|
SAM-IV Riboswitch
SAM-IV riboswitches are a kind of riboswitch that specifically binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a cofactor used in many methylation reactions. Originally identified by bioinformatics, SAM-IV riboswitches are largely confined to the Actinomycetales, an order of Bacteria. Conserved features of SAM-IV riboswitch and experiments imply that they probably share a similar SAM-binding site to another class of SAM-binding riboswitches called SAM-I riboswitches. However, the scaffolds of these two types of riboswitch appear to be quite distinct. The structural relationship between these riboswitch types has been studied. See also * SAM-I riboswitch * SAM-II riboswitch The SAM-II riboswitch is a RNA element found predominantly in Alphaproteobacteria that binds S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). Its structure and sequence appear to be unrelated to the SAM riboswitch found in Gram-positive bacteria. This SAM riboswit ... * SAM-III riboswitch * SAM-V riboswitch * SAM-VI riboswitch R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) or proteins across species ( orthologous sequences), or within a genome ( paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa ( xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the RNA components of ribosomes present in all domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics and mathematics. History The discovery of the role of DNA in heredity, and observations by Frederick Sanger of variation between animal insulins in 1949, promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riboswitch
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules. The original definition of the term "riboswitch" specified that they directly sense small-molecule metabolite concentrations. Although this definition remains in common use, some biologists have used a broader definition that includes other cis-regulatory RNAs. However, this article will discuss only metabolite-binding riboswitches. Most known riboswitches occur in bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
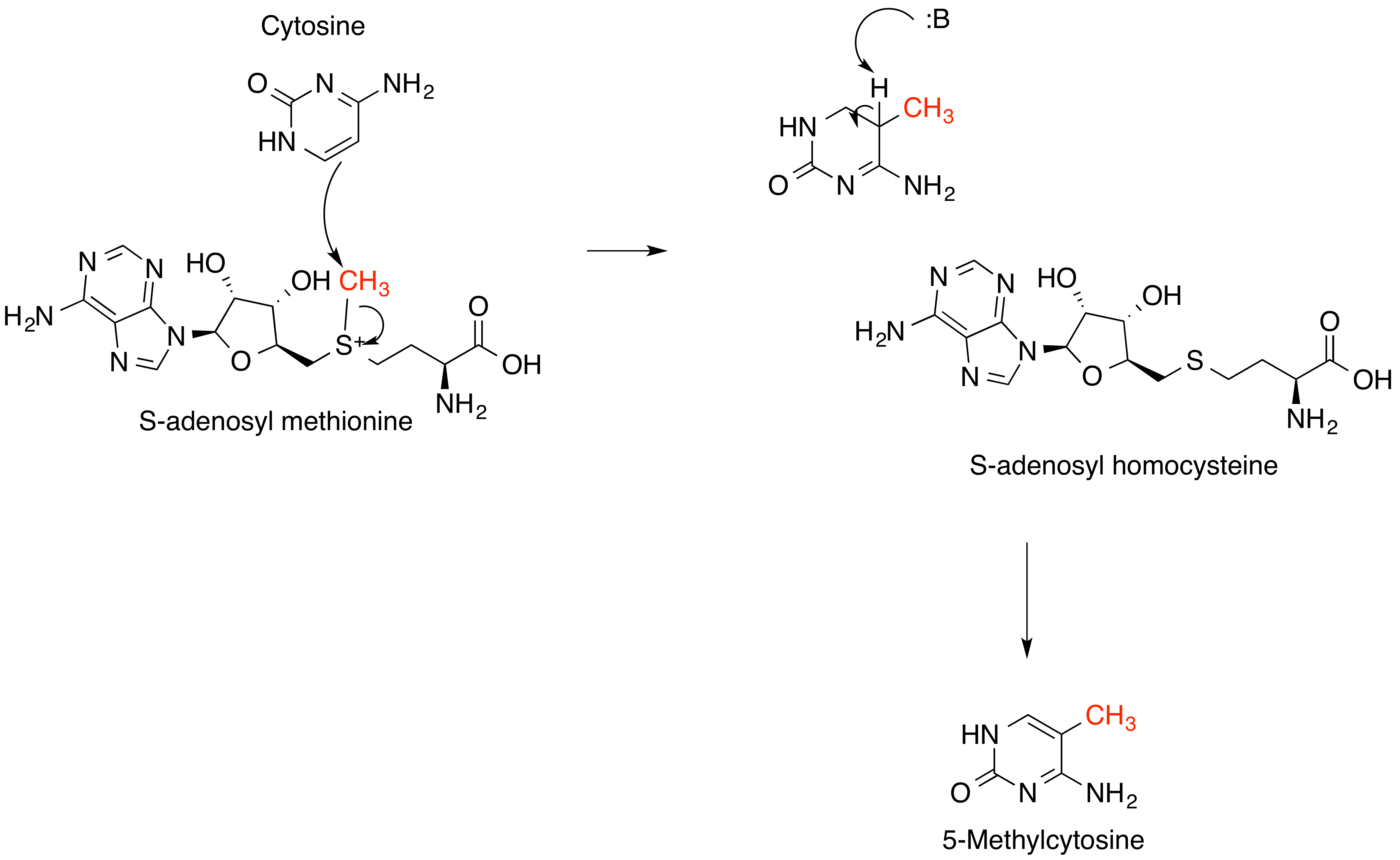
S-adenosylmethionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinomycetales
The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycetes can form rod- or coccoid-shaped forms, while others can form spores on aerial hyphae. Actinomycetales bacteria can be infected by bacteriophages, which are called actinophages. Actinomycetales can range from harmless bacteria to pathogens with resistance to antibiotics. Reproduction Actinomycetales have 2 main forms of reproduction: spore formation and hyphae fragmentation. During reproduction, Actinomycetales can form conidiophores, sporangiospores, and oidiospores. In reproducing through hyphae fragmentation, the hyphae formed by Actinomycetales can be a fifth to half the size of fungal hyphae, and bear long spore chains. Presence and associations Actinomycetales can be found mostly in soil and decaying organic matter, as well as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAM Riboswitch
The SAM riboswitch (also known as the S-box leader and the SAM-I riboswitch) is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in ''Bacillus subtilis'' that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase to read-through the downstream gene.Winkler, W., Nahvi, A., Sudarsan, N., Barrick, J., and Breaker, R. (2003) An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding S-adenosylmethionine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAM Riboswitch (S-box Leader)
The SAM riboswitch (also known as the S-box leader and the SAM-I riboswitch) is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in ''Bacillus subtilis'' that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase to read-through the downstream gene.Winkler, W., Nahvi, A., Sudarsan, N., Barrick, J., and Breaker, R. (2003) An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding S-adenosylmethionine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAM-II Riboswitch
The SAM-II riboswitch is a RNA element found predominantly in Alphaproteobacteria that binds S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). Its structure and sequence appear to be unrelated to the SAM riboswitch found in Gram-positive bacteria. This SAM riboswitch is located upstream of the metA and metC genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and other methionine and SAM biosynthesis genes in other alpha-proteobacteria. Like the other SAM riboswitch, it probably functions to turn off expression of these genes in response to elevated SAM levels. A significant variant of SAM-II riboswitches was found in ''Pelagibacter ubique'' and related marine bacteria and called SAM-V. Also, like many structured RNAs, SAM-II riboswitches can tolerate long loops between their stems. Structure The SAM-II riboswitch is short with less than 70 nucleotides and is structurally relatively simple being composed of a single hairpin A hairpin or hair pin is a long device used to hold a person's hair in place. It ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMK Box Riboswitch
The SMKbox riboswitch (also known as SAM-III) is an RNA element that regulates gene expression in bacteria. The SMK box riboswitch is found in the 5' UTR of the MetK gene in lactic acid bacteria. The structure of this element changes upon binding to S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) to a conformation that blocks the shine-dalgarno sequence and blocks translation of the gene. There are other known SAM-binding riboswitches such as SAM-I and SAM-II, but these appear to share no similarity in sequence or structure to SAM-III. Structure The crystal structure of the riboswitch from ''E. faecalis'' was solved by X-ray crystallography. The structure showed that the most conserved nucleotides involved in SAM binding were organised around a junction between three helices. In some species there are large insertions of up to 210 nucleotides within this structure. See also * SAH riboswitch * SAM-I riboswitch * SAM-II riboswitch * SAM-IV riboswitch SAM-IV riboswitches are a kind of ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |