|
Syzygys
Syzygys is a Japanese organ-violin duo composed of Hitomi Shimizu on organ and Hiromi Nishida on violin. Formed in 1985, they play "microtonal pop music", specifically just intonation in the form of Harry Partch's 43-tone scale.Louise Duchesneau, Wolfgang Marx (2011). ''György Ligeti: Of Foreign Lands and Strange Sounds'', p.136. Boydell & Brewer. . "The music of Syzygys...which is based on Partch's 43-tone scale, remains an individual case. Nishida studied Arabic style violin with Abdo Dagir. They have released albums on Tzadik Records, including ''Syzygys: Complete Studio Recordings'' (2003, Tzadik #7240). , ''Huygens-Fokker.org''. Accessed: December 09 2016. György Ligeti
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitomi Shimizu
Hitomi Shimizu (冷水ひとみ) is a keyboardist and composer of live action films, television programs, animated shorts and videogames. She is part of a musical duo with violinist Hiromi Nishida called Syzygys. Born in Nara, Japan, she majored in music composition at the Toho Gakuen School of Music. Her score for the 2001 comedy ''Waterboys'', composed with Gakuji Matsuda, won the Japan Academy Prize for best film score. She also contributed music to the short film ''Mt. Head'', by Kōji Yamamura, which won the top prize at the 27th Annecy International Animation Film Festival, and was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Animated Short Film. That film also won the Best Soundtrack Creation Award at the Clermont-Ferrand International Short Film Festival. Shimizu has written music for several horror projects. She was the composer of the television series ‘’ Gakkou no Kaidan’’ (School Ghost Story)’’ with Gary Ashiya. Following this series, both musicians co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzadik Records
Tzadik Records is a record label in New York City that specializes in avant-garde and experimental music. The label was established by composer and saxophonist John Zorn in 1995. He is the executive producer of all Tzadik releases. Tzadik is a not-for-profit, cooperative record label. Tzadik has released over 400 albums by a variety of artists with diverse musical backgrounds, including free improvisation, jazz, noise, klezmer, rock, and experimental composition. On the label's catalogue are releases by Zorn himself and his multifaceted "songbook" group Masada; singer Mike Patton; guitarists Derek Bailey, Yoshihide Otomo, Tim Sparks, Buckethead and Keiji Haino; noise music icon Merzbow; composers Gordon Mumma, Frank Denyer, Arnold Dreyblatt, and Teiji Ito; experimental groups Kayo Dot, Time of Orchids and Rashanim, microtonalists Syzygys; drummer Tatsuya Yoshida and his bands Ruins and Korekyojinn; trumpeter Wadada Leo Smith; electroacoustic composer Noah Creshevsky; and jazz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pump Organ
The pump organ is a type of free-reed organ that generates sound as air flows past a vibrating piece of thin metal in a frame. The piece of metal is called a reed. Specific types of pump organ include the reed organ, harmonium, and melodeon. The idea for the free reed was imported from China through Russia after 1750, and the first Western free-reed instrument was made in 1780 in Denmark. More portable than pipe organs, free-reed organs were widely used in smaller churches and in private homes in the 19th century, but their volume and tonal range were limited. They generally had one or sometimes two manuals, with pedal-boards being rare. The finer pump organs had a wider range of tones, and the cabinets of those intended for churches and affluent homes were often excellent pieces of furniture. Several million free-reed organs and melodeons were made in the US and Canada between the 1850s and the 1920s, some of which were exported. The Cable Company, Estey Organ, and Mason & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violin
The violin, sometimes known as a ''fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone (string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular use. The violin typically has four strings (music), strings (some can have five-string violin, five), usually tuned in perfect fifths with notes G3, D4, A4, E5, and is most commonly played by drawing a bow (music), bow across its strings. It can also be played by plucking the strings with the fingers (pizzicato) and, in specialized cases, by striking the strings with the wooden side of the bow (col legno). Violins are important instruments in a wide variety of musical genres. They are most prominent in the Western classical music, Western classical tradition, both in ensembles (from chamber music to orchestras) and as solo instruments. Violins are also important in many varieties of folk music, including country music, bluegrass music, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtonal
Microtonal music or microtonality is the use in music of microtones—intervals smaller than a semitone, also called "microintervals". It may also be extended to include any music using intervals not found in the customary Western tuning of twelve equal intervals per octave. In other words, a microtone may be thought of as a note that falls between the keys of a piano tuned in equal temperament. In ''Revising the musical equal temperament,'' Haye Hinrichsen defines equal temperament as “the frequency ratios of all intervals are invariant under transposition (translational shifts along the keyboard), i.e., to be constant. The standard twelve-tone ''equal temperament'' (ET), which was originally invented in ancient China and rediscovered in Europe in the 16th century, is determined by two additional conditions. Firstly the octave is divided into twelve semitones. Secondly the octave, the most fundamental of all intervals, is postulated to be pure (beatless), as described by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just Intonation
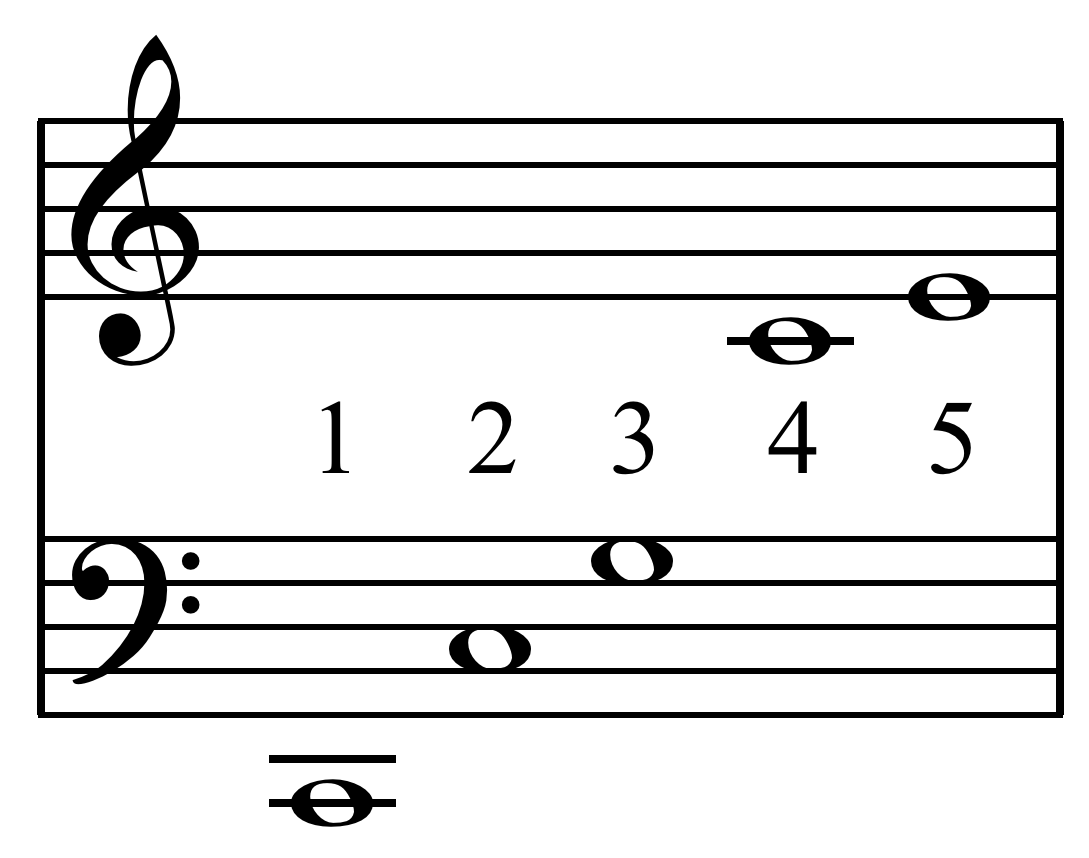
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals Interval may refer to: Mathematics and physics * Interval (mathematics), a range of numbers ** Partially ordered set#Intervals, its generalization from numbers to arbitrary partially ordered sets * A statistical level of measurement * Interval e ... as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of Frequency, frequencies. An interval (music), interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Partch
Harry Partch (June 24, 1901 – September 3, 1974) was an American composer, music theorist, and creator of unique musical instruments. He composed using scales of unequal intervals in just intonation, and was one of the first 20th-century composers in the West to work systematically with microtonal scales, alongside Lou Harrison. He built custom-made instruments in these tunings on which to play his compositions, and described the method behind his theory and practice in his book '' Genesis of a Music'' (1947). Partch composed with scales dividing the octave into 43 unequal tones derived from the natural harmonic series; these scales allowed for more tones of smaller intervals than in standard Western tuning, which uses twelve equal intervals to the octave. To play his music, Partch built many unique instruments, with such names as the Chromelodeon, the Quadrangularis Reversum, and the Zymo-Xyl. Partch described his music as corporeal, and distinguished it from abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Partch's 43-tone Scale
The 43-tone scale is a just intonation scale with 43 pitches in each octave. It is based on an eleven-limit tonality diamond, similar to the seven-limit diamond previously devised by Max Friedrich Meyer and refined by Harry Partch. The first of Partch's "four concepts" is "The scale of musical intervals begins with absolute consonance ( 1 to 1) and gradually progresses into an infinitude of dissonance, the consonance of the intervals decreasing as the odd numbers of their ratios increase." Almost all of Partch's music is written in the 43-tone scale, and although most of his instruments can play only subsets of the full scale, he used it as an all-encompassing framework. Construction Partch chose the 11 limit (i.e. all rational numbers with odd factors of numerator and denominator not exceeding 11) as the basis of his music, because the 11th harmonic is the first that is utterly foreign to Western ears. The seventh harmonic is poorly approximated by 12-tone equal temperament, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Tone System
The modern Arab tone system, or system of musical tuning, is based upon the theoretical division of the octave into twenty-four equal divisions or 24-tone equal temperament (24-TET), the distance between each successive note being a quarter tone (50 cents). Each tone has its own name not repeated in different octaves, unlike systems featuring octave equivalency. The lowest tone is named ''yakah'' and is determined by the lowest pitch in the range of the singer. The next higher octave is ''nawa'' and the second ''tuti''. However, from these twenty-four tones, seven are selected to produce a scale and thus the interval of a quarter tone is never used and the three-quarter tone or neutral second should be considered the characteristic interval. By contrast, in the European equally tempered scale the octave is divided into twelve equal divisions, or exactly half as many as the Arab system. Thus the system is written in European musical notation using a slashed flat for quarter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdo Dagir
In Medicine, abdo is short for abdominal. As a name, notable people called Abdo, Abdou or Abdu include: People A masculine Arabic name, and a nickname for Abdul. The name is also of Syriac origin and is a variant of 'Abdā, meaning 'servant' or 'slave'. Given name *Abdo Al-Edresi (born 1986), Yemeni football player *Abdou Alassane Dji Bo (born 1979), Nigerien judoka *Abdou Cherif, Moroccan singer *Abdou Diouf (born 1935), second president of Senegal *Abdou Doumbia (born 1990), French footballer *Abdou Soulé Elbak (born 1954), president of the autonomous island of Grande Comore *Abdo Hakim (born 1973), Lebanese actor and voice actor *Abdu al-Hamuli (1836–1901), Egyptian musician *Abdo Hussameddin (born 1954), Syrian politician and minister *Abdo Khal (born 1962), Saudi Arabian author *Abdou El-Kholti (born 1980), French footballer * Abdoh Otaif (born 1984), Saudi Arabian football player *Abdou Sall (born 1980), Senegalese footballer *Abdu Shaher, English martial artist *Abdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdu Dagher
In Medicine, abdo is short for abdominal. As a name, notable people called Abdo, Abdou or Abdu include: People A masculine Arabic name, and a nickname for Abdul. The name is also of Syriac origin and is a variant of 'Abdā, meaning 'servant' or 'slave'. Given name *Abdo Al-Edresi (born 1986), Yemeni football player *Abdou Alassane Dji Bo (born 1979), Nigerien judoka *Abdou Cherif, Moroccan singer *Abdou Diouf (born 1935), second president of Senegal *Abdou Doumbia (born 1990), French footballer *Abdou Soulé Elbak (born 1954), president of the autonomous island of Grande Comore *Abdo Hakim (born 1973), Lebanese actor and voice actor *Abdu al-Hamuli (1836–1901), Egyptian musician *Abdo Hussameddin (born 1954), Syrian politician and minister *Abdo Khal (born 1962), Saudi Arabian author *Abdou El-Kholti (born 1980), French footballer * Abdoh Otaif (born 1984), Saudi Arabian football player *Abdou Sall (born 1980), Senegalese footballer *Abdu Shaher, English martial artist *Abdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
György Ligeti
György Sándor Ligeti (; ; 28 May 1923 – 12 June 2006) was a Hungarian-Austrian composer of contemporary classical music. He has been described as "one of the most important avant-garde composers in the latter half of the twentieth century" and "one of the most innovative and influential among progressive figures of his time". Born in Transylvania, Romania, he lived in the Hungarian People's Republic before emigrating to Austria in 1956. He became an Austrian citizen in 1968. In 1973 he became professor of composition at the Hamburg Hochschule für Musik und Theater, where he worked until retiring in 1989. He died in Vienna in 2006. Restricted in his musical style by the authorities of Communist Hungary, only when he reached the West in 1956 could Ligeti fully realise his passion for avant-garde music and develop new compositional techniques. After experimenting with electronic music in Cologne, Germany, his breakthrough came with orchestral works such as ''Atmosphères'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)