|
Syrtis Major Quadrangle
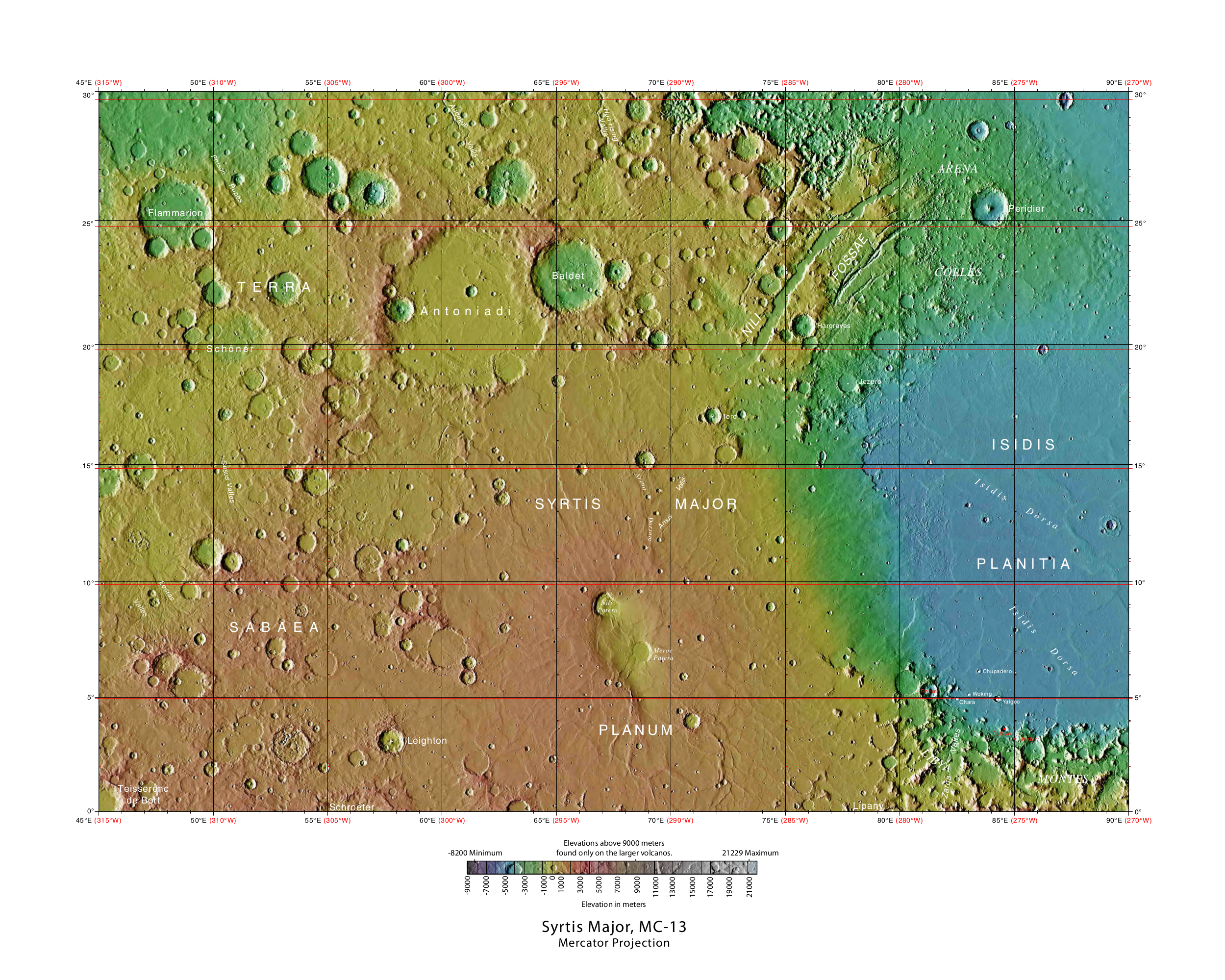
The Syrtis Major quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Syrtis Major quadrangle is also referred to as MC-13 (Mars Chart-13). The quadrangle covers longitudes 270° to 315° west and latitudes 0° to 30° north on Mars. Syrtis Major quadrangle includes Syrtis Major Planum and parts of Terra Sabaea and Isidis Planitia. Syrtis Major is an old shield volcano with a central depression that is elongated in a north–south direction. It contains the calderas Meroe Patera and Nili Patera. Interesting features in the area include dikes and inverted terrain. The '' Beagle 2'' lander was about to land near the quadrangle, particularly in the eastern part of Isidis Planitia, in December 2003, when contact with the craft was lost. In January 2015, NASA reported the ''Beagle 2'' had been found on the surface in Isidis Planitia (location is about ). High-resolution images captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrangle (geography)
A "quadrangle" is a topographic map produced by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) covering the United States. The maps are usually named after local physiographic features. The shorthand "quad" is also used, especially with the name of the map; for example, "the Ranger Creek, Texas quad". A quadrangle is defined by north and south boundaries of Circle of latitude, constant latitude (which are not great circles so are curved), and by east and west boundaries of constant longitude. From approximately 1947–1992, the USGS produced the 7.5 minute series, with each map covering an area one-quarter of the older 15-minute quad series, which it replaced. A 7.5 minute quadrangle map covers an area of . Both map series were produced via photogrammetry, photogrammetric analysis of aerial photography using stereoplotters supplemented by field surveys. These maps employ the 1927 North American Datum (NAD27); conversion or a change in settings is necessary when using a GPS which by d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as '' spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Flammarion
Nicolas Camille Flammarion FRAS (; 26 February 1842 – 3 June 1925) was a French astronomer and author. He was a prolific author of more than fifty titles, including popular science works about astronomy, several notable early science fiction novels, and works on psychical research and related topics. He also published the magazine '' L'Astronomie'', starting in 1882. He maintained a private observatory at Juvisy-sur-Orge, France. Biography Camille Flammarion was born in Montigny-le-Roi, Haute-Marne, France. He was the brother of Ernest Flammarion (1846–1936), the founder of the Groupe Flammarion publishing house. In 1858, he became a professional at computery at the Paris Observatory. He was a founder and the first president of the '' Société astronomique de France'', which originally had its own independent journal, ''BSAF'' (''Bulletin de la Société astronomique de France''), which was first published in 1887. In January 1895, after 13 volumes of '' L'Astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden Observatory
Leiden Observatory () is an astronomical institute of Leiden University, in the Netherlands. Established in 1633 to house the quadrant of Willebrord Snellius, it is the oldest operating university observatory in the world, with the only older still existing observatory being the Vatican Observatory. The observatory was initially located on the university building in the centre of Leiden before a new observatory building and dome were constructed in the university's botanical garden in 1860. It remained there until 1974 when the department moved to the science campus north-west of the city. Notable astronomers that have worked or directed the observatory include Willem de Sitter, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Jan Oort. History 1633–1860 Leiden University established the observatory in 1633; astronomy had been on the curriculum for a long time, and due to possession of a large quadrant built by Rudolph Snellius, Jacobus Golius requested an observatory in which to use it. The obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederik Kaiser
Frederik Kaiser (Amsterdam, 10 June 1808 – Leiden, 28 July 1872) was a Dutch astronomer. He was director of the Leiden Observatory from 1838 until his death. He is credited with the advancement of Dutch astronomy through his scientific contributions of positional measurements, his popularization of astronomy in the Netherlands, and by helping to build a state-of-the-art observatory in 1861. Today it is known as the "Old Observatory"). Among his students were Jean Abraham Chrétien Oudemans, Johannes van der Waals, H. G. van de Sande Bakhuyzen, Hendricus Gerardus van de Sande Bakhuyzen and Hendrik Antoon Lorentz. Kaiser made a series of drawings of Mars at its opposition in 1862 and made a fairly precise determination of its rotational period by comparing his drawings with those of Christiaan Huygens. Impact crater, Craters on Kaiser (Martian crater), Mars and on the Kaiser (lunar crater), Moon are named in his honour, as well as asteroid 1694 Kaiser. In Richard Proctor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Proctor
Richard Anthony Proctor FRAS (23 March 1837 – 12 September 1888) was an English astronomer. He is best remembered for having produced one of the earliest maps of Mars in 1867 from 27 drawings by the English observer William Rutter Dawes. His map was later superseded by those of Giovanni Schiaparelli and Eugène Antoniadi and his nomenclature was dropped (for instance, his "Kaiser Sea" became Syrtis Major Planum). He used old drawings of Mars dating back to 1666 to try to determine the sidereal day of Mars. His final estimate, in 1873, was 24h 37m 22.713s, very close to the modern value of 24h 37m 22.663s. The crater Proctor on Mars is named after him. Biography Richard Proctor's father died in 1850 and his mother attended to his education. He was sent to King's College London and subsequently earned a scholarship at St John's College, Cambridge. He graduated in 1860 as 23rd wrangler. Proctor then read for the bar, but turned to astronomy and authorship instead, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Von Mädler
Johann Heinrich von Mädler (29 May 1794, Berlin – 14 March 1874, Hannover) was a German astronomer. Life and work His father was a master tailor and when 12 he studied at the Friedrich‐Werdersche Gymnasium in Berlin. He was orphaned at age 19 by an outbreak of typhus, and found himself responsible for raising three younger sisters. He began giving academic lessons as a private tutor and in this way met Wilhelm Beer, a wealthy banker, in 1824. In 1829 Beer decided to set up a private observatory in Berlin, with a 95 mm refractor telescope made by Joseph von Fraunhofer, and Mädler worked there. In 1830 they began producing drawings of Mars which later became the first true maps of that planet. They were the first to choose what is today known as Sinus Meridiani as the prime meridian for Martian maps. They made a preliminary determination for Mars's rotation period, which was off by almost 13 seconds. A later determination in 1837 was off by only 1.1 seconds. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartographer
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate the mapped object's characteristics that are irrelevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of Cartographic generalization, generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Halen, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , ; ; also spelled Huyghens; ; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor who is regarded as a key figure in the Scientific Revolution. In physics, Huygens made seminal contributions to optics and mechanics, while as an astronomer he studied the rings of Saturn and discovered its largest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. As an engineer and inventor, he improved the design of telescopes and invented the pendulum clock, the most accurate timekeeper for almost 300 years. A talented mathematician and physicist, his works contain the first idealization of a physical problem by a set of Mathematical model, mathematical parameters, and the first mathematical and mechanistic explanation of an unobservable physical phenomenon.Dijksterhuis, F.J. (2008) Stevin, Huygens and the Dutch republic. ''Nieuw archief voor wiskunde'', ''5'', pp. 100–10/ref> Huygens first identified the correct la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion (astrophysics), accretion. The word ''planet'' comes from the Greek () . In Classical antiquity, antiquity, this word referred to the Sun, Moon, and five points of light visible to the naked eye that moved across the background of the stars—namely, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, also known as ''Pentapolis'' ("Five Cities") in antiquity, was part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into ''Libya Pentapolis'' and ''Libya Sicca''. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as ''Barqa'', after the city of Barca. Cyrenaica became an Italian colony in 1911. After the 1934 formation of Italian Libya, the Cyrenaica province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country. During World War II, it fell under British military and civil administration from 1943 until 1951, and finally in the Kingdom of Libya from 1951 until 1963. The region that used to be Cyrenaica officially until 1963 has formed several shabiyat, the administrative divisions of Libya, since 1995. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. With an area of almost , it is the 4th-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya claims 32,000 square kilometres of southeastern Algeria, south of the Libyan town of Ghat, Libya, Ghat. The largest city and capital is Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, which is located in northwestern Libya and contains over a million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berber people, Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |