, the largest being the public sector, with the Scottish Government owning most of the northern part of the island. Glendale is a community-owned estate in Duirinish, and the Sleat Community Trust, the local development trust, is active in various regeneration projects.
Small firms dominate employment in the private sector. The Talisker Distillery
Talisker Distillery is an island single malt Scotch whisky distillery based in Carbost, Scotland on the Minginish Peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The distillery is operated by Diageo and Taliskers’ 10 year old whisky has been nominated as par ...
, which produces a single malt whisky, is beside Loch Harport on the west coast of the island. Torabhaig distillery located in Teangue opened in 2017 and also produces whisky. Three other whiskies— ("son of the sea"), ("wee dram of the isles") and ("black pot")—are produced by blender ("smugglers den by the Sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by ...
of Sleat"), based at . These are marketed using predominantly Gaelic-language labels. The blended whisky branded as "Isle of Skye" is produced not on the island but by the Glengoyne Distillery at Killearn north of Glasgow, though the website of the owners, Ian Macleod Distillers Ltd., boasts a "high proportion of Island malts" and contains advertisements for tourist businesses in the island. There is also an established software presence on Skye, with Portree-based Sitekit having expanded in recent years.
Crofting is still important, but although there are about 2,000 crofts on Skye only 100 or so are large enough to enable a crofter to earn a livelihood entirely from the land. In recent years, families have complained about the increasing prices for land that make it difficult for young people to start their own crofts.
Cod and herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Ocea ...
stocks have declined but commercial fishing remains important, especially fish farming of salmon and shellfish such as scampi. The west coast of Scotland has a considerable renewable energy potential and the Isle of Skye Renewables Co-op has recently bought a stake in the Ben Aketil wind farm near Dunvegan. There is a thriving arts and crafts sector.
The unemployment rate in the area tends to be higher than in the Highlands as a whole, and is seasonal in nature, in part due to the impact of tourism. The population is growing and in common with many other scenic rural areas in Scotland, significant increases are expected in the percentage of the population aged 45 to 64 years.
The restrictions required by the worldwide pandemic increased unemployment in the Highlands and Islands in summer 2020 to 5.7%; that was significantly higher than the 2.4 per cent in 2019. The rates were said to be highest in "Lochaber, Skye and Wester Ross and Argyll and the Islands". A December 2020 report stated that between March (just before the effects of pandemic were noted) and December, the unemployment rate in the region increased by "more than 97%" and suggested that the outlook was even worse for spring 2021.
Tourism
 A report published in mid-2020 indicated that visitors to Skye added £211 million in 2019 to the island's economy, prior to travel restrictions imposed because of the
A report published in mid-2020 indicated that visitors to Skye added £211 million in 2019 to the island's economy, prior to travel restrictions imposed because of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
. The report added that "Skye and Raasay attracted 650,000 visitors n 2018and supported 2,850 jobs". The government estimated that tourism in Scotland would decline by over 50% as a result of the pandemic. "Skye is highly vulnerable to the downturn in international visitors that will continue for much of 2020 and beyond", Professor John Lennon of Glasgow Caledonian University told a reporter in July 2020.
Tourism in the Highlands and Islands was negatively impacted by the pandemic, the effects of which continued into 2021. A September 2020 report stated that the region "has been disproportionately impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic to date, when compared to Scotland and the UK as a whole". The industry required short term support for "business survival and recovery" and that was expected to continue as the sector was "severely impacted for as long as physical distancing and travel restrictions". A scheme called Island Equivalent was introduced by the Scottish government in early 2021 to financially assist hospitality and retail businesses "affected by Level 3 coronavirus restrictions". Previous schemes in 2020 included the Strategic Framework Business Fund and the Coronavirus Business Support Fund.
Prior to the pandemic, during summer 2017, islanders complained about an excessive number of tourists, which was causing overcrowding in popular locations such Glen Brittle, the Neist Point lighthouse and at the Quiraing and the Old Man of Storr. "Skye is buckling under the weight of increased tourism this year", said the operator of a self-catering cottage; the problem was most significant at "the key iconic destinations, like the Old Man of Storr and the Quiraing", he added. Chris Taylor of VisitScotland
VisitScotland, formerly the Scottish Tourist Board, is a national tourism organisation for Scotland. It is an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government, with offices in Edinburgh, Glasgow, Aberdeen, Inverness, and other ...
sympathised with the concerns and said that the agency was working on a long-term solution. "But the benefits to Skye of bringing in international visitors and increased spending are huge," he added.
An article published in 2020 confirmed that (prior to the pandemic), the Talisker Distillery and Dunvegan Castle were still overcrowded in peak periods; other areas where parking was a problem due to large crowds included "the Old Man of Storr, Kilt Rock, the Quiraing, the Fairy Pools, and Neist Point. This source also stated that Portree was "the busiest place on the island" during peak periods and suggested that some tourists might prefer accommodations in quieter areas such as "Dunvegan, Kyleakin and the Broadford and Breakish area".
Transport
Skye is linked to the mainland by the Skye Bridge, while ferries sail from Armadale on the island to Mallaig, and from Kylerhea to Glenelg, crossing the Kyle Rhea strait. Ferries also run fromUig UIG, Uig or uig is a placename meaning "bay" (from Norse) and may refer to:
Places
* Uig, Coll, a hamlet on the island of Coll, Argyll and Bute, Scotland
* Uig, Duirinish, a hamlet near Totaig, on the Isle of Skye, Highland Scotland
* Uig, Lewi ...
to Tarbert on Harris and Lochmaddy on North Uist, and from Sconser
Sconser ( gd, Sgonnsair) is a small crofting township on the island of Skye, in Scotland, situated on the south shore of Loch Sligachan. The main A87 road of Skye passes through Sconser and the ferry to Raasay departs from the pier.
Less than ...
to Raasay.
private finance initiative
The private finance initiative (PFI) was a United Kingdom government procurement policy aimed at creating " public–private partnerships" (PPPs) where private firms are contracted to complete and manage public projects. Initially launched in 1 ...
and the high tolls charged (£5.70 each way for summer visitors) met with widespread opposition, spearheaded by the pressure group SKAT (Skye and Kyle Against Tolls). On 21 December 2004 it was announced that the Scottish Executive had purchased the bridge from its owners and the tolls were immediately removed.
Bus services run to Inverness and Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated pop ...
, and there are local services on the island, mainly starting from Portree or Broadford. Train services run from Kyle of Lochalsh at the mainland end of the Skye Bridge to Inverness, as well as from Glasgow to Mallaig from where the ferry can be caught to Armadale.
The island's airfield at , near Broadford, is used by private aircraft and occasionally by NHS Highland and the Scottish Ambulance Service for transferring patients to hospitals on the mainland."Potential use of Skye's Ashaig airstrip re-examined"BBC News Online
BBC News Online is the website of BBC News, the division of the BBC responsible for newsgathering and production. It is one of the most popular news websites, with 1.2 billion website visits in April 2021, as well as being used by 60% of the ...
. (11 July 2012) Retrieved 13 July 2012.
The A87 trunk road traverses the island from the Skye Bridge to Uig, linking most of the major settlements. Many of the island's roads have been widened in the past forty years although there are still substantial sections of single track road.
Culture, media, and the arts
Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
and a smaller number of Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, many residents of Skye belong to the Free Church of Scotland Free Church of Scotland may refer to:
* Free Church of Scotland (1843–1900), seceded in 1843 from the Church of Scotland. The majority merged in 1900 into the United Free Church of Scotland; historical
* Free Church of Scotland (since 1900), rema ...
, known for its strict observance of the Sabbath.
Skye has a strong folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has ...
tradition, although in recent years dance and rock music have been growing in popularity on the island. Gaelic folk rock band Runrig started in Skye and former singer Donnie Munro still works on the island. Runrig's second single and a concert staple is entitled ''Skye'', the lyrics being partly in English and partly in Gaelic and they have released other songs such as "Nightfall on Marsco" that were inspired by the island. Ex-Runrig member Blair Douglas, a highly regarded accordionist and composer in his own right, was born on the island and is still based there to this day. Celtic fusion band the Peatbog Faeries
The Peatbog Faeries are a largely instrumental Celtic fusion band. Formed in 1991, they are based in Dunvegan on the Isle of Skye, Scotland.
Their music embodies many styles and influences, including folk, electronica, African pop, rock and ...
are based on Skye. Jethro Tull singer Ian Anderson owned an estate at Strathaird on Skye at one time. Several Tull songs are written about Skye, including ''Dun Ringil'', ''Broadford Bazaar'', and ''Acres Wild'' (which contains the lines "Come with me to the Winged Isle, / Northern father's western child..." in reference to the island itself). The Isle of Skye Music Festival featured sets from The Fun Lovin' Criminals and Sparks
Sparks may refer to:
Places
*Sparks, Georgia
* Sparks, Kansas
*Sparks, Kentucky
*Sparks, Maryland
* Sparks, Nebraska
*Sparks, Nevada
*Sparks, Oklahoma
*Sparks, Texas
* Sparks, Bell County, Texas
* Sparks, West Virginia
Books
* ''Sparks'' (Raffi ...
, but collapsed in 2007. Electronic music
Electronic music is a Music genre, genre of music that employs electronic musical instruments, digital instruments, or electronics, circuitry-based music technology in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromech ...
ian Mylo was born on Skye.
 The poet Sorley MacLean, a native of the Isle of Raasay, which lies off the island's east coast, lived much of his life on Skye. The island has been immortalised in the traditional song " The Skye Boat Song" and is the notional setting for the novel '' To the Lighthouse'' by
The poet Sorley MacLean, a native of the Isle of Raasay, which lies off the island's east coast, lived much of his life on Skye. The island has been immortalised in the traditional song " The Skye Boat Song" and is the notional setting for the novel '' To the Lighthouse'' by Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born ...
, although the Skye of the novel bears little relation to the real island. John Buchan's descriptions of Skye, as featured in his Richard Hannay
Major-General Sir Richard Hannay, KCB, OBE, DSO, is a fictional character created by Scottish novelist John Buchan and further made popular by the 1935 Alfred Hitchcock film '' The 39 Steps'' (and other later film adaptations), very loosely b ...
novel '' Mr Standfast'', are more true to life. is a 2004 Italian language work of non-fiction by . The international bestsellerThe Ice Twins
by S K Tremayne, published around the world in 2015–2016, is set in southern Skye, especially around the settlement and islands of Isleornsay.
 Skye has been used as a location for a number of feature films. The Ashaig aerodrome was used for the opening scenes of the 1980 film '' Flash Gordon''. ''
Skye has been used as a location for a number of feature films. The Ashaig aerodrome was used for the opening scenes of the 1980 film '' Flash Gordon''. ''Stardust
Stardust may refer to:
* A type of cosmic dust, composed of particles in space
Entertainment Songs
* “Stardust” (1927 song), by Hoagy Carmichael
* “Stardust” (David Essex song), 1974
* “Stardust” (Lena Meyer-Landrut song), 2012
* ...
'', released in 2007 and starring Robert De Niro and Michelle Pfeiffer, featured scenes near Uig, Loch Coruisk and the Quiraing. Another 2007 film, '' : The Inaccessible Pinnacle'', was shot almost entirely in various locations on the island. The Justin Kurzel adaption of Macbeth starring Michael Fassbender was also filmed on the Island. Some of the opening scenes in Ridley Scott
Sir Ridley Scott (born 30 November 1937) is a British film director and producer. Directing, among others, science fiction films, his work is known for its atmospheric and highly concentrated visual style. Scott has received many accolades th ...
's 2012 feature film ''Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, know ...
'' were shot and set at the Old Man of Storr."Prometheus Filming Location Round-up". Prometheus News. Retrieved 4 July 2012. In 1973 '' The Highlands and Islands - a Royal Tour'', a documentary about Prince Charles's visit to the Highlands and Islands, directed by Oscar Marzaroli, was shot partly on Skye. Scenes from the Scottish Gaelic-language BBC Alba television series '' Bannan'' were filmed on the island.
 The '' West Highland Free Press'' is published at Broadford. This weekly newspaper takes as its motto ("The Land, the Language and the People"), which reflects its radical, campaigning priorities. The ''Free Press'' was founded in 1972 and circulates in Skye, Wester Ross and the Outer Hebrides.
The '' West Highland Free Press'' is published at Broadford. This weekly newspaper takes as its motto ("The Land, the Language and the People"), which reflects its radical, campaigning priorities. The ''Free Press'' was founded in 1972 and circulates in Skye, Wester Ross and the Outer Hebrides. Shinty
Shinty ( gd, camanachd, iomain) is a team game played with sticks and a ball. Shinty is now played mainly in the Scottish Highlands and amongst Highland migrants to the big cities of Scotland, but it was formerly more widespread in Scotland, and ...
is a popular sport played throughout the island and Portree-based Skye Camanachd won the Camanachd Cup in 1990.
Whilst Skye had unofficial flags in the past, including the popular "Bratach nan Daoine" (Flag of the People) design which represented the Cuillins in sky blue against a white sky symbolising the Gaelic language, land struggle and the fairy flag of Dunvegan, the Island received its first official flag "Bratach an Eilein" (The Skye Flag) approved by the Lord Lyon after a public vote in August 2020. The design by Calum Alasdair Munrreflects the Island's Gaelic heritage, the Viking heritage and the history of Flora MacDonald. The flag has a birlinn in the canton, and there are five oars representing the five areas of Skye, Trotternish, Waternish, Duirinish, Minginish and Sleat. Yellow represents the MacLeods, and Blue the MacDonalds or the MacKinnons.

Wildlife
The Hebrides generally lack the biodiversity of mainland Britain, but like most of the larger islands, Skye still has a wide variety of species. Observing the abundance of game birds Martin wrote: Similarly, Samuel Johnson noted that: In the modern era avian life includes the corncrake, red-throated diver, kittiwake, tystie, Atlantic puffin, goldeneye and
In the modern era avian life includes the corncrake, red-throated diver, kittiwake, tystie, Atlantic puffin, goldeneye and golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
. The eggs of the last breeding pair of white-tailed sea eagle in the UK were taken by an egg collector on Skye in 1916 but the species has recently been re-introduced. The chough last bred on the island in 1900. Mountain hare (apparently absent in the 18th century) and rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
are now abundant and preyed upon by wild cat and pine marten. The rich fresh water streams contain brown trout, Atlantic salmon and water shrew. Offshore the edible crab and edible oyster
''Ostrea edulis'', commonly known as the European flat oyster, is a species of oyster native to Europe. In Britain and Ireland, regional names include Colchester native oyster, mud oyster, or edible oyster. In France, ''Ostrea edulis'' are known ...
are also found, the latter especially in the Sound of Scalpay. There are nationally important horse mussel and brittlestar beds in the sea lochs and in 2012 a bed of 100 million flame shell
''Limaria hians'', the flame shell, is a species of small saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Limidae. This species is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean.
Biology
The flame shell resembles a scallop with a bright ...
s was found during a survey of Loch Alsh. Grey Seals can be seen off the Southern coast.
Heather moor containing ling, bell heather, cross-leaved heath, bog myrtle and fescue
''Festuca'' (fescue) is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the grass family Poaceae (subfamily Pooideae). They are evergreen or herbaceous perennial tufted grasses with a height range of and a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on e ...
s is everywhere abundant. The high Black Cuillins weather too slowly to produce a soil that sustains a rich plant life, but each of the main peninsulas has an individual flora. The basalt underpinnings of Trotternish produce a diversity of Arctic and alpine plants including alpine pearlwort
''Sagina saginoides'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common names arctic pearlwort or alpine pearlwort. It has a circumboreal distribution; it can be found throughout the northern latitudes of the Nor ...
and mossy cyphal. The low-lying fields of Waternish contain corn marigold
''Glebionis segetum'' (syn. ''Chrysanthemum segetum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, probably native only to the eastern Mediterranean region but now naturalized in western and northern Europe as well as China and par ...
and corn spurry
''Spergula arvensis'', the corn spurry, stickwort, starwort or spurrey, is a species of plant in the genus '' Spergula''.
Description
Corn spurry is a summer or winter annual broadleaf plant, and its seeds buried in the soil can survive for s ...
. The sea cliffs of Duirinish boast mountain avens and fir clubmoss
''Huperzia selago'', the northern firmoss or fir clubmoss, is a vascular plant in the family Lycopodiaceae. It has a circumpolar distribution in temperate and boreal regions in both hemispheres.
Distribution and habitat
It is found in the no ...
. Minginish produces fairy flax, cats-ear and black bog rush. There is a fine example of ''Brachypodium
''Brachypodium'' is a genus of plants in the grass family, widespread across much of Africa, Eurasia, and Latin America. The genus is classified in its own tribe Brachypodieae.
Flimsy upright stems form tussocks. Flowers appear in compact s ...
''-rich ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
woodland at Tokavaig in Sleat incorporating silver birch, hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999 ...
, bird cherry, and hawthorn.
The local Biodiversity Action Plan recommends land management measures to control the spread of ragwort and bracken and identifies four non-native, invasive species as threatening native biodiversity: Japanese knotweed, rhododendron, New Zealand flatworm and mink. It also identifies problems of over-grazing resulting in the impoverishment of moorland and upland habitats and a loss of native woodland, caused by the large numbers of red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
and sheep.
In 2020 Clan MacLeod chief Hugh MacLeod announced a plan to reintroduce 370,000 native trees along with beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
and red squirrel populations to the clan estates on Skye, with a view to restoring a "wet desert" landscape which had depleted from years of overgrazing.Mike Merritt''Clan chief Hugh Macleod’s forest will rewild Skye landscape''
The Times, 2 December 2020

See also
* List of islands of Scotland * :Mountains and hills of the Isle of Skye * Timeline of prehistoric ScotlandNotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * First published in 1947 under title: ''Natural history in the Highlands & Islands''; by F. Fraser Darling. * * Gammeltoft, Peder "Scandinavian Naming-Systems in the Hebrides – A Way of Understanding how the Scandinavians were in Contact with Gaels and Picts?" in * * * * Jennings, Andrew, and Kruse, Arne, "One Coast – Three Peoples: Names and Ethnicity in the Scottish West during the Early Viking period" in * * * * First printed for Andrew Bell and others, London. * * * * *External links
Skye - Wikivoyage
edited by
Francis H. Groome
Francis Hindes Groome (30 August 1851 – 24 January 1902), son of Robert Hindes Groome, Archdeacon of Suffolk, was a writer and foremost commentator of his time on the Romani people, their language, life, history, customs, beliefs, and lore.
Li ...
. Originally published between 1882 and 1885 and provided on-line by the '' Gazetteer for Scotland''.
Skye photos
Skye Birding Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Skye, Isle of Islands of Highland (council area) Islands of the Inner Hebrides Islands of the United Kingdom Cleared places in the Inner Hebrides