|
Scinax X-signatus
''Scinax x-signatus'' (common name: Venezuela snouted treefrog or Venezuelan snouted treefrog) is a species of frog in the family Hylidae. It is found in Brazil, the Guyanas (Guyana, French Guiana, Suriname), Venezuela and Colombia. Introduced populations exist on Guadeloupe and two nearby smaller islands, Marie Galante and La Désirade, and on Martinique. It may represent more than one species. ''Scinax x-signatus'' is a very common frog inhabiting tropical savannas, forest edges, and open areas, and is very adaptable to habitat modification. It is considered an invasive species on Guadeloupe, threatening native frogs through competition. Breeding takes place in standing water, both permanent and seasonal. Males call from the vegetation above and around ponds. References External links *''Scinax x-signatus''at the Encyclopedia of Life The ''Encyclopedia of Life'' (''EOL'') is a free, online encyclopedia intended to document all of the 1.9 million living species known to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Baptist Von Spix
Johann Baptist Ritter von Spix (9 February 1781 – 13 March 1826) was a German natural history, biologist. From his expedition to Brazil, he brought to Germany a large variety of specimens of plants, insects, mammals, birds, amphibians and fish. They constitute an important basis for today's National Zoological Collection in Munich. Numerous examples of his ethnographic collections, such as dance masks and the like, are now part of the collection of the Museum Five Continents, Museum of Ethnography in Munich. Biography Spix was born in Höchstadt, in present-day Middle Franconia, as the seventh of eleven children. His childhood home is the site of the Spix Museum, open to the public since 2004. He studied philosophy in Bamberg and graduated with a doctoral degree. Later he studied theology in Würzburg. After attending lectures of the young professor Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling, F. W. J. Schelling, Spix became interested in nature. He quit his theology studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
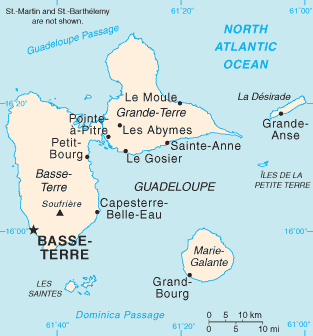
Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It has a land area of and a population of 364,508 inhabitants as of January 2019.Populations légales 2019: 972 Martinique INSEE One of the , it is directly north of Saint Lucia, northwest of |
Amphibians Of Venezuela
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of Suriname
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of Guyana
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of French Guiana
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of Colombia
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of Brazil
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scinax
''Scinax'' is a genus of frogs (snouted treefrogs) in the family Hylidae found in eastern and southern Mexico to Argentina and Uruguay, Trinidad and Tobago, and Saint Lucia Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindian .... These are small to moderate-sized tree frogs, drably colored. Duellman and Wiens resurrected this genus in 1992. The name originates from the Greek word ''skinos'', meaning quick or nimble. Species This following species are recognised in the genus ''Scinax:'' References * 1992. The status of the hylid frog genus Ololygon and the recognition of Scinax Wagler, 1830. ''Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History of the University of Kansas''. 151:1-23. * 1993. Hylid frogs of the genus Scinax Wagler, 1830, in Amazonian Ecuador and Peru. ''Occasional P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Life
The ''Encyclopedia of Life'' (''EOL'') is a free, online encyclopedia intended to document all of the 1.9 million living species known to science. It is compiled from existing trusted databases curated by experts and with the assistance of non-experts throughout the world. It aims to build one "infinitely expandable" page for each species, including video, sound, images, graphics, as well as text. In addition, the Encyclopedia incorporates content from the Biodiversity Heritage Library, which digitizes millions of pages of printed literature from the world's major natural history libraries. The project was initially backed by a US$50 million funding commitment, led by the MacArthur Foundation and the Sloan Foundation, who provided US$20 million and US$5 million, respectively. The additional US$25 million came from five cornerstone institutions—the Field Museum, Harvard University, the Marine Biological Laboratory, the Missouri Botanical Garden, and the Smithsonian Institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food webfor example the purple sea urchin (''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'') which has decimated kelp forests along the northern California coast due to overharvesting of its natural predator, the California sea otter (''Enhydra lutris''). Since the 20th century, invasive species have become a serious economic, social, and environmental threat. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France. History Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian population lived on La Désirade from the 3rd to the 16th centuries. Spanish colonization Deseada was the first island sighted by Christopher Columbus in 1493. When he landed there during his second voyage to America, he took possession of the island on behalf of the Spanish crown, followed by the island of Marie-Galante. Like other Antillean islands, it served as a hideout for pirates or corsairs who attacked Spanish overseas possessions. Some sources indicate that the island owes its name to the relief of the members of Columbus crew who saw the first dry land since leaving the Canary Islands of Spain. They cried out: "Oh, desired island" The French name ''La Désirade'' is an adaptation of its historical name in Spanish (''La Deseada'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)