|
Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe
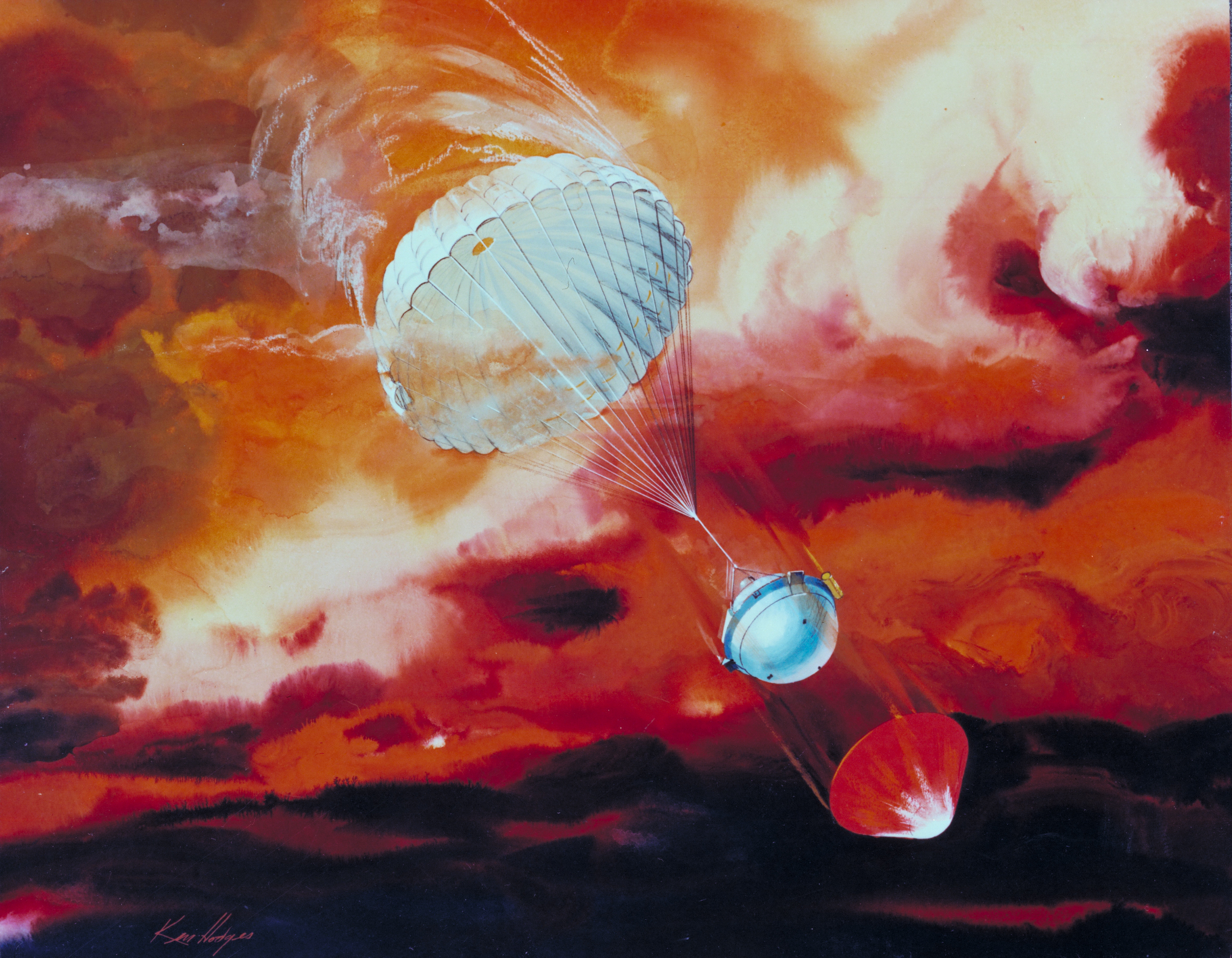
The Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe is a mission concept study for a robotic spacecraft to deliver a single probe into Saturn to study its atmosphere. The concept study was done to support the NASA 2010 Planetary Science Decadal Survey (Archived from the original). Due to the orbits and relative positions of Saturn and Earth, launch was proposed for 30 August 2027 for a 22 June 2034 arrival. The mission was studied for the NASA Planetary Science Decadal Survey as a possible NASA New Frontiers Program, New Frontiers-class mission. Overview To unveil the processes of outer planet formation and Solar System evolution, detailed studies of the composition, structure, and dynamics of giant planet interiors and atmospheres would be necessary. To constrain the internal structure of gas giants, a combination of both ''in-situ'' entry-probe missions and remote-sensing studies of the giant planets would be needed. The Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe mission would consist of a carrier-rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To Saturn
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to: Organised activities Religion *Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity *Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints *The Christian Mission, the former name of the Salvation Army Government and military *Bolivarian missions, a series of social programs created during Hugo Chávez's rule of Venezuela *Diplomatic mission, a diplomatic outpost in a foreign territory *Military operation *Mission statement, a formal, short, written articulation of an organization's purpose *Sortie or combat mission, a deployment or dispatch of a military unit *Space mission, a journey of craft into outer space Geography Australia * Mission River, Queensland, a locality in the Shire of Cook and the Aboriginal Shire of Napranum *Mission River (Queensland), a river in Australia Canada *Mission, British Columbia, a district municipality *Mission, Calgary, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPRITE (spacecraft)
SPRITE (Saturn PRobe Interior and aTmospheric Explorer) was a proposed Saturn atmospheric probe mission concept of the NASA. SPRITE is a design for an atmospheric entry probe that would travel to Saturn from Earth on its own cruise stage, then enter the atmosphere of Saturn, and descend taking measurements ''in situ''. Overview Many fundamental questions about Saturn have not have been fully investigated at the end of the ''Cassini'' mission in September 2017, because of limitations in its implementation and science instrumentation. Direct measurements of the atmospheric structure and noble gas and elemental abundances of Saturn are needed to distinguish between competing models of Solar System formation, as well as to provide an improved context for exoplanet systems. The SPRITE probe would revolutionize our understanding of Saturn's atmospheric structure and composition, and allow better understanding of extrasolar giant planets. ''SPRITE'' was proposed by Caltech's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megameter
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octilliont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information. The prefix mega (symbol M) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 106 (1 million), and therefore :1 megabit = = = 1000 kilobits. The megabit has the unit symbol Mbit or Mb. The lowercase 'b' in Mb distinguishes it from MB (for megabyte). The megabit is closely related to the mebibit, a unit multiple derived from the binary prefix mebi (symbol Mi) of the same order of magnitude, which is equal to = , or approximately 5% larger than the megabit. Despite the definitions of these new prefixes for binary-based quantities of storage by international standards organizations, memory semiconductor chips are still marketed using the metric prefix names to designate binary multiples. Using the common byte size of eight bits and the standard decimal definition of megabit and kilobyte, 1 megabit is equal to 125 kilobytes (kB) or approximately 122 kibibytes (KiB). The megab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Probe
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. ''Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (spacecraft)
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all of the argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete octe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


