|
Santiago Roth
Santiago Roth (14 June 1850 – 4 August 1924) was a Swiss Argentine paleontologist and academic known for his fossil collections and Patagonian expeditions. Life Kaspar Jakob (Spanish: Santiago) was born and raised in Herisau, Canton Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Switzerland, as the oldest of 12 children. He attended school in the nearby town of St. Gallen, where his teacher Bernhard Wartmann raised his interest in the science of nature. Wartmann was a well known botanist and director of the Museum of History of Nature in St. Gallen.Weigelt, Gertrud: ''Santiago Roth 1850-1924. Ein Berner als wissenschaftlicher Pionier in Südamerika'', Berner Zeitschrift für Geschichte und Heimatkunde, Paul Haupt Bern, 1951/1, pp. 19–39 For economic reasons the Roth family emigrated to Argentina in 1866, where they initially settled in the Colonia Baradero (Buenos Aires Province). There, Roth started a small business with leather goods. In his sparetime he collected plants, butterflies and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Argentine
Swiss Argentines are Argentine citizens of Swiss ancestry or people who emigrated from Switzerland and reside in Argentina. The Swiss Argentine community is the largest group of the Swiss diaspora in South America. Approximately 44,000 Swiss emigrated to Argentina until 1940, who settled mainly in the provinces of Córdoba and Santa Fe and, to a lesser extent, in Buenos Aires. In 1856, 200 families of immigrants from Switzerland, Germany, France, Italy, Belgium and Luxembourg founded the city of Esperanza, the forerunner of agricultural colonies in Argentina, thus kickstarting a long process of European colonization and immigration. In Río Negro, Swiss settlement began in the late 19th century in the village of Colonia Suiza ("Swiss Colony"). An Argentine of Swiss origin, Dr. Ernesto Alemann, founded the Colegio Pestalozzi in 1934 with the aim of creating a place for free and humanistic education in accordance with the philosophy of Swiss pedagogue Johann Heinrich Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 26 May. 2012 . "Rio de la Plata". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. 26 May. 2012 Among South American rivers, it is second in length only to the Amazon River. It merges with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean. The first European to go up the Paraná River was the Venetian explorer Sebastian Cabot, in 1526, while working for Spain. A drought hit the river in 2021, causing a 77-year low. Etymology In eastern South America there is "an immense number of river names containing the element ''para-'' or ''parana-''", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuel Huapi Lake
Nahuel Huapi Lake ( es, Lago Nahuel Huapí) is a lake in the lake region of northern Patagonia between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén, in Argentina. The tourist center of Bariloche is on the southern shore of the lake. The June 2011 eruption of the Puyehue-Cordón Caulle volcanic complex, in neighboring Chile, caused parts of the lake's surface to be blanketed in volcanic ash. During the Last Glacial Maximum of the Llanquihue glaciation the lake basin was wholly occupied by a glacier. Etymology The name of the lake derives from the toponym of its major island in Mapudungun (Mapuche language): "Island of Puma", from ''nahuel'', 'puma', and ''huapí'', 'island'. There is, however, more to the word "Nahuel"—it can also signify 'a man who by sorcery has been transformed to a puma'. Geography Nahuel Huapi lake, located within the Nahuel Huapi National Park, has a surface of , rests above the sea level, and has a maximum measured depth (as of 2007) of . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limay River
The Limay River is an important river in the northwestern Argentine Patagonia (the region of Comahue). It originates at the eastern end of the Nahuel Huapi Lake and flows in a meandering path for about , collecting the waters of several tributaries, such as the Traful River, the Pichileufú and the Collón Curá. It then meets the Neuquén River and together they become the Río Negro. At this confluence lies the city of Neuquén. The river serves as natural border between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén. Its deep waters are clear, and carry a large flow, on average. Its drainage basin has an area of and includes almost all the rivers and streams of the Atlantic basin in the region, as well as an extensive network of lakes. The waters of the Limay are used to generate hydroelectricity at the five dams built on its course: Alicurá, Piedra del Águila, Pichi Picún Leufú, El Chocón, and Arroyito; together with the Cerros Colorados Complex on the Neuquén River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Negro (Argentina)
Río Negro (Spanish and Portuguese, 'Black River') may refer to: Rivers Brazil * Rio Negro (Amazon), tributary of the Amazon River * Rio Negro (Mato Grosso do Sul) * Rio Negro (Paraná) * Rio Negro (Rio de Janeiro) * Rio Negro (Rondônia) * Rio Negro (Tocantins) South America (except Brazil) * Río Negro (Argentina), in Patagonia * Río Negro (Los Lagos), in Southern Chile * Río Negro (Uruguay), tributary of the Uruguay River * Río Negro (Chaco Province), in Argentina, tributary of the Paraná River Central America * Río Negro (Central America), forming part of the border between Honduras and Nicaragua * Chixoy River, also known as the Río Negro, in Guatemala Political divisions South America * Río Negro Province, Argentina * Rio Negro, Paraná, a municipality in Brazil * Rio Negro, Mato Grosso do Sul, a municipality in Brazil * Río Negro, Chile, a city and commune in Osorno Province * Río Negro, Palena, a town in Palena Province, Chile * Rionegro, a city and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter Berto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenarthra
Xenarthra (; from Ancient Greek ξένος, xénos, "foreign, alien" + ἄρθρον, árthron, "joint") is a major clade of placental mammals native to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and armadillos. Extinct xenarthrans include the glyptodonts, pampatheres and ground sloths. Xenarthrans originated in South America during the late Paleocene about 60 million years ago. They evolved and diversified extensively in South America during the continent's long period of isolation in the early to mid Cenozoic Era. They spread to the Antilles by the early Miocene and, starting about 3 Mya, spread to Central and North America as part of the Great American Interchange. Nearly all of the formerly abundant megafaunal xenarthrans became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene. Xenarthrans share several characteristics not present in other placental mammals, which suggest their ancestors were subterranean diggers for insects. The name Xenarthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
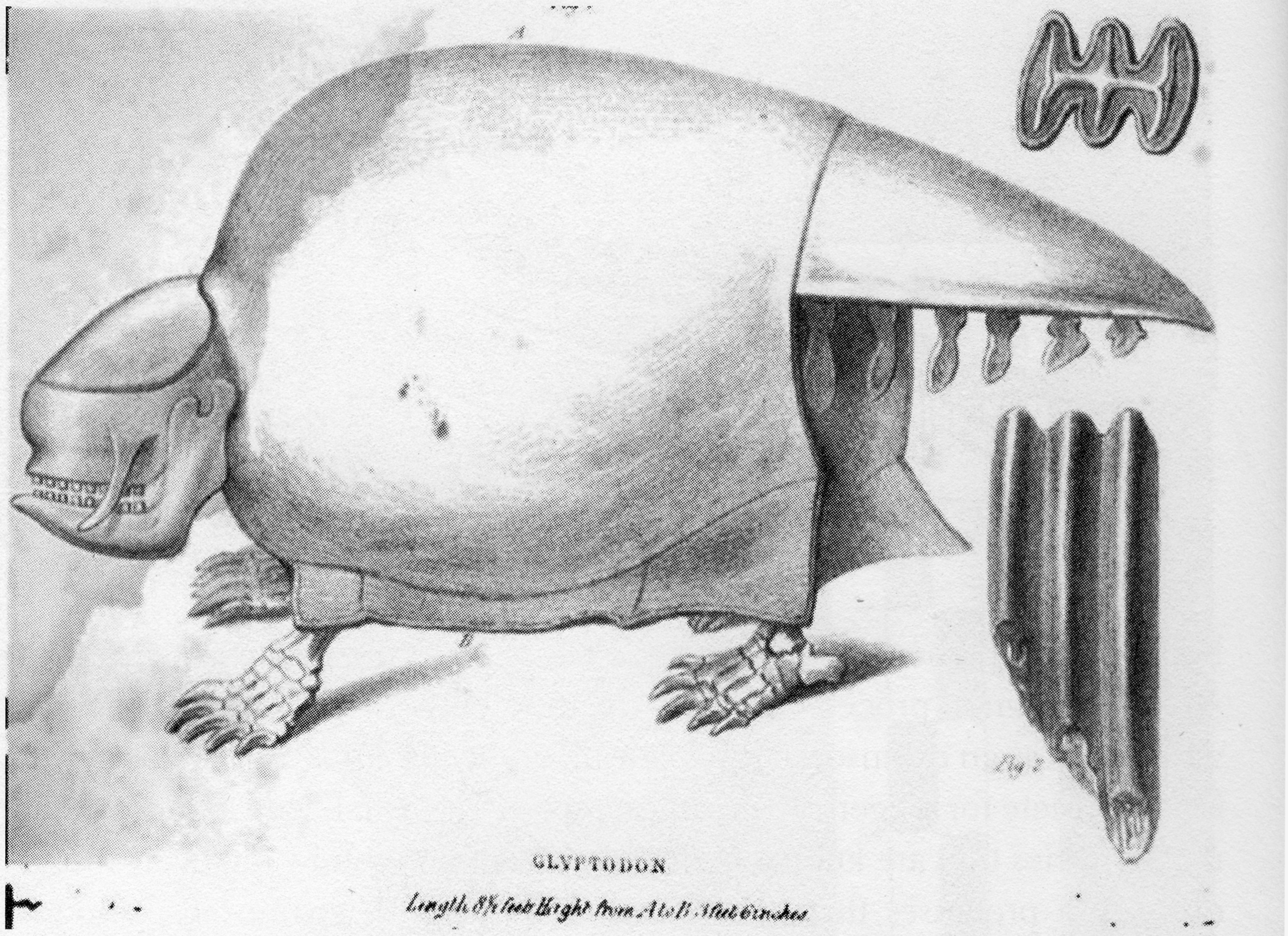
Glyptodon
''Glyptodon'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved tooth': γλυπτός 'sculptured' and ὀδοντ-, ὀδούς 'tooth') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Pleistocene, around 2.5 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia. It was the first named extinct cingulate and is the type genus of Glyptodontinae, and, or, Glyptodontinae. Many species have been named for the genus, though few are considered valid, and it is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. Hundreds of specimens have been referred to the genus, but the holotype, or name specimen, of the type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle, 800–840 kg (1,760–1,850 lb). With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megatherium
''Megatherium'' ( ; from Greek () 'great' + () 'beast') is an extinct genus of ground sloths endemic to South America that lived from the Early Pliocene through the end of the Pleistocene. It is best known for the elephant-sized type species ''M. americanum'', sometimes called the giant ground sloth, or the megathere, native to the Pampas through southern Bolivia during the Pleistocene. Various other smaller species belonging to the subgenus ''Pseudomegatherium'' are known from the Andes. ''Megatherium'' is part of the sloth family Megatheriidae, which also includes the similarly giant ''Eremotherium'', comparable in size to ''M. americanum,'' which was native to tropical South America, Central America and North America as far north as the southern United States. Only a few other land mammals equaled or exceeded ''M. americanum'' in size, such as large proboscideans (e.g., elephants) and the giant rhinoceros ''Paraceratherium''. ''Megatherium'' was first discovered in 1788 on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. The term is used to refer to all extinct sloths because of the large size of the earliest forms discovered, compared to existing tree sloths. The Caribbean ground sloths, the most recent survivors, lived in the Antilles, possibly until 1550 BCE. However, radiocarbon dating suggests an age of between 2819 and 2660 BCE for the last occurrence of '' Megalocnus'' in Cuba. Ground sloths had been extinct on the mainland of North and South America for 10,000 years or more. They survived 5,000–6,000 years longer in the Caribbean than on the American mainland, which correlates with the later colonization of this area by humans. Much ground sloth evolution took place during the late Paleogene and Neogene of South America, while the continent was isolated. At their earliest appearance in the fossil record, the ground sloths were already distinct at the family level. The presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETH Zurich
(colloquially) , former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule , image = ETHZ.JPG , image_size = , established = , type = Public , budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021) , rector = Günther Dissertori , president = Joël Mesot , academic_staff = 6,612 (including doctoral students, excluding 527 professors of all ranks, 34% female, 65% foreign nationals) (full-time equivalents 2021) , administrative_staff = 3,106 (40% female, 19% foreign nationals, full-time equivalents 2021) , students = 24,534 (headcount 2021, 33.3% female, 37% foreign nationals) , undergrad = 10,642 , postgrad = 8,299 , doctoral = 4,460 , other = 1,133 , address = Rämistrasse 101CH-8092 ZürichSwitzerland , city = Zürich , coor = , campus = Urban , language = German, English (Masters and upwards, sometimes Bachelor) , affiliations = CESAER, EUA, GlobalTech, IARU, IDEA League, UNITECH , website ethz.ch, colors = Black and White , logo = ETH Zürich Logo black.svg ETH Zür ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)