|
Sąjūdis
The Sąjūdis (, ), initially known as the Reform Movement of Lithuania (), is a political organisation which led the struggle for Lithuanian independence in the late 1980s and early 1990s. It was established on 3 June 1988 as the first opposition party in Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Lithuania, and was led by Vytautas Landsbergis. Its goal was to seek the return of independent status for Lithuania. Historical background In the mid-1980s, Lithuania's Communist Party leadership hesitated to embrace Gorbachev's perestroika and glasnost. The death of Petras Griškevičius, first secretary of the Communist Party of Lithuania, in 1987 was merely followed by the appointment of another rigid communist, Ringaudas Songaila. However, encouraged by the rhetoric of Mikhail Gorbachev, noting the strengthening position of Solidarity (Polish trade union), Solidarity in Poland and encouraged by the Pope and the U.S. Government, Baltic independence activists began to hold publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sąjūdis Rally (1988)
The Sąjūdis rally was a commemoration event organized by the Lithuanian Reform Movement (Sąjūdis) in Vingis Park, Vilnius, Lithuanian SSR, to mark the anniversary of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. The rally took place on August 23, 1988, and was attended by approximately 250,000 people. Organization and Location Initially, the rally was planned to be held in Cathedral Square, where protests and a hunger strike organized by the Lithuanian Freedom League had been taking place since mid-August, demanding the release of political prisoners. However, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Lithuania refused to grant permission for Cathedral Square, instead suggesting Vingis Park. The Sąjūdis leadership agreed on the condition that they be allowed to announce the location change on television. The televised announcement was made by Vytautas Landsbergis, who also referenced the conspiracy between Joseph Stalin and Adolf Hitler and their crimes. Speeches and Key Partici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vytautas Landsbergis
Vytautas Landsbergis (; born 18 October 1932) is a Lithuanian politician and former Member of the European Parliament. He was the first Speaker of Reconstituent Seimas of Lithuania after its independence declaration from the Soviet Union. He has written 20 books on a variety of topics, including a biography of Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis, as well as works on politics and music. He is a founding signatory of the Prague Declaration, and a member of the international advisory council of the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. Biography Vytautas Landsbergis, member of an old German Landsberg family, was born in Kaunas, Lithuania. His father was the architect Vytautas Landsbergis-Žemkalnis. His mother, ophthalmologist Dr. Ona Jablonskytė-Landsbergienė, assisted her sister's family in sheltering a Jewish child, Avivit Kissin, from the Holocaust. She brought Kissin to her sister's home and produced a forged birth certificate with a Lithuanian for Kissin. Her s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian exclave, semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.89 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities include Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians who are the titular nation and form the majority of the country's population, belong to the ethnolinguistic group of Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian. For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringaudas Songaila
Ringaudas Bronislovas Songaila (20 April 1929 – 25 June 2019) was a communist politician and Nomenklatura of the Lithuanian SSR. He was the last First Secretary of the Communist Party of Lithuania ('' de facto'' leader of Lithuanian SSR) from 1987–1988. Biography Songaila was born in Klaipėda. He graduated from a veterinary school and within five years became a deputy of the Minister of Agriculture. In 1962, at the age of 33, he became Minister of Production of Agricultural Products and Resources. In agriculture, he worked on increasing the size of kolkhozs (collective farms), increasing centralization and specialization of agricultural production, elimination of khutors (single homesteads), and implementation of land improvements. Songaila was a member of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Lithuania (1962–1981), Chairman of the Council of Ministers (1981–1985; equivalent to Prime Minister), Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Academy Of Sciences
The Lithuanian Academy of Sciences or LMA (, ) is a state-funded independent organization in Lithuania dedicated for science and research. Its mission is to mobilize prominent scientists and initiate activities that would strengthen the welfare of Lithuania and contribute to the scientific, social, cultural and economic development of the country. History The idea of establishing the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences was proposed in 1773 by Martynas Počobutas and other members of Vilnius University in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, but it was not implemented due to wars and conflicts in the region. The idea of an independent institution for science and research was revived during the Lithuanian National Revival with the main proponents of it being the members of the Lithuanian Scientific Society, including Jonas Basanavičius and Jonas Šliūpas. However, the implementation began only in 1939, initially with the establishment of the Institute of the Lithuanian Language. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language. Lithuanian is closely related to neighbouring Latvian language, Latvian, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible. It is written in a Latin script. In some respects, some linguists consider it to be the most conservative (language), conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Sovietism
Anti-Sovietism or anti-Soviet sentiment are activities that were actually or allegedly aimed against the Soviet Union or government power within the Soviet Union. Three common uses of the term include the following: * Anti-Sovietism in international politics, such as the Western opposition to the Soviet Union during the Cold War as part of broader anti-communism. * Anti-Soviet opponents of the Bolsheviks shortly after the Russian Revolution and during the Russian Civil War. * Soviet citizens (allegedly or actually) involved in anti-government activities. History In the Soviet Union During the Russian Civil War that followed the October Revolution of 1917, the anti-Soviet side was the White movement. During the Interwar period, some resistance movements, particularly in the 1920s, were cultivated by Polish intelligence in the form of the Promethean project. After Germany's attack on the Soviet Union in 1941, anti-Soviet forces were created and led primarily by Nazi Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targa Sajudis
Targa or TARGA may refer to: Car racing events *Targa Adelaide, in Australia * Targa Canada West, in British Columbia *Targa Florio, in Sicily, Italy, 1906–1977 * Targa Florio Rally, in Sicily, Italy, from 1978 * Targa High Country, in Victoria, Australia * Targa New Zealand * Targa Newfoundland, in Canada * Targa Rignano, in Italy, 1902–1904 * Targa Tasmania, Australia * Targa West, in Western Australia * Targa Wrest Point, in Tasmania, Australia Places * Targa, Kasur, Pakistan * Targa, Sialkot, Pakistan * Targa, Tasmania, Australia * Tarġa Battery, in Malta Other uses * Targa top, or targa, a car body style **Targa, versions of the Porsche 911 * Targa, a range of boats made by Fairline * Targa, a range of boats used by the Metropolitan Police Marine Policing Unit * ''Targa'', unreleased version of video game '' Rendering Ranger: R2'' * Targa, a pen by Sheaffer * Truevision TGA, or TARGA, an image file format * UP Targa, a German paraglider design See also * Targe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
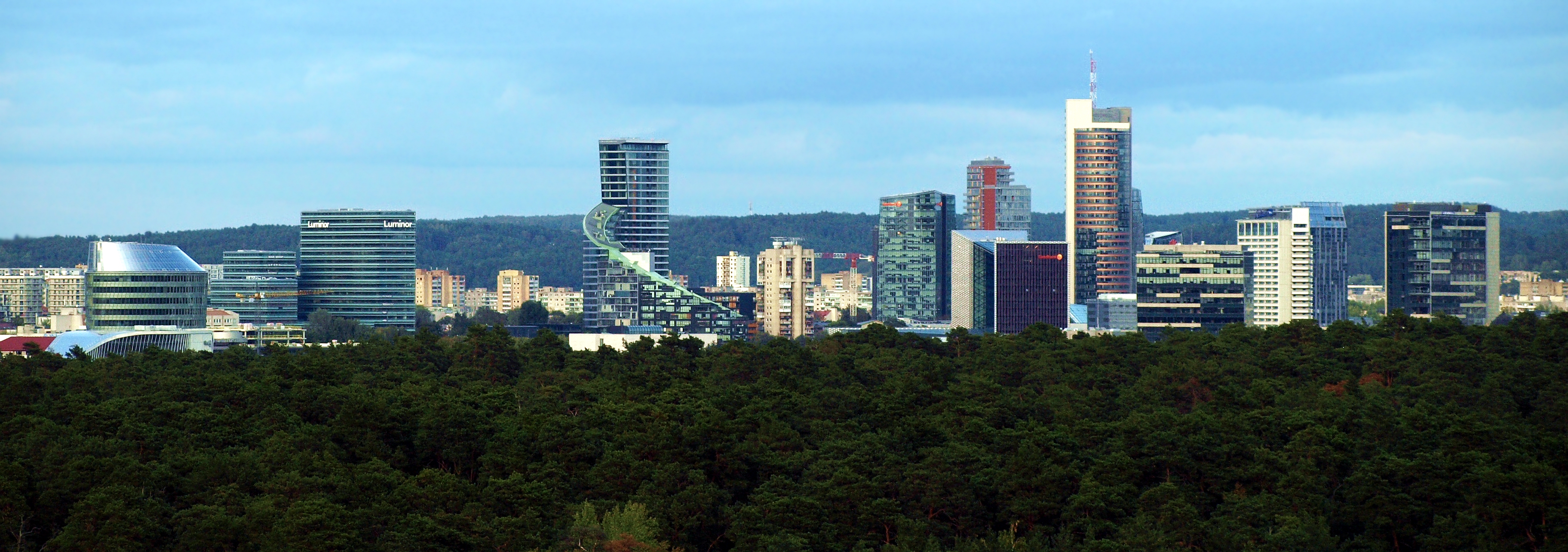
Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population was 607,667, and the Vilnius urban area (which extends beyond the city limits) has an estimated population of 747,864. Vilnius is notable for the architecture of its Vilnius Old Town, Old Town, considered one of Europe's largest and best-preserved old towns. The city was declared a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The architectural style known as Vilnian Baroque is named after the city, which is farthest to the east among Baroque architecture, Baroque cities and the largest such city north of the Alps. The city was noted for its #Demographics, multicultural population during the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, with contemporary sources comparing it to Babylon. Before World War II and The Holocaust in Lithuania, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, with a secret protocol establishing Soviet and German spheres of influence across Eastern Europe. The pact was signed in Moscow on 24 August 1939 (backdated 23 August 1939) by Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop. The treaty was the culmination of negotiations around Nazi–Soviet economic relations (1934–1941)#1938–1939 deal discussions, the 1938–1939 deal discussions, after tripartite discussions between the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom and France had broken down. The Soviet-German pact committed both sides to neither aid nor ally itself with an enemy of the other for the following 10 years. Under the Secret Protocol, Second Polish Republic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant
The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant () is a Nuclear decommissioning, decommissioned two-unit RBMK-1500 nuclear power plant, nuclear power station in Visaginas Municipality, Lithuania. It was named after the nearby city of Ignalina. Due to the plant's similarities to the infamous Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in both reactor design and lack of a robust containment building, Lithuania agreed to close the plant as part of its agreement of 2004 enlargement of the European Union, accession to the European Union. Unit 1 was closed in December 2004; Unit 2 in December 2009. The plant accounted for 25% of Lithuania's electricity generating capacity and supplied about 70% of Lithuania's electrical demand. It was closed on 31 December 2009. Proposals have been made to construct a new nuclear power plant at the site, but such plans have yet to come to fruition. Reactors The Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant contained two Soviet Union, Soviet-designed RBMK-1500 water-cooled graphite-neutron mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vingis Park
Vingis Park () is the largest park in Vilnius, Lithuania, covering . It is located in Vilkpėdė eldership near a curve of the Neris River, hence its Lithuanian name "vingis" which means "bend" or "curve". A pedestrian bridge connects the park with Žvėrynas. It is used as a venue for various events, especially concerts and sports competitions. It contains a stadium, an amphitheater and a department of the Botanical Garden of Vilnius University. History The park's history dates back several centuries. Palace in Zakret Vingis has also a historical Polish name of the location: Zakręt (with the same meaning). It was the site of a Palace in Zakret, that eventually was bought by the Local Russian governor general of Vilna Governorate, Levin August von Bennigsen in 1801. Prior to his purchase, it was a Jesuit palace built on a design by Johann Christoph Glaubitz. Bennigsen's palace in Zakret is where, during a ball that took place on the night of 24/25 June 1812, Tzar A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |