|
Sarmazenil
Sarmazenil (Ro15-3505) is a drug from the benzodiazepine family. It acts as a partial inverse agonist of benzodiazepine receptors, meaning that it causes the opposite effects to most benzodiazepine drugs, and instead acts as an anxiogenic and convulsant. It is used in veterinary medicine Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutri ... to reverse the effects of benzodiazepine sedative drugs in order to rapidly re-awaken anesthetized animals. See also * GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator * GABAA receptor § Ligands References Anxiogenics Carboxylate esters Chloroarenes Convulsants Ethyl esters GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulators Imidazobenzodiazepines Lactams {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convulsant
A convulsant is a drug which induces convulsions and/or epileptic seizures, the opposite of an anticonvulsant. These drugs generally act as stimulants at low doses, but are not used for this purpose due to the risk of convulsions and consequent excitotoxicity. Most convulsants are antagonists (or inverse agonists) at either the GABAA or glycine receptors, or ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists. Many other drugs may cause convulsions as a side effect at high doses (e.g. bupropion, tramadol, pethidine, dextropropoxyphene, clomipramine) but only drugs whose primary action is to cause convulsions are known as convulsants. Nerve agents such as sarin, which were developed as chemical weapons, produce convulsions as a major part of their toxidrome, but also produce a number of other effects in the body and are usually classified separately. Dieldrin which was developed as an insecticide blocks chloride influx into the neurons causing hyperexcitability of the CNS and convulsions. The I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convulsants
A convulsant is a drug which induces convulsions and/or epileptic seizures, the opposite of an anticonvulsant. These drugs generally act as stimulants at low doses, but are not used for this purpose due to the risk of convulsions and consequent excitotoxicity. Most convulsants are antagonists (or inverse agonists) at either the GABAA or glycine receptors, or ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists. Many other drugs may cause convulsions as a side effect at high doses (e.g. bupropion, tramadol, pethidine, dextropropoxyphene, clomipramine) but only drugs whose primary action is to cause convulsions are known as convulsants. Nerve agents such as sarin, which were developed as chemical weapons, produce convulsions as a major part of their toxidrome, but also produce a number of other effects in the body and are usually classified separately. Dieldrin which was developed as an insecticide blocks chloride influx into the neurons causing hyperexcitability of the CNS and convulsions. The I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
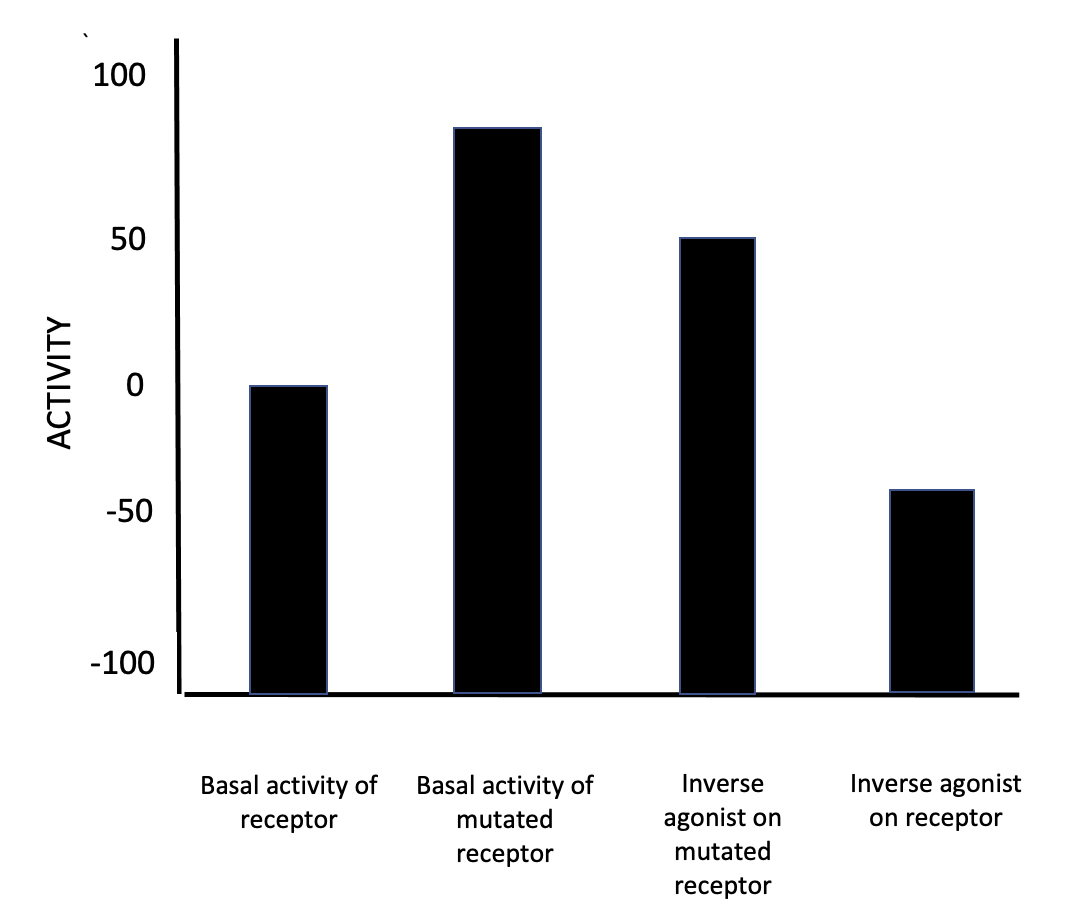
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiogenic
An anxiogenic or panicogenic substance is one that causes anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiolytic agents, which inhibits anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds. Anxiogenic effects can be measured by, for example, the hole-board test in rats and mice. A number of agents are used to provoke anxiety (anxiogens) or panic (panicogens) in experimental models. Some of the most common substances are: carbon dioxide (as carbogen), sodium lactate, cocaine, substituted amphetamines, caffeine, L-DOPA, methylphenidate, modafinil, GABA antagonists such as DMCM, FG-7142 and ZK-93426, serotonergic agents such as mCPP and LY-293,284, adrenergic agents such as yohimbine, psychoactive agents such as THC and LSD in susceptible individuals, antipsychotics/dopamine antagonists such as ecopipam and reserpine, and cholecystokinin (CCK) (especially the tetrapeptide and octapeptide fragments CCK-4 and CCK-8). Sodium lactate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutrition, and product development. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both domesticated and wild, with a wide range of conditions that can affect different species. Veterinary medicine is widely practiced, both with and without professional supervision. Professional care is most often led by a veterinary physician (also known as a veterinarian, veterinary surgeon, or "vet"), but also by paraveterinary workers, such as veterinary nurses or technicians. This can be augmented by other paraprofessionals with specific specialties, such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species-relevant roles such as farriers. Veterinary science helps human health through the monitoring and control of zoonotic disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor Negative Allosteric Modulator
A GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator is a negative allosteric modulator (NAM), or inhibitor, of the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They are closely related and similar to GABAA receptor antagonists. The effects of GABAA receptor NAMs are functionally the opposite of those of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) like the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and ethanol (alcohol). Non-selective GABAA receptor NAMs can produce a variety of effects including convulsions, neurotoxicity, and anxiety, among others. Flumazenil is a competitive antagonist of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor and hence is a GABAA receptor NAM of sorts. It is used to reverse benzodiazepine overdose. The drug can provoke seizures in those with benzodiazepine dependence. Selective NAMs (or "inverse agonists") of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors, such as basmisanil and α5IA, do not have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylate Esters
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, (or ). It is an ion with negative charge. Carboxylate salts are salts that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,...; ''carboxylate esters'' have the general formula (or ). R and R′ are organic groups; R′ ≠ H. Synthesis Carboxylate ions can be formed by deprotonation of carboxylic acids. Such acids typically have p''K''a of less than 5, meaning that they can be deprotonated by many bases, such as sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate. :RCOOH + NaOH -> RCOONa + H2O Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion Carboxylic acids easily dissociate into a carboxylate anion and a positively charged hydrogen ion (proton), much more readily than alcohols do (into an alkoxide ion and a proton), because the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance. The negative charge that is left after deprotonation of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |