|
Savoyard Crusade
The Savoyard crusade was a crusading expedition to the Balkans in 1366–67. It was born out of the same planning that led to the Alexandrian Crusade and was the brainchild of Pope Urban V. It was led by Count Amadeus VI of Savoy and directed against the growing Ottoman Empire in eastern Europe. Although intended as a collaboration with the Kingdom of Hungary and the Byzantine Empire, the crusade was diverted from its main purpose to attack the Second Bulgarian Empire. There the crusaders made small gains that they handed over to the Byzantines. It did take back some territory from the Ottomans in the vicinity of Constantinople and on Gallipoli. Noting the greater attention paid to Bulgaria than to the Turks, historian Nicolae Iorga argued "it was not the same thing as a crusade, this expedition that better resembled an escapade." Still, the taking of Gallipoli, according to Oskar Halecki, was "the first success achieved by the Christians in their struggle for the defense of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savoyard Crusaders
Savoyard refers to: Regional and political * Savoyard dialect, a Franco-Provençal language * Savoyard League, a political party based in the Savoy region of France * A member of the House of Savoy, the ruling dynasty of the Duchy of Savoy, a medieval and early modern state ** Savoyard state, collective term for states ruled by the Duke of Savoy * A resident of Savoie, a department in France * A resident of Haute-Savoie, a department in France The arts * American Savoyards, a former light opera company * Washington Savoyards, a former light opera company * Fans of the Savoy operas * Members of the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company, which performed at the Savoy Theatre * ''The Savoyard'', the former magazine of the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company Other uses * Savoyard (grape), an Italian wine grape also known as the Dolcetto * Savoyard Centre, an office building in Detroit, Michigan See also * * Savoy (other) Savoy is a historical country in western Europe, heart of the Savoyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter I Of Cyprus
Peter I (9 October 1328 – 17 January 1369) was King of Cyprus and titular King of Jerusalem from his father's abdication on 24 November 1358 until his death in 1369. He was invested as titular Count of Tripoli in 1346. As King of Cyprus, he had some military successes, but he was unable to complete many of his plans due to internal disputes that culminated in his assassination at the hands of three of his knights. Early life and crowning Peter was born in Nicosia in 1328, the second son of Hugh IV of Cyprus, the first by his second wife Alice of Ibelin. Hugh's heir apparent was his first born son, Guy, who had married Marie of Bourbon. Guy died before his father, however; and though his son, also named Hugh, demanded the throne, Peter was crowned King of Cyprus by Guy of Ibelin, bishop of Limassol in the Cathedral of Santa Sophia, Nicosia on 24 November 1359. In 1349 he traveled secretly to Europe with his brother John. This upset their father who sent ships to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Sratsimir Of Bulgaria
Ivan Sratsimir (), or Ivan Stratsimir ( bg, Иван Страцимир), was emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria in Vidin from 1356 to 1396. He was born in 1324 or 1325, and he died in or after 1397. Despite being the eldest surviving son of Ivan Alexander, Ivan Sratsimir was disinherited in favour of his half-brother Ivan Shishman and proclaimed himself emperor in Vidin. When the Hungarians attacked and occupied his domains, he received assistance from his father and the invaders were driven away. After the death of Ivan Alexander in 1371 Ivan Sratsimir broke off ties with Tarnovo and even placed the archbishop of Vidin under the jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Constantinople to demonstrate his independence. Due to its geographical position, Vidin was initially safe from attacks by the Ottoman Turks who were ravaging the Balkans to the south and Ivan Sratsimir made no attempts to assist Ivan Shishman in his struggle against the Ottomans. Only after the fall of Tarnovo in 1393 did his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
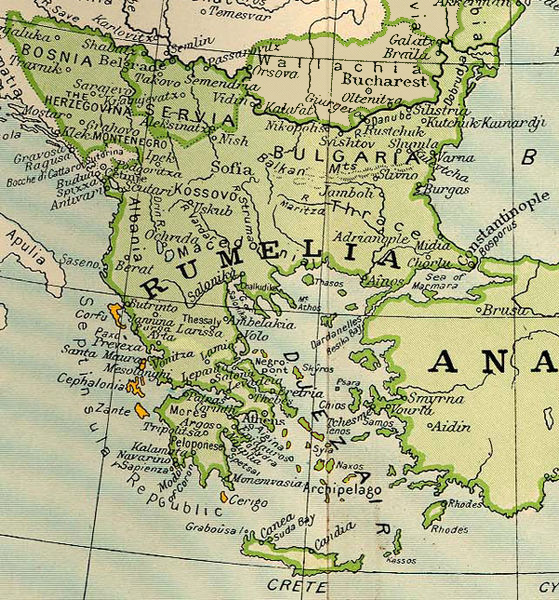
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Names of the Greeks#Romans (Ῥωμαῖοι), Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine Rite, Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Ottoman Empire, Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stretching from the island of Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar and Šibenik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, who lived in the area in classical antiquity. Later it became a Dalmatia (Roman province), Roman province, and as result a Romance languages, Romance culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zadar
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian: ); see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serves as the seat of Zadar County and of the wider northern Dalmatian region. The city proper covers with a population of 75,082 , making it the second-largest city of the region of Dalmatia and the fifth-largest city in the country. Today, Zadar is a historical center of Dalmatia, Zadar County's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, educational, and transportation centre. Zadar is also the episcopal see of the Archdiocese of Zadar. Because of its rich heritage, Zadar is today one of the most popular Croatian tourist destinations, named "entertainment center of the Adriatic" by ''The Times'' and "Croatia's new capital of cool" by ''The Guardian''. UNESCO's World Heritage Site list included the fortified city of Zadar as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It largely corresponds with the modern administrative region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and includes the departments of Var, Bouches-du-Rhône, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, as well as parts of Alpes-Maritimes and Vaucluse.''Le Petit Robert, Dictionnaire Universel des Noms Propres'' (1988). The largest city of the region and its modern-day capital is Marseille. The Romans made the region the first Roman province beyond the Alps and called it ''Provincia Romana'', which evolved into the present name. Until 1481 it was ruled by the Counts of Provence from their capital in Aix-en-Provence, then became a province of the Kings of France. While it has been part of France for more than 500 years, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis I Of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great ( hu, Nagy Lajos; hr, Ludovik Veliki; sk, Ľudovít Veľký) or Louis the Hungarian ( pl, Ludwik Węgierski; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. He was the first child of Charles I of Hungary and his wife, Elizabeth of Poland, to survive infancy. A 1338 treaty between his father and Casimir III of Poland, Louis's maternal uncle, confirmed Louis's right to inherit the Kingdom of Poland if his uncle died without a son. In exchange, Louis was obliged to assist his uncle to reoccupy the lands that Poland had lost in previous decades. He bore the title of Duke of Transylvania between 1339 and 1342 but did not administer the province. Louis was of age when he succeeded his father in 1342, but his deeply religious mother exerted a powerful influence on him. He inherited a centralized kingdom and a rich treasury from his father. During the first years of his reign, Louis launched a cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bulgarian Empire After 1371
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units ( SI) is more precise:The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. Uses Analog clocks and watches often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the ''Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Church of the East, Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Mother of God. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have considerably lesser status. The New Testament of the Bible provides the earliest documented references to Mary by name, mainly in the canonical Gospels. She is described as a young virgin who was chosen by God to conceive Jesus through the Holy Spirit. After giving birth to Jesus in Bethlehem, she raised him in the city of Nazareth in Galilee, and was in Jerusal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Black Swan
The Order of the Black Swan (french: Companie du Cigne Noir or ) was a short-lived chivalric order founded by Amadeus VI of Savoy in 1350. It was defunct by 1364, when Amadeus founded the Order of the Collar in its stead. Along with Amadeus, Amadeus III of Geneva and Galeazzo Visconti were the "great lords" (''grans seignours'') of the Order. At the time of its founding, the existence of black swans was unknown to Europeans. The order was originally composed of fourteen knights. The requirements of membership were the possession of a charger and a palfrey, and the ability to serve at one's own expense for one week whenever required. The Order did collect dues (at least from noblemen, ''riches hommes'') for purposes ''estreordinaire'' (extraordinary) according to rank (''puissance''): eight ''écus'' from a knight banneret, four from what they called a ''chivallier simple'', and one from any squire. Annually on Saint Andrew's Day Saint Andrew's Day, also called the Feast o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
