|
SCF Complex
Skp, Cullin, F-box containing complex (or SCF complex) is a multi-protein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that catalyzes the ubiquitination of proteins destined for 26S proteasomal degradation. Along with the anaphase-promoting complex, SCF has important roles in the ubiquitination of proteins involved in the cell cycle. The SCF complex also marks various other cellular proteins for destruction. Core components SCF contains a variable F-box protein and three core subunits: *F-box protein (FBP) – FBP contributes to the substrate specificity of the SCF complex by first aggregating to target proteins independently of the complex. Each FBP (e.g. Skp2) may recognize several different substrates in a manner that is dependent on post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation. FBP then binds to Skp1 of the SCF complex using an F-box motif, bringing the target protein into proximity with the functional E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. FBP is also essential in reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCF Is A Multisubunit Enzyme
The initials SCF (or scf) may refer to: Associations and organizations *Saba Conservation Foundation *Sahara Conservation Fund *Scientific Committee on Food *Scheduled Castes Federation, a political party in India *Singapore Chess Federation *Singapore Canoe Federation *Société Chimique de France (Chemical Society of France) *Save the Children Fund * Svenska Cykelförbundet In science and technology *Self-consistent field, an approach used in Hartree–Fock methods in quantum systems * Service Control Function in a telecommunications network *Small carbonaceous fossil *SCF-complex (Skp1/Cul1/F-box complex), a ubiquitin ligase *Supercritical fluid *Standard cubic foot of gas *Stem cell factor a cytokine. * Switched Capacitor Filter Other *Stechford railway station, West Midlands, station code *Salem Cricket Foundation Stadium *Sectional center facility, United States Postal Service *South Central Farm *Southern Cathedrals Festival * State College of Florida *Survey of Consumer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin Ligase
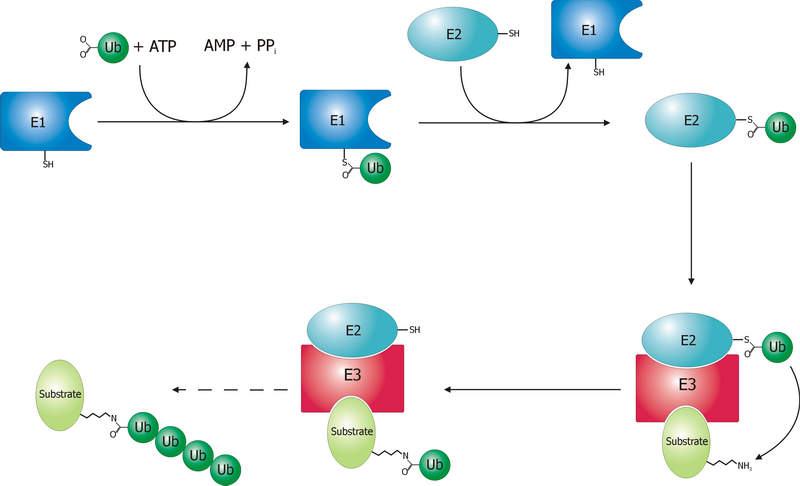
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase-promoting Complex
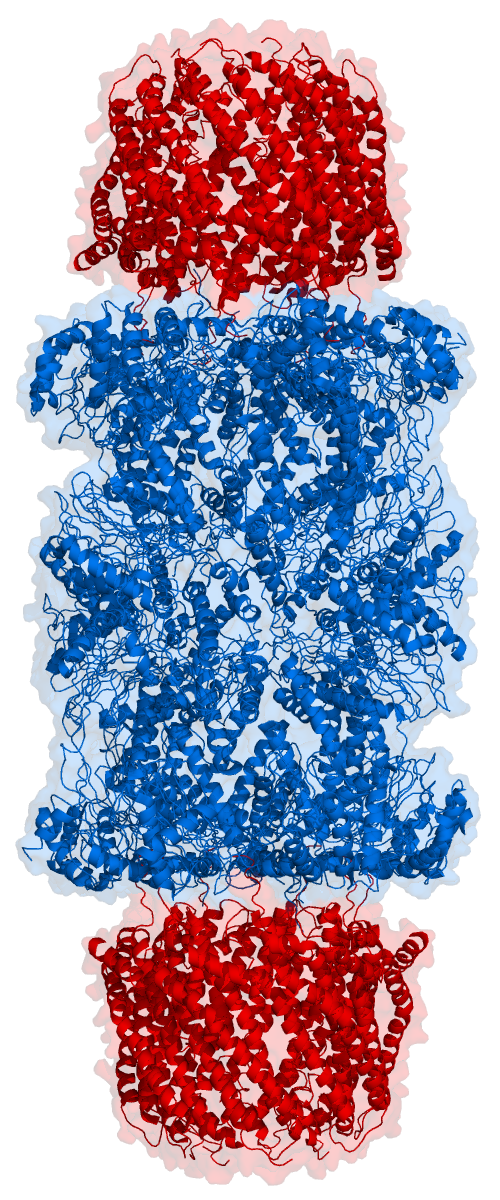
Anaphase-promoting complex (also called the cyclosome or APC/C) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that marks target cell cycle proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. The APC/C is a large complex of 11–13 subunit proteins, including a cullin (Apc2) and RING (Apc11) subunit much like SCF. Other parts of the APC/C have unknown functions but are highly conserved. It was the discovery of the APC/C (and SCF) and their key role in eukaryotic cell-cycle regulation that established the importance of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in cell biology. Once perceived as a system exclusively involved in removing damaged protein from the cell, ubiquitination and subsequent protein degradation by the proteasome is now perceived as a universal regulatory mechanism for signal transduction whose importance approaches that of protein phosphorylation. In 2014, the APC/C was mapped in 3D at a resolution of less than a nanometre, which also uncovered its secondary structure. This finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond, cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-box Protein
F-box proteins are proteins containing at least one F-box domain. The first identified F-box protein is one of three components of the SCF complex, which mediates ubiquitination of proteins targeted for degradation by the 26S proteasome. Core components F-box domain is a protein structural motif of about 50 amino acids that mediates protein–protein interactions. It has consensus sequence and varies in few positions. It was first identified in cyclin F. The F-box motif of Skp2, consisting of three alpha-helices, interacts directly with the SCF protein Skp1. F-box domains commonly exist in proteins in cancer with other protein–protein interaction motifs such as leucine-rich repeats (illustrated in the Figure) and WD repeats, which are thought to mediate interactions with SCF substrates. Function F-box proteins have also been associated with cellular functions such as signal transduction and regulation of the cell cycle. In plants, many F-box proteins are represented in gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skp1
S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SKP1'' gene. This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the SCF ubiquitin ligase protein complex. It binds to F-box proteins (proteins containing an F-box motif), such as cyclin F, S-phase kinase-associated protein 2, and other regulatory proteins involved in ubiquitin dependent proteolysis. The encoded protein also collaborates with a network of proteins to control beta-catenin levels and affects the activity level of beta-catenin dependent TCF transcription factors. Studies have also characterized the protein as an RNA polymerase II elongation factor. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 7. Interactions SKP1A has been shown to interact with: * BTRC, * CACYBP, * CDCA3, * CDK9, * CUL1, * FBXL3, * FBXO4, * FBXO5, * FBXO7, * FBXW2, * FBXW7, and * SKP2 S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cullin
Cullins are a family of hydrophobic scaffold proteins which provide support for ubiquitin ligases (E3). All eukaryotes appear to have cullins. They combine with RING proteins to form ''Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases'' (CRLs) that are highly diverse and play a role in myriad cellular processes, most notably protein degradation by ubiquitination. The human genome contains eight cullin genes * CUL1, part of SCF complex * CUL2, part of ECS complex (Elongin C - CUL2 - SOCS-box) * CUL3, part of CUL3-BTB complex * CUL4A * CUL4B * CUL5 * CUL7 * CUL9, also known as PARC There is also a more distant member called ANAPC2 (or APC2), part of the Anaphase-promoting complex. CUL1, 2, 3, 4A, 4B, 5 and 7 each form part of a multi-subunit ubiquitin complex. Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRLs), such as Cul1 (SCF) play an essential role in targeting proteins for ubiquitin-mediated destruction; as such, they are diverse in terms of composition and function, regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RBX1
RING-box protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RBX1'' gene. Function This gene encodes an evolutionarily conserved protein that interacts with cullins. The protein plays a unique role in the ubiquitination reaction by heterodimerizing with cullin-1 to catalyze ubiquitin polymerization. It also may be involved in the regulation of protein turn-over. Interactions RBX1 has been shown to interact with: * CAND1, * CUL1, * CUL2, * CUL4A, * CUL5 * CUL7, * DCUN1D1, and * P70-S6 Kinase 1 Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (S6K1), also known as p70S6 kinase (p70S6K, p70-S6K), is an enzyme (specifically, a protein kinase) that in humans is encoded by the ''RPS6KB1'' gene. It is a serine/threonine kinase that acts downstream of PIP3 .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{PDB Gallery, geneid=9978 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wee1
Wee1 is a nuclear kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases in the fission yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe'')Wee1has a molecular mass of 96 kDa and is a key regulator of cell cycle progression. It influences cell size by inhibiting the entry into mitosis, through inhibiting Cdk1. Wee1 has homologues in many other organisms, including mammals. Introduction The regulation of cell size is critical to ensure functionality of a cell. Besides environmental factors such as nutrients, growth factors and functional load, cell size is also controlled by a cellular cell size checkpoint. Wee1 is a component of this checkpoint. It is a kinase determining the timepoint of entry into mitosis, thus influencing the size of the daughter cells. Loss of Wee1 function will produce smaller than normal daughter cell, because cell division occurs prematurely. Its name is derived from the Scottish dialect word wee, meaning small - its discoverer Paul Nurse was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |