|
SPATA21
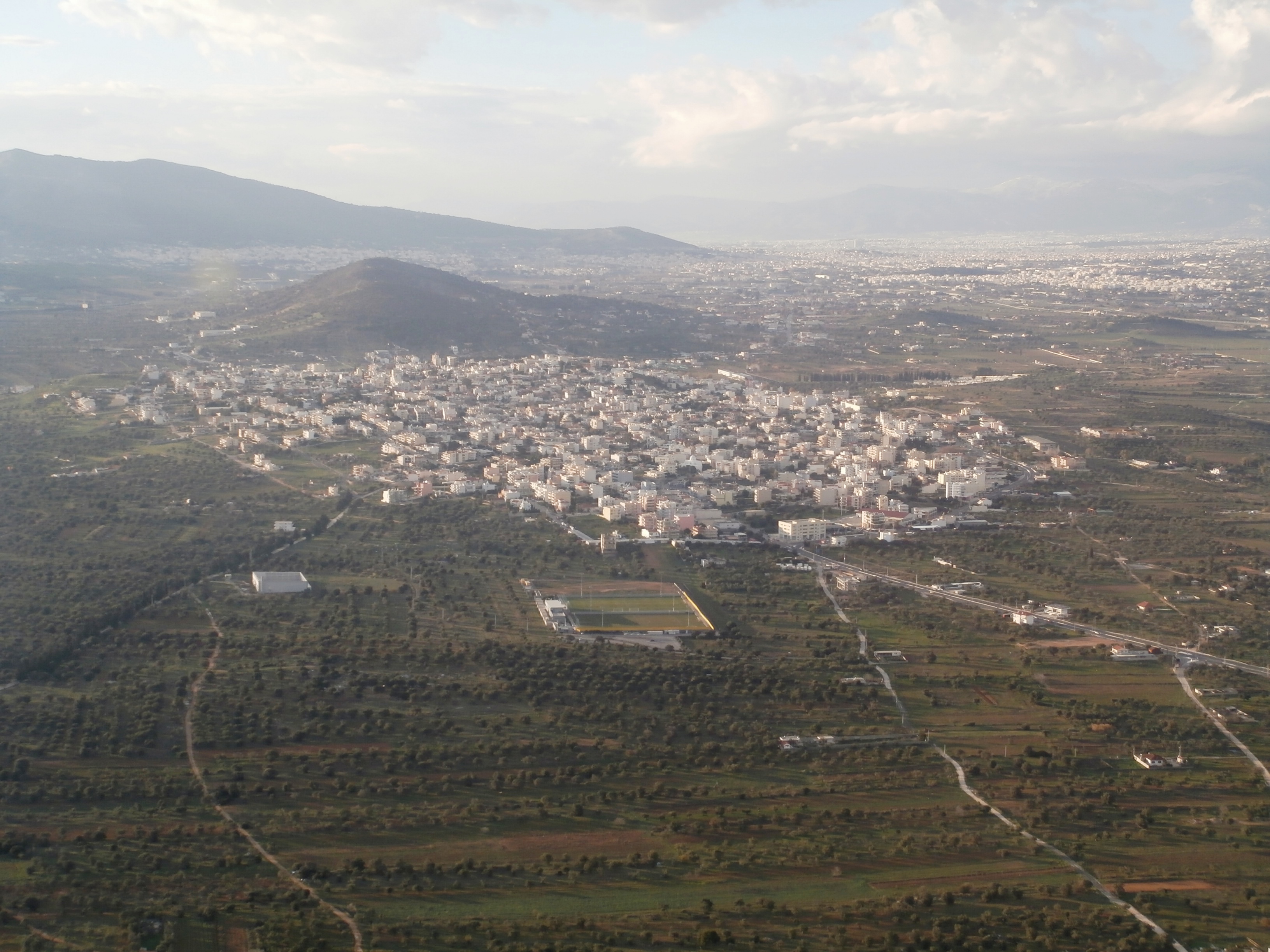
Spata ( el, Σπάτα), is a town east of downtown Athens, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Spata-Artemida, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit (officially named Spata-Loutsa) has an area of 55.042 km2. It is part of Athens metropolitan area. Geography and economy Spata is situated in the middle of the Mesogeia plain, east of Mount Hymettus and west of the Aegean Sea coast. Athens International Airport ("Eleftherios Venizelos") covers the eastern portion of Spata. It is located southeast of Pallini, southwest of Rafina, west of Artemida and about east south east of Athens city center. The town proper is made up of residential neighborhoods. Farmland, mostly vineyards and olive groves, lie around. Retsina wine was the traditional cash crop of the whole area, complemented with olives and olive oil, figs, almonds, pistachios, and wheat. Nowadays viticulture is dwindling as a mass occupation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica (region)
Attica ( el, Περιφέρεια Αττικής, translit=Periféria Attikís, ) is an administrative region of Greece, that encompasses the entire metropolitan area of Athens, the country's capital and largest city. The region is coextensive with the former Attica Prefecture of Central Greece. It covers a greater area than the historical region of Attica. Overview Located on the eastern edge of Central Greece, Attica covers about 3,808 square kilometers. In addition to Athens, it contains within its area the cities of Elefsina, Megara, Laurium, and Marathon, as well as a small part of the Peloponnese peninsula and the islands of Salamis, Aegina, Angistri, Poros, Hydra, Spetses, Kythira, and Antikythera. About 3,800,000 people live in the region, of whom more than 95% are inhabitants of the Athens metropolitan area. In 2019, Attica had the HDI of 0.912, the highest in Greece. Administration The region was established in the 1987 administrative reform, and until 2010 it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spata Training Centre
The Spata Training Centre ( el, Προπονητικό Κέντρο Σπάτων) is the name given to AEK Athens' training complex, located outside Athens in Spata near Athens International Airport. Also hosting the club's youth academy, the facility replaced the old Thrakomakedones Training Centre, which was in use until 2010. History The new architecturally designed AEK Training Centre has been built since 2010 and it is located in Spata, Attica. It is the home of the club's team and academy and is recognized as one of the best in the Balkans. The modern facility - which includes two natural grass pitches, an artificial pitch, world-class player preparation areas, pool and hydrotherapy complex, altitude room, large-scale gymnasium and specialist sports rehabilitation suites - will support the club's ambitions to attract, develop and retain the highest quality talent. Dimitris Melissanidis recently managed to buy another 70 acres of land at this area, in order to enlarge the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
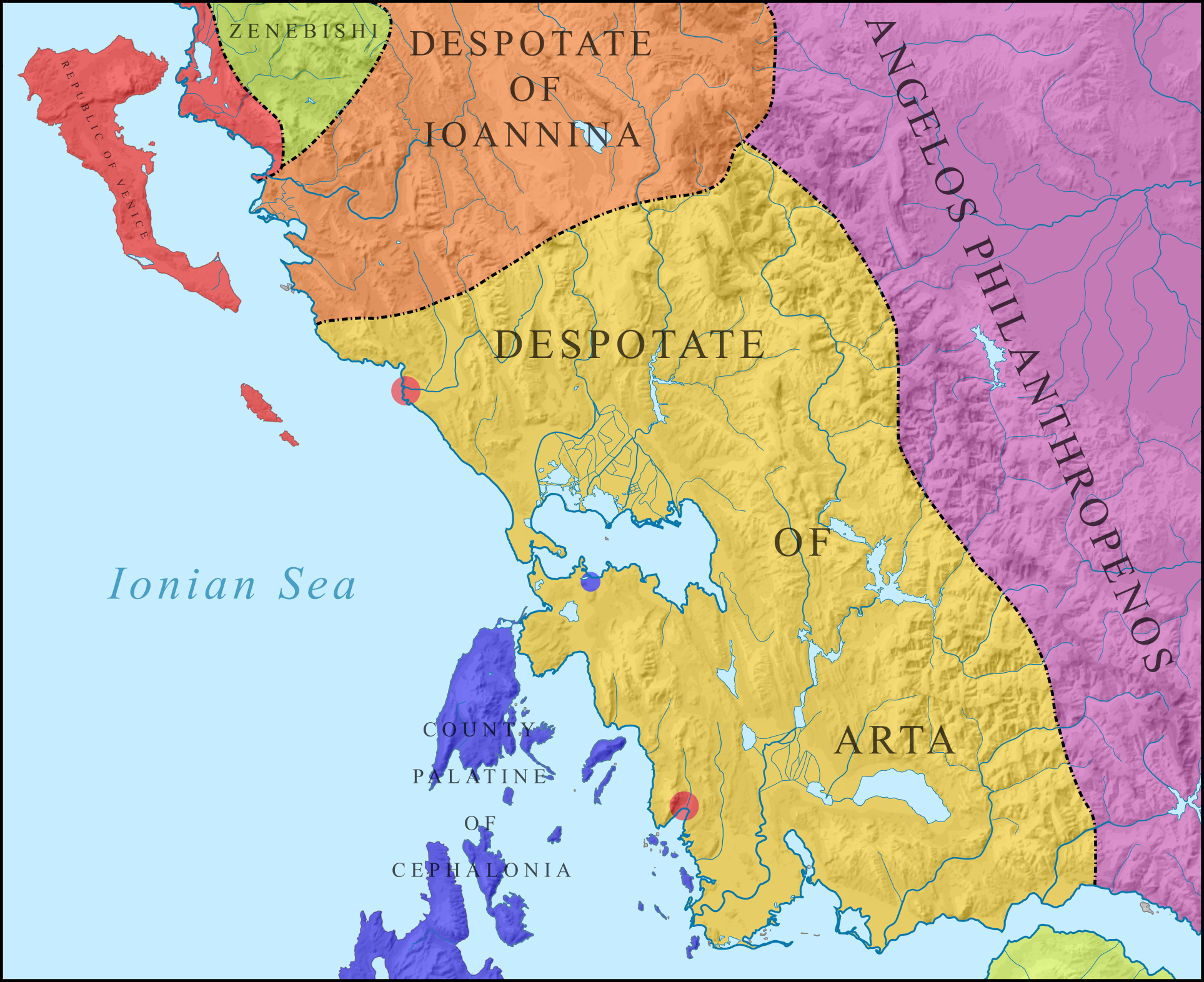
John Spata
Gjin Bua Shpata (sometimes anglicized as ''John Spata'') ( 1358 – 29 October 1399) was an Albanian ruler in Western Greece with the title of Despot. Together with Peter Losha, he led raids into Epirus, Acarnania and Aetolia in 1358. He was recognized as Despot by the titular Eastern Roman Emperor in the early 1360s and ruled Aetolia (1360s–?), Angelokastron (?–1399), Naupactus (1378–1399), and Arta (1370s–1399). Name The word ''spata'', in Albanian ''shpatë'', pl. ''shpata'', 'sword'. According to Orel (1998), the word was borrowed from Latin ''spāta''. Hammond thus believes that he was called "John the Sword". Spatha being a type of Roman sword. Life Karl Hopf's genealogy of the Shpata family is "altogether inaccurate"; according to it, his father was Pietro, the lord of Angelokastron and Delvina (1354) during the reign of Serbian emperor Stefan Dušan (r. 1331–55). It is known that Shpata had a brother, Sgouros Spata. In 1358, some Albanian commanders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru , native_name_lang = , settlement_type = Historical region , image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg , map_alt = , map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich Kiepert, 1902 , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Present status , subdivision_name = Divided between Greece and Albania [Baidu] |
Spata Family
The Spata family ( sq, Shpata, gr, Σπάτα, Σπάτας) was an Albanian noble family active in the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries, initially as Venetian vassals and later as Ottoman vassals. The family's progenitors were the brothers John Spata and Sgouros Spata. Shpata means "sword" in Albanian. In the first half of the 14th century, mercenaries, raiders and migrants known in Greek as ''Άλβανοί'' (''Albanoi'' or "Albanians") flooded into Greece (specifically raiding Thessaly in 1325 and 1334). In 1358, Albanians overran the regions of Epirus, Acarnania and Aetolia and established two principalities under their leaders, John Spata and Peter Losha.. Naupactus (Lepanto) was later taken in 1378. The Spata family frequently collaborated with the Ottomans and saw them as protectors. Although German historian Karl Hopf provided a genealogy of the Spata family, it is deemed by modern scholarship as "altogether inaccurate".. *John Spata, recognized as a ruler in Epirus an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosks
Tosks ( sq, Toskët) are one of two major dialectal subgroups of Albanians (the other being the Ghegs) differentiated by their cultural, linguistic, social and religious characteristics. Territory ''Tosk'' may refer to the Tosk-speaking Albanian population of southern Albania and internal subgroups include the Myzeqars of Myzeqe. The Labs of Labëria (name version in sq, sing: Lab, pl. Lebër, also dial. sing.: Lap) and Chams of Çamëria are separate southern Albanian subgroups "In fact the Liaps and Tsams claimed to be autonomous tribes, distinct and separate from the Gegs and Tosks" "The Albanians are divided into two subgroups: southerners (Tosks, Labs and Chams) and northerners (Gegs), with a border formed by the river Shkumbin." "In historical literature the Chams are thought to form one of the four Albanian tribes (the Labs, Tosks and Gegs are the other three)." which at times are also included in the category of Tosks due to ethno-cultural and dialectal similarities. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvanites
Arvanites (; Arvanitika: , or , ; Greek: , ) are a bilingual population group in Greece of Albanian origin. They traditionally speak Arvanitika, an Albanian language variety, along with Greek. Their ancestors were first recorded as settlers who came to what is today southern Greece in the late 13th and early 14th century. They were the dominant population element in parts of the Peloponnese, Attica and Boeotia until the 19th century.Trudgill (2000: 255). They call themselves Arvanites (in Greek) and Arbëror (in their language). Arvanites today self-identify as Greeks as a result of a process of cultural assimilation,GHM (1995). and do not consider themselves Albanian.Trudgill/Tzavaras (1977). Arvanitika is in a state of attrition due to language shift towards Greek and large-scale internal migration to the cities and subsequent intermingling of the population during the 20th century. Names The name Arvanites and its equivalents are today used both in Greek (, singular form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Archaeological Museum Of Athens
The National Archaeological Museum ( el, Εθνικό Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο) in Athens houses some of the most important artifacts from a variety of archaeological locations around Greece from prehistory to late antiquity. It is considered one of the greatest museums in the world and contains the richest collection of Greek Antiquity artifacts worldwide. It is situated in the Exarcheia area in central Athens between Epirus Street, Bouboulinas Street and Tositsas Street while its entrance is on the Patission Street adjacent to the historical building of the Athens Polytechnic university. History The first national archaeological museum in Greece was established by the governor of Greece Ioannis Kapodistrias in Aigina in 1829. Subsequently, the archaeological collection was relocated to a number of exhibition places until 1858, when an international architectural competition was announced for the location and the architectural design of the new museum.The Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panagiotis Stamatakis
Panagiotis Stamatakis ( el, Παναγιώτης Σταµατάκης) (c.1840–1885) (sometimes anglicised as Panayotis or Stamatakes) was a Greek archaeologist. He is noted particularly for his role in supervising the excavations of Heinrich Schliemann at Mycenae in 1876, and his role in recording and preserving the archaeological remains at the site. Stamatakis was a leading figure of his day in Greek archaeology, being promoted to the country's highest archaeological office ( Ephor General of Antiquities) in 1884. In the wider scholarly community, however, his work and significance was largely forgotten after his death. Modern reassessment of the excavations at Mycenae, fuelled in large part by the rediscovery in the early 21st century of Stamatakis' notebooks from the site, led in turn to a re-evaluation of his importance to the Mycenae excavations and to archaeology more generally: he has been described as 'one of the great Greek archaeologists of the nineteenth century'. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Period
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.Lazaridis, Iosif et al.Genetic origins of the Minoans and Mycenaeans. ''Nature'', 2017Supplementary Information "The Mycenaeans", pp. 2–3).. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, Athens in Central Greece and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)