|
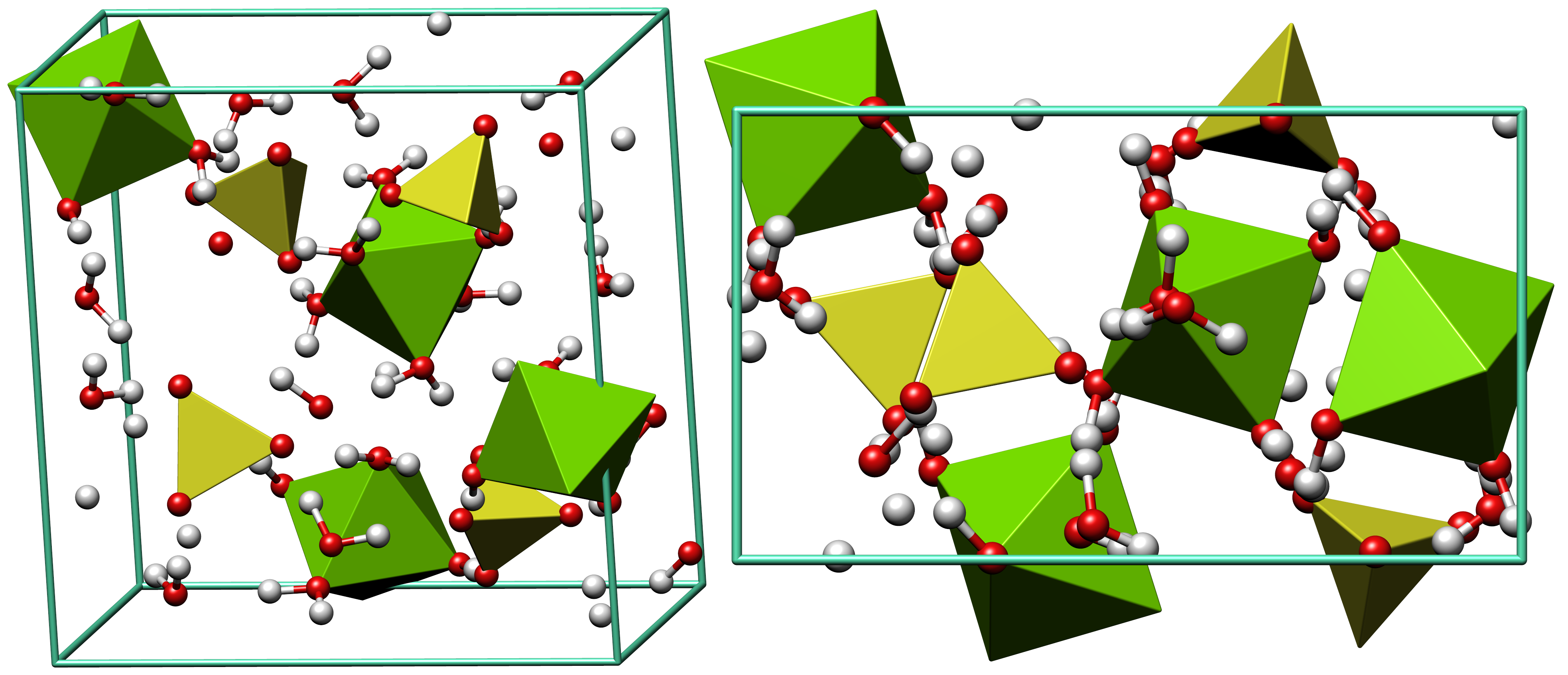
Schönite
Picromerite (synonyms: schoenite, schönite) is a mineral from the class of hydrous sulfates lacking additional anions, and containing medium to large cations according to the Nickel–Strunz classification. Etymology The name comes from the Greek words πικρός ikrosfor "bitter" and μέρος eros for "part", and relates to the bitter taste of the mineral. Occurrence Picromerite is found on comparatively few places, currently (2015) only about 40 localities are known. It was first identified in active volcanic fumaroles on Mount Vesuvius by Arcangelo Scacchi in 1855 and has also been found in volcanic deposits on Mount Etna and on Hawai'i. It is more commonly found in the kainite zones of some marine salt deposits, among them salt mines in Thuringia, Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt (Germany), near Hall in Tirol, Hallstatt and Bad Ischl (Austria), near Whitby (UK), and in the Carlsbad Potash District (New Mexico), also on salt lakes in western China. Picromerite can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Mineral
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal veins and as secondary minerals in the oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates **Barite BaSO4 ** Celestite SrSO4 **Anglesite PbSO4 **Anhydrite CaSO4 **Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates **Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O **Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O **Kieserite MgSO4·H2O ** Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O **Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O **Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O **Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O **Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O **Antlerite Cu3SO4(OH)4 **Brochantite Cu4SO4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Ischl
Bad Ischl (Austrian German ) is a spa town in Austria. It lies in the southern part of Upper Austria, at the Traun River in the centre of the Salzkammergut region. The town consists of the Katastralgemeinden ''Ahorn'', ''Bad Ischl'', ''Haiden'', ''Jainzen'', ''Kaltenbach'', ''Lauffen'', ''Lindau'', ''Pfandl'', ''Perneck'', ''Reiterndorf'' and ''Rettenbach''. It is connected to the village of Strobl by the river Ischl, which drains from the Wolfgangsee, and to the Traunsee, into which the stream empties. It is home to the Kaiservilla, summer residence of Austro-Hungarian monarchs Emperor Franz Joseph I and Empress Elisabeth. In 2024, Bad Ischl will be one of the European Capitals of Culture – the third city in Austria after Graz (2003) and Linz (2009). History Bad Ischl was a settlement area since the Hallstatt culture, first mentioned in a 1262 deed as ''Iselen''. In 1419 Archduke Albert V of Austria established the local seat of the Salt Chamber (''Salzkammer'') at ''Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerals In Space Group 14
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Minerals
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Minerals
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, that is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge – a cation, that combines with anions to form salts. Potassium in nature occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac- colored flame. It is found dissolved in sea water (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonite
Leonite is a hydrated double sulfate of magnesium and potassium. It has the formula K2SO4·MgSO4·4H2O. The mineral was named after Leo Strippelmann, who was director of the salt works at Westeregeln in Germany. The mineral is part of the blodite group of hydrated double sulfate minerals. Properties Leonite has a bitter taste. When leonite is analyzed for elements, it is usually contaminated with sodium and chloride ions, as it commonly occurs with sodium chloride. Crystal structure In the mineral family of leonite, the lattice contains sulfate tetrahedrons, a divalent element in an octahedral position surrounded by oxygen, and water and univalent metal (potassium) linking these other components together. One sulfate group is disordered at room temperature. The disordered sulfate becomes fixed in position as temperature is lowered. The crystal form also changes at lower temperatures, so two other crystalline forms of leonite exist at lower temperatures. The divalent meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals. It commonly occurs with other evaporite deposit minerals such as several of the sulfates, halides, and borates. The name ''halite'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word for "salt", ἅλς (''háls''). Occurrence Halite dominantly occurs within sedimentary rocks where it has formed from the evaporation of seawater or salty lake water. Vast beds of sedimentary evaporite minerals, including halite, can result from the drying up of enclosed lakes and restricted seas. Such salt beds may be hundreds of meters thick and underlie broad areas. Halite occurs at the surface today in playas in regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O. Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massive encrustations. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. The Mohs hardness is 2 to 2.5 and it has a low specific gravity of 1.67. It is readily soluble in water. It absorbs water from the air and converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. Discovery and occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone cavern walls and mine timbers and walls, rarely as volcanic fumarole deposits, and as rare beds in evaporite layers such as those found in certain bodies of salt water. It occurs in association with melanterite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhydrite
Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the orthorhombic barium ( baryte) and strontium ( celestine) sulfates, as might be expected from the chemical formulas. Distinctly developed crystals are somewhat rare, the mineral usually presenting the form of cleavage masses. The Mohs hardness is 3.5, and the specific gravity is 2.9. The color is white, sometimes greyish, bluish, or purple. On the best developed of the three cleavages, the lustre is pearly; on other surfaces it is glassy. When exposed to water, anhydrite readily transforms to the more commonly occurring gypsum, (CaSO4·2H2O) by the absorption of water. This transformation is reversible, with gypsum or calcium sulfate hemihydrate forming anhydrite by heating to around under normal atmospheric conditions. Anhydrite is comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |